Jurisdictio refers to the authority granted to a legal body or court to hear and decide cases within a specific geographic area or subject matter. Understanding the scope and limits of jurisdictio is crucial for determining where a legal dispute should be filed and resolved. Explore the article to learn how jurisdictio affects your legal rights and the proper venue for your case.
Table of Comparison
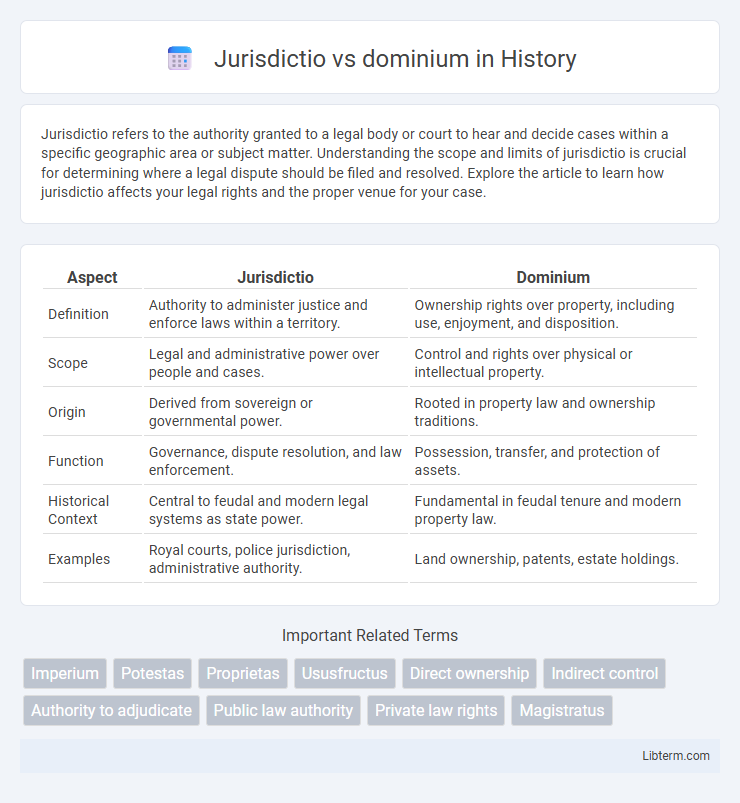
| Aspect | Jurisdictio | Dominium |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authority to administer justice and enforce laws within a territory. | Ownership rights over property, including use, enjoyment, and disposition. |
| Scope | Legal and administrative power over people and cases. | Control and rights over physical or intellectual property. |
| Origin | Derived from sovereign or governmental power. | Rooted in property law and ownership traditions. |
| Function | Governance, dispute resolution, and law enforcement. | Possession, transfer, and protection of assets. |
| Historical Context | Central to feudal and modern legal systems as state power. | Fundamental in feudal tenure and modern property law. |
| Examples | Royal courts, police jurisdiction, administrative authority. | Land ownership, patents, estate holdings. |
Introduction to Jurisdictio and Dominium
Jurisdictio refers to the legal authority or power to govern, regulate, or make decisions within a particular territory or over specific persons, establishing control through enforcement of laws and judicial processes. Dominium denotes ownership rights over property, encompassing the ability to use, enjoy, and dispose of assets with exclusive control recognized by law. Understanding the distinction highlights that Jurisdictio involves public sovereignty and governance, while Dominium concerns private rights of ownership in legal property systems.
Historical Origins of Jurisdictio and Dominium
Jurisdictio originated in Roman law as the legal authority to administer justice and govern people within a territory, establishing state power and public order. Dominium, also rooted in Roman law, referred to the private ownership rights over property, emphasizing control and exclusive use of assets. The distinction between jurisdictio as public sovereign authority and dominium as private property rights shaped medieval and modern legal systems.
Defining Jurisdictio: Legal Authority Explained
Jurisdictio refers to the legal authority or power granted to a court or governmental body to make decisions and enforce laws within a specific territory or over certain subjects. Unlike dominium, which denotes ownership or property rights, jurisdictio emphasizes control and governance through the application of law. This authority includes the capacity to adjudicate disputes, issue binding rulings, and regulate conduct under the legal framework.
Understanding Dominium: Concept of Ownership
Dominium represents the full ownership rights over property, encompassing the legal authority to use, enjoy, and dispose of the asset. In contrast to jurisdictio, which refers to authority or control typically exercised by a governing entity, dominium emphasizes the individual's proprietary rights. Understanding dominium is crucial for grasping property law as it defines the scope of ownership, including transfer, possession, and exclusive control of the asset.
Key Differences Between Jurisdictio and Dominium
Jurisdictio refers to the legal authority or right to govern, administer justice, or enforce laws within a specific territory, while dominium denotes the full ownership and control over property or assets. The key difference lies in jurisdictio encompassing public power exercised by sovereign entities, whereas dominium represents private ownership rights held by individuals or entities. Jurisdictio grants rights related to governance and legal enforcement, contrasting with dominium's emphasis on exclusive possession and use of property.
Interplay of Jurisdictio and Dominium in Roman Law
In Roman law, jurisdictio refers to the legal authority to adjudicate disputes and enforce laws, while dominium denotes ownership rights over property. The interplay between jurisdictio and dominium is crucial, as jurisdictio establishes the state's power to regulate and protect dominium, ensuring owners' rights are recognized and disputes resolved. This dynamic underscores how the state's legal authority sustains property rights within the Roman legal framework.
Jurisdictio in Modern Legal Systems
Jurisdictio in modern legal systems refers to the authority granted to courts and governmental bodies to interpret and apply laws within a defined territory, ensuring legal order and dispute resolution. This concept distinguishes from dominium, which pertains to property ownership rights, by emphasizing the state's regulatory power rather than individual ownership. Jurisdictio encompasses various types such as territorial, personal, and subject-matter jurisdiction, providing a framework for exercising legal authority effectively.
Dominium and Property Rights Today
Dominium represents the absolute ownership right over property, encompassing the authority to use, enjoy, and dispose of assets without limitation, distinguishing it from jurisdictio, which refers to legal authority or jurisdiction. In property rights today, dominium remains central in defining individual ownership, ensuring the owner's control extends to transfer, modification, or destruction of the property. Modern legal systems often balance dominium with public regulations, recognizing that property rights are subject to limitations for societal and environmental considerations.
Practical Implications in Court Decisions
The practical implications of jurisdictio versus dominium in court decisions revolve around the distinction between exercising authority over a person or property (jurisdictio) and possessing full ownership rights (dominium). Courts often evaluate jurisdictio to determine the extent of control or regulatory power an entity holds, particularly in administrative or family law cases, while dominium is critical in property disputes to establish rightful ownership and transfer rights. This differentiation guides judicial rulings on enforcement actions, possession claims, and the legitimacy of property transactions.
Conclusion: The Relevance of Jurisdictio vs Dominium
Jurisdictio and dominium represent fundamental legal concepts distinguishing authority from ownership, where jurisdictio denotes the power to govern or exercise legal control, and dominium refers to the right of property ownership. Their relevance emerges in property law, constitutional law, and administrative law, guiding the limits of state power versus individual rights. Understanding the distinction ensures clarity in legal decision-making, particularly in disputes involving sovereignty, property rights, and governmental authority.
Jurisdictio Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com