Conservative values emphasize tradition, personal responsibility, and limited government intervention in both economic and social affairs. This approach often prioritizes preserving cultural heritage while promoting free market principles and individual freedoms. Discover how conservative ideologies impact policies and daily life by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
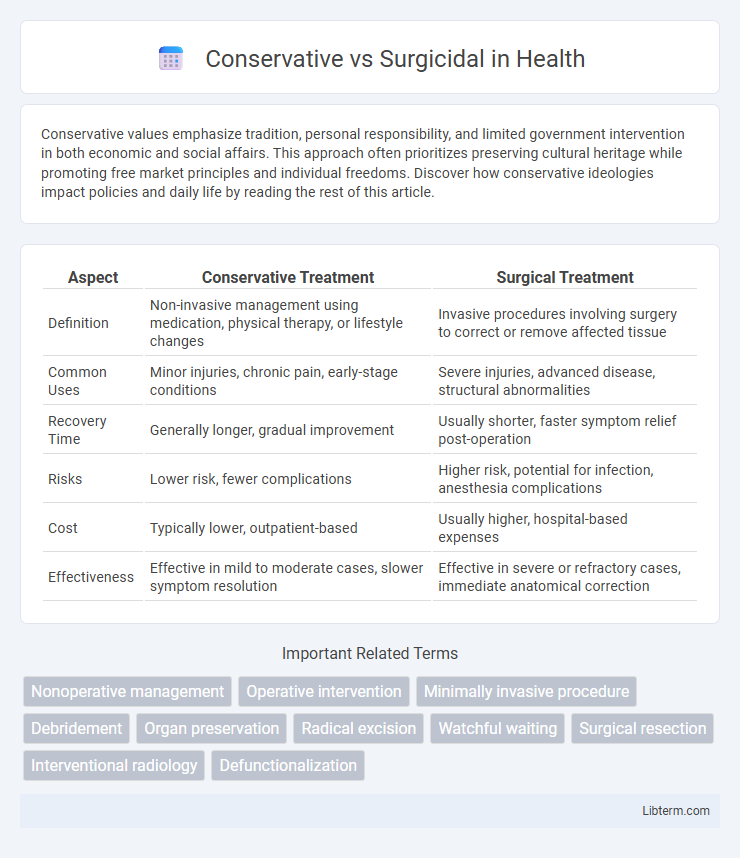
| Aspect | Conservative Treatment | Surgical Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-invasive management using medication, physical therapy, or lifestyle changes | Invasive procedures involving surgery to correct or remove affected tissue |
| Common Uses | Minor injuries, chronic pain, early-stage conditions | Severe injuries, advanced disease, structural abnormalities |
| Recovery Time | Generally longer, gradual improvement | Usually shorter, faster symptom relief post-operation |
| Risks | Lower risk, fewer complications | Higher risk, potential for infection, anesthesia complications |
| Cost | Typically lower, outpatient-based | Usually higher, hospital-based expenses |
| Effectiveness | Effective in mild to moderate cases, slower symptom resolution | Effective in severe or refractory cases, immediate anatomical correction |
Understanding Conservative vs. Surgical Management
Conservative management involves non-invasive treatments such as medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications aimed at symptom relief and functional improvement without surgery. Surgical management entails operative procedures to directly address the underlying pathology, often providing definitive treatment when conservative methods fail or are insufficient. Decision-making between conservative and surgical options depends on factors like severity of symptoms, underlying condition, patient health status, and expected outcomes.
Key Differences Between Conservative and Surgical Approaches
Conservative approaches prioritize non-invasive treatments such as medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications aimed at symptom management and functional improvement without altering body structure. Surgical approaches involve operative procedures to directly correct or remove the underlying pathological issue, offering definitive treatment but with increased risks and recovery time. Understanding these key differences helps guide treatment decisions based on severity, patient health status, and long-term outcomes.
Indications for Conservative Treatment
Conservative treatment is primarily indicated for patients with mild to moderate symptoms of musculoskeletal conditions, stable fractures, or early-stage degenerative diseases where structural integrity remains intact. Non-surgical management is preferred in cases with contraindications for surgery, such as comorbidities, or when the risk of surgical complications outweighs benefits. Effective conservative approaches include physical therapy, pharmacological pain management, and lifestyle modifications aimed at symptom relief and functional preservation.
Indications for Surgical Intervention
Surgical intervention is indicated when conservative treatments fail to alleviate symptoms or when there is evidence of structural damage such as severe spinal instability, significant neurological deficits, or progressive deformities. Indications include persistent pain despite extensive physical therapy and medication, large herniated discs causing nerve compression, and trauma resulting in fractures requiring stabilization. Early surgical action is essential in cases with cauda equina syndrome or acute neurological deterioration to prevent permanent disability.
Pros and Cons of Conservative Management
Conservative management offers the advantage of being less invasive, reducing the risks of surgical complications such as infections and anesthesia-related issues while promoting natural healing processes. It allows for continuous monitoring and adjustment based on patient response but may result in prolonged recovery times and the potential for incomplete resolution of the underlying problem. Delayed intervention in some cases could lead to worsening conditions, requiring eventual surgical treatment.
Advantages and Risks of Surgical Solutions
Surgical solutions in medical treatments offer precise removal or repair of affected tissues, often leading to faster recovery and potentially definitive resolution of the condition. Advantages include targeted intervention, reduced recurrence rates, and improved symptom relief compared to conservative management. However, surgical risks involve complications such as infection, anesthesia reactions, longer hospital stays, and potential for postoperative pain or functional impairment.
Patient Selection Criteria: Conservative vs. Surgical
Patient selection criteria for conservative management prioritize stable fractures with minimal displacement, absence of neurovascular compromise, and patients with comorbidities that increase surgical risks. Surgical intervention is favored for unstable fractures, significant displacement, open fractures, or cases with associated vascular or neurological injury requiring immediate anatomical alignment. Accurate diagnostic imaging and patient health status are critical determinants guiding the choice between conservative and surgical treatment modalities.
Recovery and Outcomes: What to Expect
Conservative treatment typically involves non-invasive methods such as medication and physical therapy, leading to gradual symptom relief and a quicker day-to-day functional recovery. Surgical intervention often results in more significant structural correction, but recovery includes a longer hospital stay and rehabilitation period, with potential risks and complications. Patients undergoing surgery generally experience more definitive outcomes in severe cases, while conservative care suits mild to moderate conditions with a focus on symptom management and quality of life.
Common Conditions: Case Examples
Conservative treatment approaches for common conditions like osteoarthritis and minor fractures emphasize pain management, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to promote healing without surgical risks. Surgicidal interventions, often employed in severe cases such as complex fractures or advanced degenerative joint disease, involve procedures like joint replacement or fracture fixation to restore function and alleviate symptoms. Comparing case examples demonstrates that patient-specific factors including severity, comorbidities, and recovery goals determine the optimal treatment strategy between conservative and surgical options.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
When deciding between conservative and surgicidal approaches, evaluating patient-specific factors such as the severity of the condition, overall health, and recovery goals is crucial. Conservative treatment typically involves non-invasive methods like medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, suitable for mild to moderate cases. Surgicidal options, including targeted surgical interventions, are preferred for severe or unresponsive conditions, offering definitive resolutions but requiring careful consideration of risks and post-operative rehabilitation.
Conservative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com