Hieroglyphics, the intricate system of writing used by ancient Egyptians, combined logographic and alphabetic elements to convey complex meanings through symbolic characters. This form of script was primarily utilized for religious texts, monumental inscriptions, and official documentation, reflecting the civilization's rich cultural and spiritual heritage. Discover how this fascinating writing system evolved and influenced communication in ancient times by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
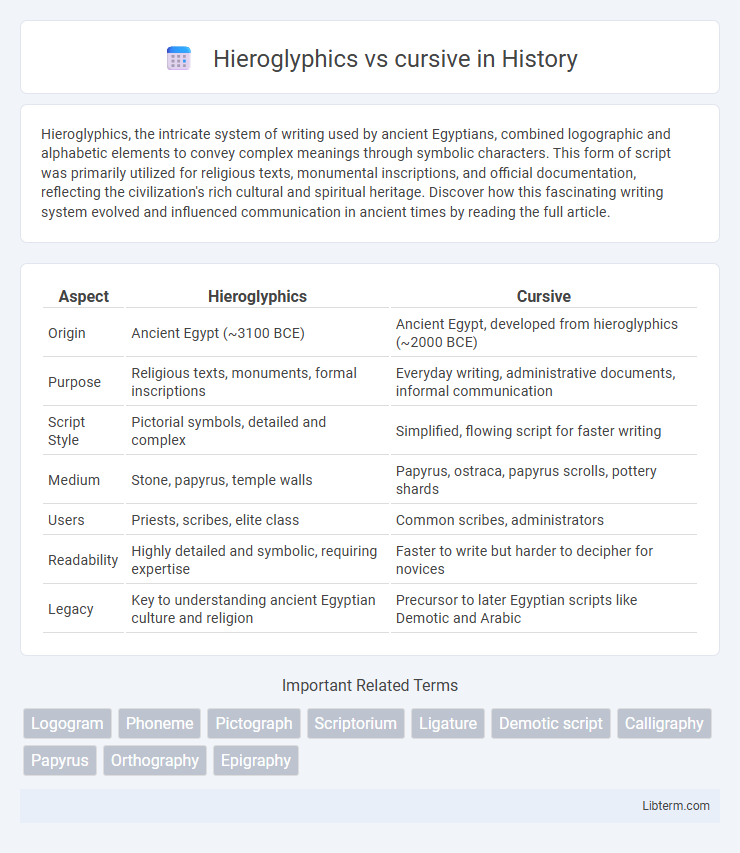
| Aspect | Hieroglyphics | Cursive |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Ancient Egypt (~3100 BCE) | Ancient Egypt, developed from hieroglyphics (~2000 BCE) |
| Purpose | Religious texts, monuments, formal inscriptions | Everyday writing, administrative documents, informal communication |
| Script Style | Pictorial symbols, detailed and complex | Simplified, flowing script for faster writing |
| Medium | Stone, papyrus, temple walls | Papyrus, ostraca, papyrus scrolls, pottery shards |
| Users | Priests, scribes, elite class | Common scribes, administrators |
| Readability | Highly detailed and symbolic, requiring expertise | Faster to write but harder to decipher for novices |
| Legacy | Key to understanding ancient Egyptian culture and religion | Precursor to later Egyptian scripts like Demotic and Arabic |
Introduction to Hieroglyphics and Cursive
Hieroglyphics represent an ancient Egyptian writing system consisting of pictorial symbols that convey objects, sounds, and ideas, primarily used in religious texts and monumental inscriptions. Cursive, in contrast, is a flowing, connected script developed for swift handwriting, commonly used in everyday communication and record-keeping across various languages. The complexity of hieroglyphics emphasizes symbolic representation, while cursive focuses on efficiency and legibility in writing.
Historical Origins and Development
Hieroglyphics originated around 3100 BCE in ancient Egypt as a complex system of pictorial writing used primarily for religious and monumental inscriptions. Cursive scripts evolved later as practical, faster handwriting forms, with Egyptian hieratic and demotic scripts developing from hieroglyphics to facilitate administrative and everyday writing. The transition from rigid hieroglyphs to fluid cursive scripts marked a significant shift in the accessibility and functionality of written communication in ancient Egyptian society.
Visual Characteristics and Styles
Hieroglyphics feature intricate pictorial symbols representing words or sounds with a highly detailed and formal visual style used primarily in monumental inscriptions. Cursive, by contrast, is characterized by fluid, connected strokes designed for speedy handwriting, often appearing more abstract and simplified compared to the precise and elaborate forms of hieroglyphics. The visual contrast reflects their differing functions: hieroglyphics serve ceremonial and decorative purposes, while cursive prioritizes practicality and efficiency in everyday writing.
Writing Materials and Tools Used
Hieroglyphics were typically inscribed on stone, walls, and papyrus using chisels or reed brushes dipped in ink, emphasizing durability and ceremonial importance. Cursive script employed reed pens and ink on papyrus or parchment, prioritizing speed and efficiency for everyday writing and record-keeping. The choice of materials and tools directly influenced the style and complexity of each script, with hieroglyphics favoring precision and cursive adapting to fluid, rapid strokes.
Purpose and Functions in Society
Hieroglyphics served primarily as a formal script used in religious texts, monumental inscriptions, and official documentation in ancient Egypt, symbolizing divine and ceremonial communication. Cursive writing evolved to facilitate faster, practical record-keeping, personal correspondence, and administrative tasks, becoming essential for everyday societal functions. Each script reflects distinct social purposes: hieroglyphics conveyed sacred meaning and authority, while cursive addressed the need for efficiency and accessibility in daily life.
Decipherment and Interpretation Difficulties
Hieroglyphics present complex decipherment challenges due to their pictographic nature, with symbols representing sounds, ideas, or objects, often requiring contextual understanding for accurate interpretation. Cursive scripts, such as ancient Egyptian hieratic, offer faster writing but increase difficulties in distinguishing characters because of their highly stylized, abbreviated forms. The decipherment of hieroglyphics was notably advanced by the Rosetta Stone, while cursive texts demand expertise in paleography to resolve ambiguities and ensure precise translation.
Influence on Later Scripts
Hieroglyphics significantly influenced the development of later writing systems by inspiring the use of pictorial symbols and phonetic elements in scripts such as the Phoenician alphabet. Cursive, evolving from hieroglyphics through hieratic and demotic scripts, introduced faster, more practical writing styles essential for administration and daily communication. These transformations laid the foundation for modern alphabets and contributed to the diversification of written language across cultures.
Educational Value and Modern Relevance
Hieroglyphics offer significant educational value by providing insights into ancient Egyptian culture, language, and art, making them essential for historical and linguistic studies. In contrast, cursive writing enhances modern relevance through its practical application in daily communication, fostering cognitive development and fine motor skills. Understanding both scripts enriches a comprehensive approach to literacy, bridging ancient history with contemporary educational practices.
Preservation and Representation in Art
Hieroglyphics provide detailed and visually rich representations that preserve ancient Egyptian culture through intricate symbols and pictograms, often found on monumental art and tombs, ensuring long-lasting durability. Cursive script, such as hieratic, prioritizes faster writing and practical communication on papyrus, sacrificing visual complexity but allowing broader dissemination of information and everyday record-keeping. The contrast in preservation highlights hieroglyphics' role in ceremonial and religious art, while cursive scripts capture dynamic aspects of historical life and administration.
Comparative Analysis: Symbolism vs Fluidity
Hieroglyphics emphasize intricate symbolism with detailed pictorial characters representing objects, ideas, and sounds, conveying meaning through visual complexity. In contrast, cursive script prioritizes fluidity and speed, utilizing continuous, connected strokes to allow faster writing and easier legibility. The symbolic density of hieroglyphics serves ceremonial and monumental purposes, while cursive's streamlined form enhances everyday communication efficiency.
Hieroglyphics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com