Misophonia is a condition where certain sounds trigger intense emotional reactions such as anger or anxiety, impacting daily life and relationships. Common triggers include chewing, tapping, or breathing noises, which can cause significant distress. Explore the rest of the article to understand misophonia's causes, symptoms, and coping strategies tailored for your wellbeing.
Table of Comparison
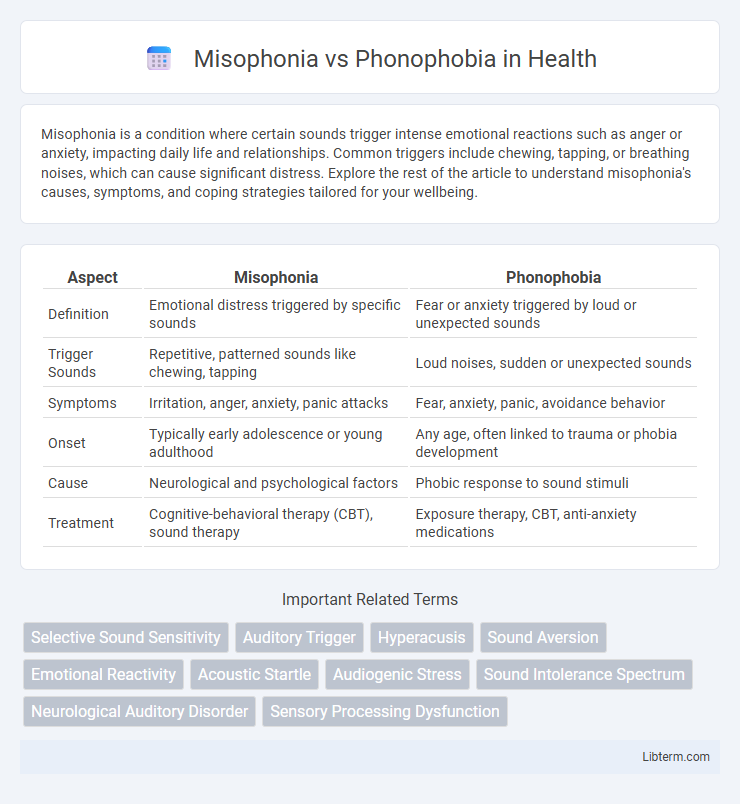
| Aspect | Misophonia | Phonophobia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional distress triggered by specific sounds | Fear or anxiety triggered by loud or unexpected sounds |
| Trigger Sounds | Repetitive, patterned sounds like chewing, tapping | Loud noises, sudden or unexpected sounds |
| Symptoms | Irritation, anger, anxiety, panic attacks | Fear, anxiety, panic, avoidance behavior |
| Onset | Typically early adolescence or young adulthood | Any age, often linked to trauma or phobia development |
| Cause | Neurological and psychological factors | Phobic response to sound stimuli |
| Treatment | Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), sound therapy | Exposure therapy, CBT, anti-anxiety medications |
Understanding Misophonia: Definition and Symptoms
Misophonia is a neurological disorder characterized by strong emotional reactions such as anger, anxiety, or disgust triggered by specific repetitive sounds like chewing, tapping, or breathing. Symptoms include intense irritation, panic attacks, and an overwhelming urge to escape the sound source, significantly impacting daily life and social interactions. Unlike phonophobia, which is a fear or aversion to loud noises, misophonia specifically involves emotional sensitivity to particular trigger sounds rather than generalized sound phobia.
What is Phonophobia? Key Characteristics
Phonophobia is an intense, irrational fear of specific sounds, often resulting in severe anxiety or panic attacks when exposed to triggers such as loud noises, repetitive sounds, or sudden disturbances. Key characteristics include heightened sensory sensitivity, avoidance behavior, and physiological symptoms like increased heart rate, sweating, and dizziness. Unlike misophonia, which involves strong emotional reactions of irritation or rage to certain sounds, phonophobia is primarily driven by fear and the anticipation of distress.
Causes and Triggers: Comparing Misophonia and Phonophobia
Misophonia is primarily caused by an abnormal emotional reaction to specific sounds, often linked to heightened neural activity in the auditory cortex and limbic system, whereas Phonophobia is typically rooted in an intense fear or anxiety of loud noises or certain sound types, often associated with traumatic experiences or anxiety disorders. Common triggers for Misophonia include repetitive sounds like chewing, tapping, or breathing, which evoke irritation or anger, while Phonophobia triggers involve sudden, loud noises such as thunderstorms, fireworks, or alarms that provoke fear and panic. Understanding these distinct causes and triggers is crucial for developing targeted interventions tailored to the neurological and psychological nature of each condition.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Misophonia triggers intense emotional reactions such as anger and anxiety in response to specific sounds, often causing social withdrawal and heightened stress levels. Phonophobia involves a fear-based psychological response to loud or sudden noises, leading to panic attacks and avoidance behaviors that significantly impair daily functioning. Both conditions disrupt mental well-being but differ in their underlying emotional drivers, with misophonia centered on irritation and phonophobia on fear.
Diagnosis: Distinguishing Between Misophonia and Phonophobia
Misophonia diagnosis involves identifying specific triggering sounds that provoke intense emotional reactions, primarily irritation or anger, without an underlying fear component. Phonophobia diagnosis centers on assessing an overwhelming fear or anxiety response to everyday noises, often linked to heightened sensory sensitivity or previous trauma. Differentiating these conditions requires comprehensive clinical interviews and psychometric assessments to evaluate emotional responses and fear-related symptoms triggered by auditory stimuli.
Common Misconceptions and Myths
Misophonia is a neurological condition characterized by intense emotional reactions to specific sounds, while phonophobia is a fear or anxiety related to loud noises. A common misconception is that misophonia is simply a dislike of certain sounds, but it involves involuntary physiological responses and distress. Many mistakenly believe phonophobia is a type of auditory sensitivity like misophonia, though it is primarily an anxiety disorder triggered by sound.
Treatment Options for Misophonia vs Phonophobia
Treatment options for misophonia primarily include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), sound therapy, and mindfulness techniques aimed at reducing emotional responses to trigger sounds. In contrast, phonophobia treatment often involves exposure therapy, anti-anxiety medications, and counseling to manage fear and anxiety related to sounds. Both conditions benefit from personalized therapeutic approaches, but misophonia focuses more on desensitization to specific triggers, while phonophobia requires anxiety reduction strategies.
Coping Strategies and Lifestyle Adjustments
Misophonia coping strategies include sound therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and using noise-canceling headphones to reduce trigger sounds. Phonophobia management often involves gradual sound desensitization, anxiety-reducing techniques, and professional counseling to address fear responses. Lifestyle adjustments such as creating quiet environments, practicing mindfulness, and establishing regular routines improve quality of life for individuals with both conditions.
Tips for Supporting Someone with Misophonia or Phonophobia
Supporting someone with misophonia or phonophobia involves creating a calm, trigger-free environment and respecting their sensory sensitivities to reduce anxiety and discomfort. Providing earplugs, noise-canceling headphones, or access to quiet spaces can help manage sound-triggered reactions effectively. Encouraging open communication about their specific triggers and avoiding judgment fosters trust and emotional support essential for their coping strategies.
Recent Research and Future Directions
Recent research differentiates misophonia as a neurological disorder characterized by strong emotional reactions to specific sounds, while phonophobia is identified as an anxiety-related fear of loud noises. Neuroimaging studies reveal hyperactivity in the anterior insular cortex in misophonia patients, suggesting distinct neural pathways from the amygdala-driven fear response in phonophobia. Future directions emphasize targeted neuromodulation therapies and longitudinal studies to better understand symptom progression and develop personalized treatment protocols.
Misophonia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com