Conservative values emphasize tradition, personal responsibility, and limited government intervention in economic and social matters. These principles often guide policies that prioritize individual freedom, fiscal discipline, and preserving cultural heritage. Explore the article to understand how conservative ideologies influence contemporary political and social landscapes.
Table of Comparison
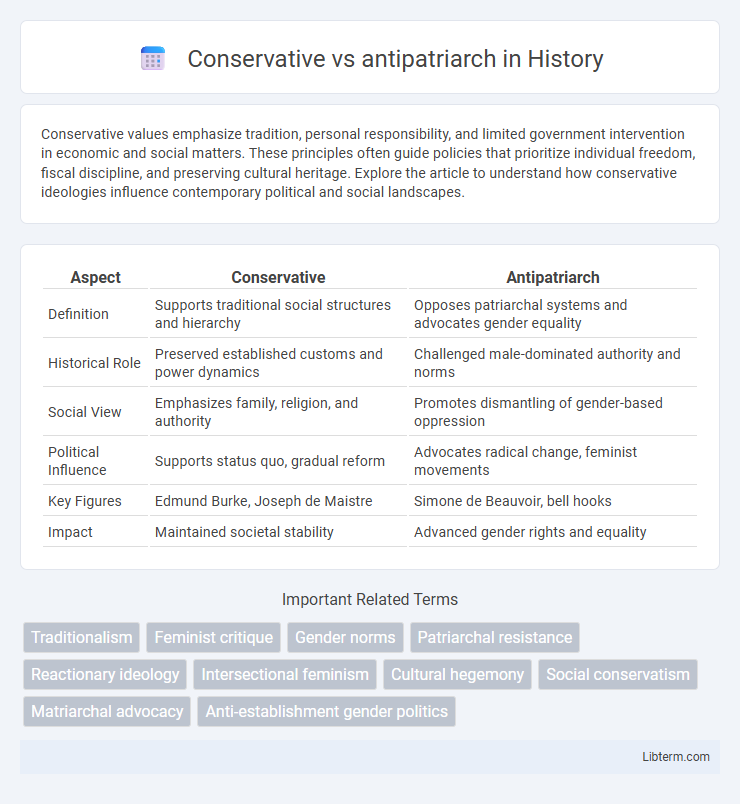
| Aspect | Conservative | Antipatriarch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supports traditional social structures and hierarchy | Opposes patriarchal systems and advocates gender equality |
| Historical Role | Preserved established customs and power dynamics | Challenged male-dominated authority and norms |
| Social View | Emphasizes family, religion, and authority | Promotes dismantling of gender-based oppression |
| Political Influence | Supports status quo, gradual reform | Advocates radical change, feminist movements |
| Key Figures | Edmund Burke, Joseph de Maistre | Simone de Beauvoir, bell hooks |
| Impact | Maintained societal stability | Advanced gender rights and equality |
Understanding Conservatism: Core Principles
Conservatism centers on preserving established traditions, social structures, and institutions that have historically provided stability and continuity within society. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining cultural heritage, respecting authority, and advocating for gradual change rather than radical reform. By valuing order, hierarchy, and community cohesion, conservatism contrasts with antipatriarchal movements that challenge traditional power dynamics and promote gender equality and social justice reforms.
Defining Antipatriarchy: Key Concepts
Antipatriarchy refers to the active opposition to the patriarchal system that enforces male dominance in social, political, and economic structures. It challenges traditional gender roles, advocates for gender equality, and seeks to dismantle institutionalized sexism and power imbalances rooted in patriarchy. Key concepts include feminism, intersectionality, and social justice, which collectively aim to transform societal norms that perpetuate gender-based oppression.
Historical Roots of Conservatism and Antipatriarchy
The historical roots of conservatism trace back to the post-French Revolution era, emphasizing tradition, social stability, and the preservation of established institutions including patriarchal family structures. Antipatriarchy movements emerged from feminist waves in the 19th and 20th centuries, challenging entrenched gender hierarchies and advocating for equality and dismantling of male-dominated systems. These opposing foundations highlight conservatism's focus on continuity and order versus antipatriarchy's pursuit of social justice and systemic change.
Political Ideologies and Gender Roles
Conservative political ideologies emphasize traditional gender roles, advocating for a patriarchal family structure where men hold authority and women primarily manage domestic responsibilities. Antipatriarchal perspectives challenge this hierarchy, promoting gender equality and critiquing the power imbalances embedded in conservative values. These opposing views influence policies on family, employment, and social norms, shaping debates around gender rights and roles in society.
Conservatism’s Stance on Social Structures
Conservatism upholds traditional social structures, emphasizing the importance of family, religion, and established institutions in maintaining societal stability. This ideology supports patriarchy as a natural and necessary hierarchy for social order and moral guidance. In contrast, antipatriarchal movements challenge these norms, advocating for gender equality and the dismantling of patriarchal systems embedded in social structures.
Antipatriarchy and Feminist Movements
Antipatriarchal and feminist movements actively challenge traditional patriarchal structures by advocating for gender equality, dismantling systemic sexism, and promoting women's rights in social, political, and economic spheres. These movements emphasize intersectionality, addressing not only gender disparities but also the interconnected impacts of race, class, and sexuality on oppression. Their activism includes campaigns for reproductive rights, wage equality, and combating gender-based violence, positioning antipatriarchy as a transformative force against entrenched conservative norms.
Common Misconceptions: Conservatism vs. Antipatriarchy
Conservatism is often mistakenly equated with resistance to all social change, while antipatriarchy specifically targets systemic gender inequalities and patriarchal norms. Conservative ideologies typically emphasize tradition, social order, and hierarchical structures, which can inadvertently support patriarchal values. Antipatriarchal movements challenge these structures by advocating for gender equity and dismantling male dominance in societal, political, and economic systems.
Policy Impacts: Laws and Social Change
Conservative policies often emphasize preserving traditional family structures and gender roles, influencing legislation that restricts abortion rights, opposes same-sex marriage, and limits gender identity protections. Antipatriarch movements advocate for laws promoting gender equality, reproductive rights, and LGBTQ+ protections, pushing for social reforms that dismantle systemic patriarchy. These contrasting approaches shape societal norms through divergent legal frameworks and policy outcomes, reflecting deeper conflicts over gender justice and social equity.
Cultural Narratives and Media Representation
Conservative cultural narratives often emphasize traditional family values, patriotism, and gender roles, presenting patriarchal structures as natural and beneficial for social stability. Antipatriarchal perspectives challenge these representations by highlighting media's role in perpetuating gender inequality, advocating for diverse and inclusive stories that disrupt dominant patriarchal norms. Media representation thus becomes a battleground where competing cultural narratives either reinforce or contest entrenched power dynamics linked to patriarchy.
Future Trends: The Evolving Debate
The future debate between conservative and antipatriarch perspectives will increasingly center on issues such as gender equality, policy reforms, and cultural narratives shaping societal norms. Technological advancements and global social movements will amplify voices challenging traditional patriarchal values, prompting legislative and educational initiatives aimed at inclusivity. Data from recent sociological studies indicates a growing demographic shift toward progressive ideals, suggesting that conservative frameworks may need adaptation to remain relevant in evolving social landscapes.
Conservative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com