Replevin is a legal remedy that allows you to recover personal property wrongfully taken or withheld by another party. It enables the rightful owner to reclaim possession through a court order before a final judgment on ownership is made. Explore the rest of this article to understand how replevin works and when it might be the best option for reclaiming your property.
Table of Comparison
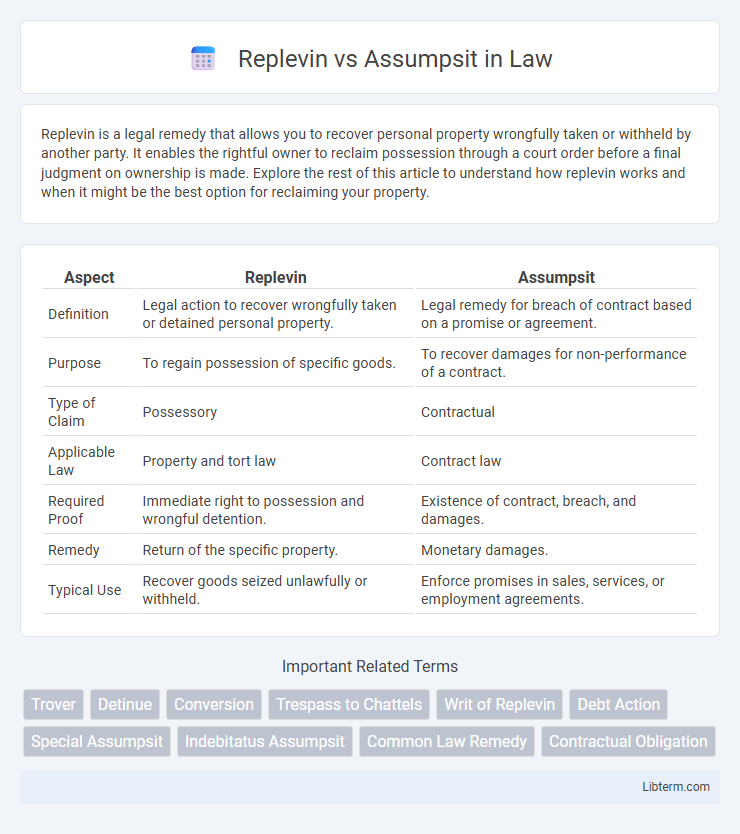
| Aspect | Replevin | Assumpsit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal action to recover wrongfully taken or detained personal property. | Legal remedy for breach of contract based on a promise or agreement. |
| Purpose | To regain possession of specific goods. | To recover damages for non-performance of a contract. |
| Type of Claim | Possessory | Contractual |
| Applicable Law | Property and tort law | Contract law |
| Required Proof | Immediate right to possession and wrongful detention. | Existence of contract, breach, and damages. |
| Remedy | Return of the specific property. | Monetary damages. |
| Typical Use | Recover goods seized unlawfully or withheld. | Enforce promises in sales, services, or employment agreements. |
Introduction to Replevin and Assumpsit
Replevin is a legal remedy used to recover specific personal property wrongfully taken or withheld, emphasizing the return of the actual item to its rightful owner. Assumpsit is a common law action for recovering damages arising from a breach of a simple contract or an agreement implied in fact or law. While replevin focuses on restoring possession of tangible goods, assumpsit addresses monetary compensation for non-performance or breach of contractual obligations.
Historical Background of Replevin
Replevin originated in medieval English common law as a legal remedy to recover wrongfully taken or detained goods before final judgment, emphasizing the protection of possessory rights. Historically, it evolved from writs issued to prevent unlawful dispossession and maintain peace by allowing immediate retrieval of personal property. This early development contrasted with assumpsit, which primarily addressed breaches of contract rather than possession disputes.
Historical Context of Assumpsit
Assumpsit originated in medieval English common law as a remedy for breach of a simple contract, emerging in the 14th century to address claims where formal writs were insufficient. It replaced older rigid forms by allowing recovery for non-performance of promises, playing a key role in the development of contract law. The evolution of assumpsit paved the way for modern contract remedies, contrasting with replevin's focus on recovery of wrongfully taken goods.
Definition and Key Features of Replevin
Replevin is a legal remedy aimed at recovering wrongfully taken or detained personal property before a final judgment on ownership is made. It involves the plaintiff reclaiming possession of specific goods, emphasizing prompt restitution rather than monetary damages. Key features include the requirement of wrongful detention, the necessity for immediate possession restoration, and the involvement of a bond to protect the defendant's interests during the claim process.
Definition and Key Features of Assumpsit
Assumpsit is a common law remedy used to enforce a contract or recover damages for its breach, especially involving a promise or agreement. It is distinct from replevin, which specifically concerns the recovery of wrongfully taken or withheld personal property. Key features of assumpsit include the requirement of a valid contract, proof of breach or non-performance, and resulting damages compensable through monetary relief.
Legal Principles Underlying Replevin
Replevin is a legal remedy designed to recover possession of wrongfully taken or detained personal property, emphasizing the protection of possessory rights rather than ownership. The fundamental principle underlying replevin is the immediate return of specific goods to the rightful possessor pending the final determination of ownership or title, distinguishing it from actions based on monetary compensation like assumpsit. This remedy involves a prompt judicial process to prevent irreparable harm caused by the deprivation of possession, ensuring that property is returned in kind rather than seeking damages for loss.
Legal Foundations of Assumpsit
Assumpsit is a common law contractual remedy grounded in the implied promise to perform a duty or pay damages for non-performance, originating from the principle of assumpsit which legally binds parties to their agreements. Unlike replevin, which focuses on the recovery of wrongfully detained chattels, assumpsit addresses breaches of contract where monetary compensation is sought for losses incurred. The legal foundation of assumpsit lies in the action on the case, evolved to enforce promises that do not fall under formal contract law, thereby expanding remedies for unjust conduct.
Procedural Differences: Replevin vs Assumpsit
Replevin involves a procedural action specifically designed for the recovery of wrongfully taken or detained personal property, requiring the plaintiff to post a bond and usually involves the immediate return of the property pending the final judgment. Assumpsit, a common law action for recovering damages due to breach of contract or non-performance, follows standard civil procedure without the necessity of recovering physical goods before judgment. Replevin emphasizes possession restoration through a swift judicial process, while Assumpsit centers on monetary compensation through dispute resolution on contractual obligations.
Practical Applications in Modern Law
Replevin is primarily used to recover wrongfully taken or detained personal property, allowing the rightful owner to regain possession quickly through a court order. Assumpsit focuses on enforcing contractual obligations or seeking damages for breach of contract when one party fails to perform agreed-upon duties. Modern legal practice applies replevin in cases of stolen goods or unlawful possession, while assumpsit handles disputes over unpaid debts and contractual non-performance.
Comparative Analysis: Replevin vs Assumpsit
Replevin and assumpsit differ primarily in purpose and legal remedy; replevin seeks the recovery of specific personal property wrongfully taken, while assumpsit addresses breach of contract for damages. Replevin involves repossessing goods and requires proof of lawful ownership, contrasting with assumpsit's focus on proving the existence of a contract and failure to fulfill agreed terms. The procedural requirements also vary: replevin often demands immediate possession through writ, whereas assumpsit proceeds through tort or contract claim for monetary compensation.
Replevin Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com