Air purification removes harmful pollutants and allergens from indoor environments, enhancing the quality of the air you breathe and promoting better health. Modern air purifiers use advanced filtration technologies such as HEPA filters, activated carbon, and UV light to effectively eliminate dust, smoke, mold spores, and bacteria. Explore the rest of this article to discover how air purification can improve your home's environment and which systems are best suited for your needs.
Table of Comparison
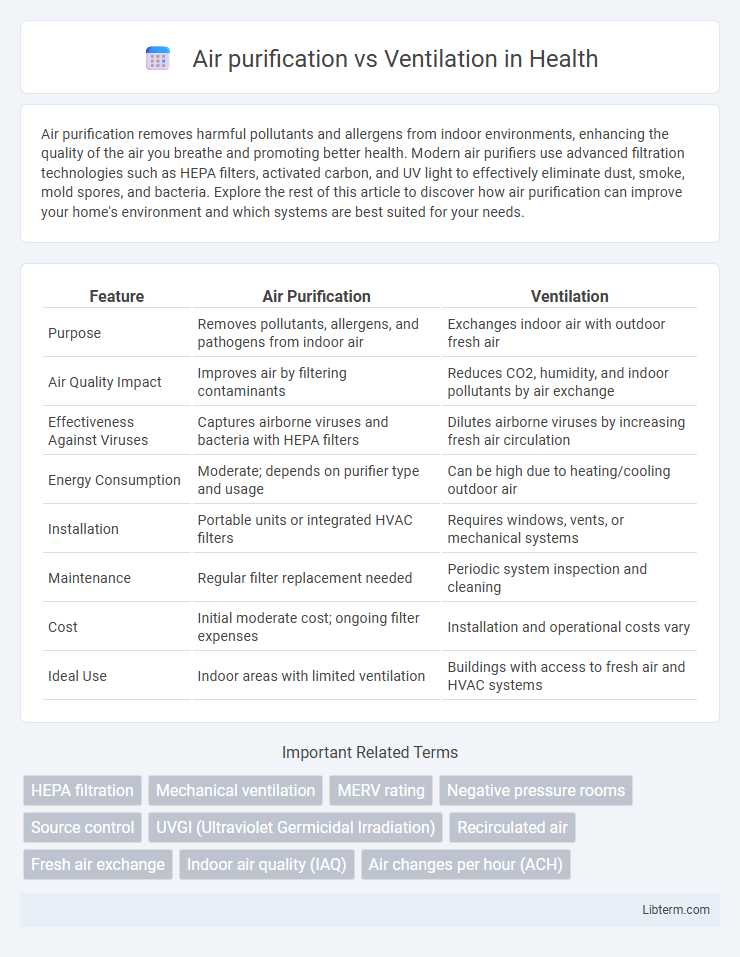
| Feature | Air Purification | Ventilation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Removes pollutants, allergens, and pathogens from indoor air | Exchanges indoor air with outdoor fresh air |
| Air Quality Impact | Improves air by filtering contaminants | Reduces CO2, humidity, and indoor pollutants by air exchange |
| Effectiveness Against Viruses | Captures airborne viruses and bacteria with HEPA filters | Dilutes airborne viruses by increasing fresh air circulation |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate; depends on purifier type and usage | Can be high due to heating/cooling outdoor air |
| Installation | Portable units or integrated HVAC filters | Requires windows, vents, or mechanical systems |
| Maintenance | Regular filter replacement needed | Periodic system inspection and cleaning |
| Cost | Initial moderate cost; ongoing filter expenses | Installation and operational costs vary |
| Ideal Use | Indoor areas with limited ventilation | Buildings with access to fresh air and HVAC systems |
Understanding Air Purification and Ventilation
Air purification involves removing pollutants and allergens from indoor air using filters, UV light, or ionizers to improve air quality. Ventilation replaces contaminated indoor air with fresh outdoor air, reducing the concentration of airborne contaminants and controlling humidity levels. Both methods contribute to healthier indoor environments by targeting different aspects of air quality management.
How Air Purifiers Work
Air purifiers cleanse indoor air by drawing it through filters that trap pollutants such as dust, pollen, pet dander, and smoke particles. Advanced models use HEPA filters, activated carbon, or UV light technology to remove allergens, odors, and airborne pathogens effectively. Unlike ventilation systems that exchange indoor and outdoor air, air purifiers recirculate and continuously purify the existing indoor air to improve air quality.
The Science Behind Ventilation
Ventilation improves indoor air quality by introducing fresh outdoor air and diluting indoor pollutants, effectively reducing airborne contaminants such as carbon dioxide, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and infectious aerosols. Mechanical ventilation systems, including exhaust fans and HVAC units with fresh air intake, enhance air exchange rates and help maintain optimal humidity and temperature levels. Scientific studies confirm that proper ventilation decreases the concentration of indoor pollutants, promoting healthier environments and reducing the transmission of airborne diseases.
Comparing Air Purification and Ventilation
Air purification removes airborne contaminants such as dust, allergens, and pathogens using filters and UV technology, improving indoor air quality by targeting pollutants directly. Ventilation replaces indoor air with outdoor air to reduce pollutant concentration and control humidity, enhancing overall air exchange and preventing buildup of stale air. Both methods are essential for healthy indoor environments, with air purification focusing on contaminant removal and ventilation emphasizing air circulation and freshness.
Key Benefits of Air Purification
Air purification enhances indoor air quality by removing pollutants such as dust, allergens, bacteria, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) through advanced filtration technologies like HEPA and activated carbon filters. This process effectively reduces airborne contaminants that ventilation alone cannot eliminate, particularly in enclosed or pollution-prone environments. Targeted air purification supports respiratory health, mitigates allergy symptoms, and creates a cleaner living or working space independent of outdoor air quality.
Advantages of Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation significantly enhances indoor air quality by continuously exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air, reducing the concentration of pollutants, allergens, and carbon dioxide. Effective ventilation systems help control humidity levels, preventing mold growth and creating a healthier living environment. Optimized airflow also supports the removal of airborne contaminants more efficiently than standalone air purification, promoting overall respiratory health and comfort.
Limitations of Air Purifiers
Air purifiers effectively remove airborne particles such as dust, pollen, and some pathogens but cannot introduce fresh air or control humidity levels like ventilation systems do. Their filtration capacity is limited by the size of the room and air changes per hour, often requiring frequent filter replacements to maintain efficiency. Air purifiers also struggle with eliminating gases, odors, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which ventilation can more effectively reduce by exchanging indoor air with outdoor air.
Challenges Associated with Ventilation
Ventilation systems often struggle with balancing adequate airflow while minimizing energy consumption and maintaining indoor air quality, especially in densely occupied or poorly designed buildings. Inconsistent distribution of fresh air can lead to dead zones where contaminants accumulate, reducing overall effectiveness. High installation and operational costs, along with difficulties in controlling outdoor pollutant ingress, present significant challenges in optimizing ventilation for healthy indoor environments.
When to Choose Air Purification vs Ventilation
Air purification is ideal for environments with limited airflow or where removing airborne pollutants like allergens, smoke, and pathogens is critical without increasing outdoor air exchange. Ventilation is essential when reducing indoor carbon dioxide levels, controlling humidity, or bringing in fresh outdoor air to dilute contaminants. Select air purification for targeted contaminant removal and ventilation for improving overall air quality through increased air exchange.
Achieving Optimal Indoor Air Quality: A Combined Approach
Effective indoor air quality is best achieved through a combined approach that integrates air purification and ventilation systems. Ventilation dilutes indoor pollutants by exchanging stale air with fresh outdoor air, while air purifiers remove airborne contaminants such as allergens, pathogens, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Utilizing both methods simultaneously enhances the removal of indoor pollutants and ensures a healthier living environment by maintaining optimal airflow and contaminant filtration.
Air purification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com