Balance disorder affects your ability to maintain a steady posture, leading to dizziness, unsteadiness, or vertigo that can interfere with daily activities. It often results from inner ear problems, neurological conditions, or medication side effects, making accurate diagnosis essential for effective treatment. Explore this article to discover the causes, symptoms, and management strategies that can help you regain stability.
Table of Comparison
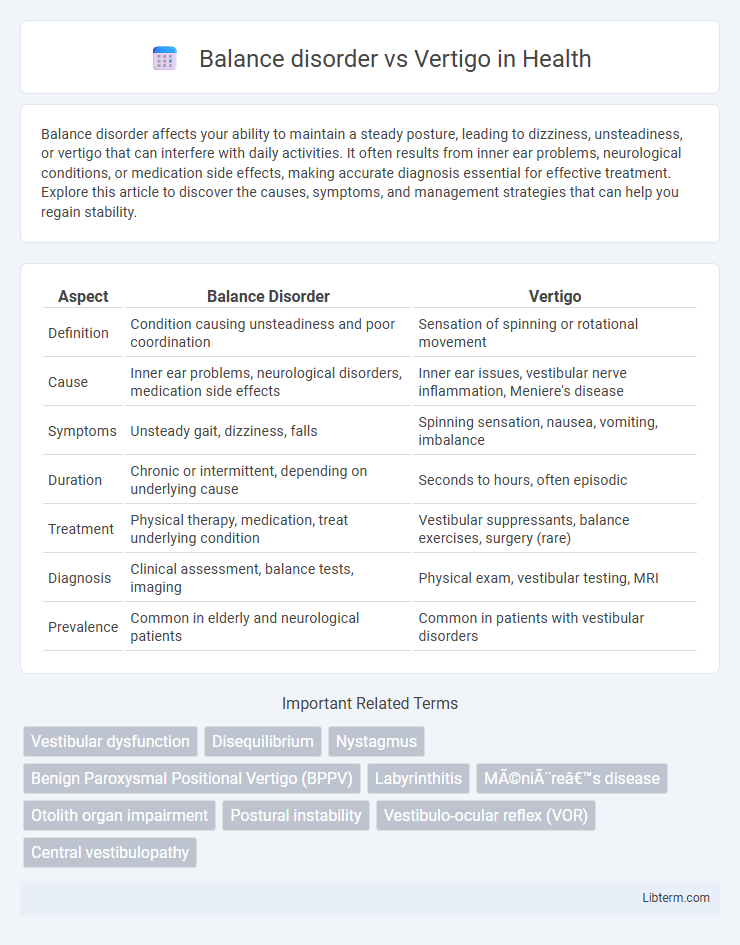
| Aspect | Balance Disorder | Vertigo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Condition causing unsteadiness and poor coordination | Sensation of spinning or rotational movement |
| Cause | Inner ear problems, neurological disorders, medication side effects | Inner ear issues, vestibular nerve inflammation, Meniere's disease |
| Symptoms | Unsteady gait, dizziness, falls | Spinning sensation, nausea, vomiting, imbalance |
| Duration | Chronic or intermittent, depending on underlying cause | Seconds to hours, often episodic |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, medication, treat underlying condition | Vestibular suppressants, balance exercises, surgery (rare) |
| Diagnosis | Clinical assessment, balance tests, imaging | Physical exam, vestibular testing, MRI |
| Prevalence | Common in elderly and neurological patients | Common in patients with vestibular disorders |
Understanding Balance Disorder: Definition and Overview
Balance disorder refers to a group of conditions that cause unsteadiness, dizziness, or spatial disorientation due to problems in the vestibular system, proprioception, or central nervous system. Vertigo is a specific type of balance disorder characterized by a false sensation of spinning or movement, often caused by inner ear issues such as benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) or vestibular neuritis. Understanding balance disorders involves recognizing the broad range of underlying causes that affect body equilibrium, while vertigo serves as a distinct symptom within this spectrum requiring targeted diagnosis and treatment.
What is Vertigo? Causes and Symptoms
Vertigo is a specific type of balance disorder characterized by a false sensation of spinning or movement, often caused by inner ear problems such as benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), vestibular neuritis, or Meniere's disease. Symptoms include dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and difficulty maintaining balance, which can impair daily activities and increase the risk of falls. Unlike general balance disorders, vertigo distinctly involves a rotational sensation triggered by disruptions in the vestibular system.
Key Differences: Balance Disorder vs. Vertigo
Balance disorder involves multiple causes related to impaired coordination of the sensory systems that control balance, including the inner ear, vision, and proprioception, resulting in unsteadiness or dizziness. Vertigo specifically refers to the sensation of spinning or rotational movement, typically caused by inner ear dysfunction or vestibular system problems. While balance disorder affects overall stability and posture, vertigo is characterized by misleading spatial orientation and a false sense of motion.
How the Vestibular System Affects Balance
The vestibular system plays a crucial role in maintaining balance by processing sensory information from the inner ear about head position and movement. Balance disorder occurs when this system is impaired, leading to difficulty stabilizing posture and coordinating movements. Vertigo, a specific symptom of vestibular dysfunction, causes a false sensation of spinning or dizziness, directly reflecting disruptions in vestibular input.
Common Causes of Balance Disorders
Balance disorders often stem from inner ear problems, neurological conditions, or medication side effects, whereas vertigo specifically originates from vestibular system dysfunction causing a false sensation of spinning. Common causes of balance disorders include vestibular neuritis, Meniere's disease, and multi-sensory impairments such as vision or proprioception deficits. Diagnosing balance disorders requires differentiating these conditions from vertigo by assessing symptoms like dizziness, unsteadiness, and duration of the episodes.
Triggers and Types of Vertigo Explained
Balance disorders stem from various causes affecting the vestibular system, with vertigo being a specific type characterized by a sensation of spinning or dizziness. Vertigo triggers include head movements, changes in position, inner ear infections, or neurological conditions, with common types such as Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV), Meniere's disease, and vestibular neuritis. Understanding these triggers and vertigo types aids in precise diagnosis and tailored treatments to improve patient outcomes.
Diagnostic Methods for Balance Disorders and Vertigo
Diagnostic methods for balance disorders and vertigo include videonystagmography (VNG), which assesses eye movements to detect inner ear problems causing dizziness, and rotational chair testing to evaluate vestibular function. Posturography analyzes body sway and stability to identify balance impairments, while audiometric tests help rule out hearing issues linked to vestibular dysfunction. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is utilized to exclude central nervous system causes when primary vestibular assessments are inconclusive.
Treatment Options: Balance Disorder vs Vertigo
Treatment options for balance disorder primarily include vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT), physical therapy, and medication to address underlying causes such as neuropathy or inner ear issues, while vertigo often requires specific vestibular suppressants like meclizine or antihistamines alongside canalith repositioning maneuvers such as the Epley maneuver. In cases of chronic balance disorders, assistive devices and lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in preventing falls and improving stability. Vertigo treatments focus on resolving the acute spinning sensation through targeted maneuvers and medication, often resulting in quicker symptom relief compared to the broader, sometimes multidisciplinary approach needed for balance disorders.
Coping Strategies and Lifestyle Adjustments
Balance disorder and vertigo require targeted coping strategies such as vestibular rehabilitation therapy to improve stability and reduce dizziness episodes. Lifestyle adjustments including avoiding sudden head movements, managing stress, and maintaining hydration help alleviate symptoms and prevent falls. Using assistive devices and creating a safe home environment further support daily functioning and enhance quality of life.
When to Seek Medical Help for Dizziness and Balance Issues
Seek medical help for dizziness and balance issues if symptoms include sudden onset of severe vertigo, persistent imbalance, difficulty walking, or associated neurological signs such as weakness, numbness, slurred speech, or vision changes. Immediate evaluation is critical when dizziness occurs alongside chest pain, shortness of breath, or fainting, as these may indicate a cardiovascular or neurological emergency. Chronic or worsening balance disorders warrant professional assessment to diagnose underlying causes like vestibular dysfunction, stroke, or inner ear disorders and to initiate appropriate treatment.
Balance disorder Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com