Bursitis occurs when the small fluid-filled sacs called bursae, which cushion your joints, become inflamed due to repetitive motion or injury, causing pain and swelling. Proper diagnosis and treatment, including rest, ice, and physical therapy, are essential to reduce discomfort and restore joint function. Explore the rest of the article to learn effective strategies for managing bursitis and preventing future flare-ups.
Table of Comparison
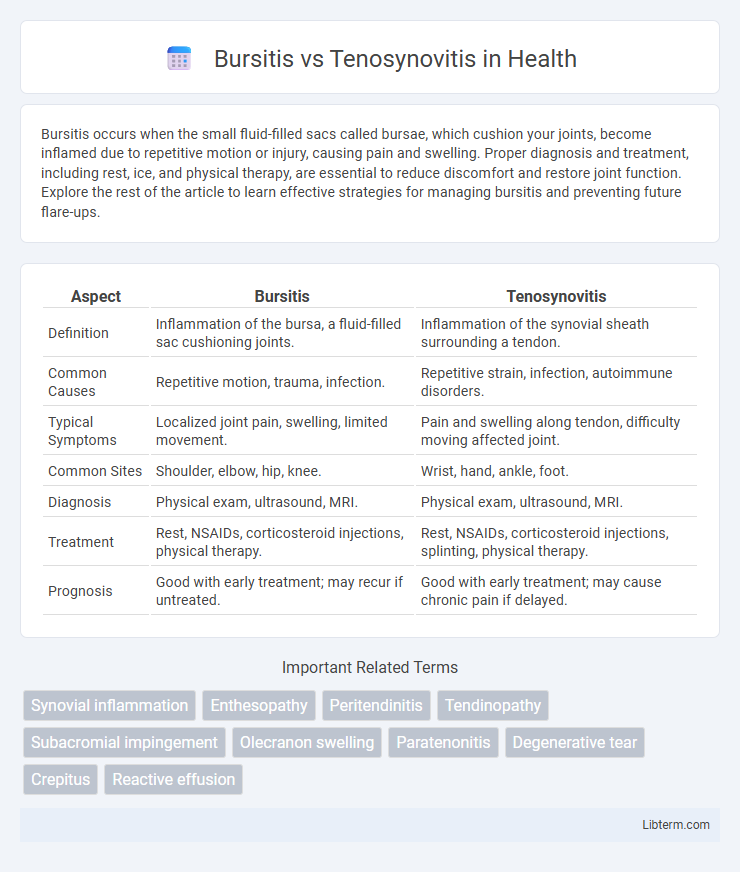
| Aspect | Bursitis | Tenosynovitis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflammation of the bursa, a fluid-filled sac cushioning joints. | Inflammation of the synovial sheath surrounding a tendon. |
| Common Causes | Repetitive motion, trauma, infection. | Repetitive strain, infection, autoimmune disorders. |
| Typical Symptoms | Localized joint pain, swelling, limited movement. | Pain and swelling along tendon, difficulty moving affected joint. |
| Common Sites | Shoulder, elbow, hip, knee. | Wrist, hand, ankle, foot. |
| Diagnosis | Physical exam, ultrasound, MRI. | Physical exam, ultrasound, MRI. |
| Treatment | Rest, NSAIDs, corticosteroid injections, physical therapy. | Rest, NSAIDs, corticosteroid injections, splinting, physical therapy. |
| Prognosis | Good with early treatment; may recur if untreated. | Good with early treatment; may cause chronic pain if delayed. |
Introduction to Bursitis and Tenosynovitis
Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between bones, tendons, and muscles near the joints, commonly affecting the shoulder, elbow, and hip. Tenosynovitis involves the inflammation of the synovial sheath surrounding a tendon, often occurring in the wrists, hands, and feet, leading to pain and restricted movement. Both conditions result from repetitive motion or injury and require accurate diagnosis for effective treatment.
Definition of Bursitis
Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between bones, tendons, and muscles around joints. This condition commonly causes pain, swelling, and reduced movement in areas such as the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Unlike tenosynovitis, which involves inflammation of the tendon sheath, bursitis specifically affects these protective sacs and results from repetitive motion, trauma, or infection.
Definition of Tenosynovitis
Tenosynovitis is the inflammation of the synovial sheath surrounding a tendon, often caused by repetitive motion or injury, leading to pain and swelling. Unlike bursitis, which affects the fluid-filled sacs cushioning joints, tenosynovitis specifically targets tendon sheaths, restricting tendon movement and causing stiffness. Common sites include the wrist, hand, and foot, where tendons are enclosed by synovial sheaths critical for smooth muscle function.
Causes of Bursitis vs Tenosynovitis
Bursitis is primarily caused by repetitive motion or prolonged pressure on the bursae, leading to inflammation of these fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints. Tenosynovitis results from inflammation of the tendon sheath, often due to overuse, injury, or infection affecting tendons in areas like the wrist or ankle. Both conditions can stem from repetitive strain but differ in the specific anatomical structures involved and their underlying triggers.
Risk Factors Comparison
Bursitis risk factors include repetitive motion, prolonged pressure, trauma, and inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, often affecting the shoulder, elbow, or hip. Tenosynovitis is commonly triggered by repetitive finger or wrist movements, infections, autoimmune diseases, and overuse injuries, with greater incidence in professions involving manual labor or typing. Both conditions share risk factors such as repetitive use and inflammatory disorders, but bursitis predominantly involves bursa inflammation, while tenosynovitis affects the tendon sheath.
Common Symptoms and Signs
Bursitis and tenosynovitis both present with localized pain, swelling, and tenderness near joints, often exacerbated by movement or pressure. Bursitis typically involves inflammation of the bursa, leading to visible swelling and warmth over the affected joint, while tenosynovitis affects the tendon sheath, causing pain during tendon movement and sometimes a noticeable creaking or popping sensation. Stiffness and limited range of motion are common in both conditions, but tenosynovitis frequently results in more pronounced tendon pain during specific activities.
Diagnosis and Testing
Bursitis is diagnosed through clinical examination highlighting localized swelling and tenderness over the bursae, often confirmed by ultrasound or MRI to detect fluid accumulation and inflammation. Tenosynovitis diagnosis relies on physical assessment revealing pain and swelling along the tendon sheaths, with ultrasound and MRI providing detailed images of tendon sheath thickening and fluid presence. Both conditions may require lab tests to rule out infection or inflammatory diseases, ensuring accurate differentiation and appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Bursitis and Tenosynovitis
Treatment options for bursitis primarily include rest, ice application, anti-inflammatory medications like NSAIDs, and corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation. Tenosynovitis treatment often involves immobilization with splints, physical therapy, NSAIDs, and in severe cases, corticosteroid injections or surgical intervention to release the tendon sheath. Both conditions benefit from early diagnosis and tailored treatment plans to prevent chronic pain and improve joint function.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing bursitis and tenosynovitis involves regularly practicing proper ergonomics and avoiding repetitive motions that strain joints and tendons. Strengthening exercises targeting muscles around affected areas, combined with adequate stretching, improve flexibility and reduce inflammation risks. Using protective gear during physical activities and maintaining healthy body weight also minimize pressure on bursae and tendon sheaths, preventing these conditions.
Prognosis and Recovery
Bursitis and tenosynovitis both involve inflammation, but bursitis affects the fluid-filled sacs cushioning joints while tenosynovitis targets the tendon sheaths. The prognosis for bursitis typically involves rapid improvement with rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy, often resolving within weeks. Tenosynovitis recovery may require a longer period of immobilization or corticosteroid injections, with chronic cases possibly leading to tendon damage or reduced joint mobility if untreated.
Bursitis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com