Commercial clauses outline essential terms governing business agreements, including payment conditions, delivery schedules, and liability limits. Clear clauses reduce disputes by defining each party's rights and obligations precisely. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these clauses protect Your interests in commercial contracts.
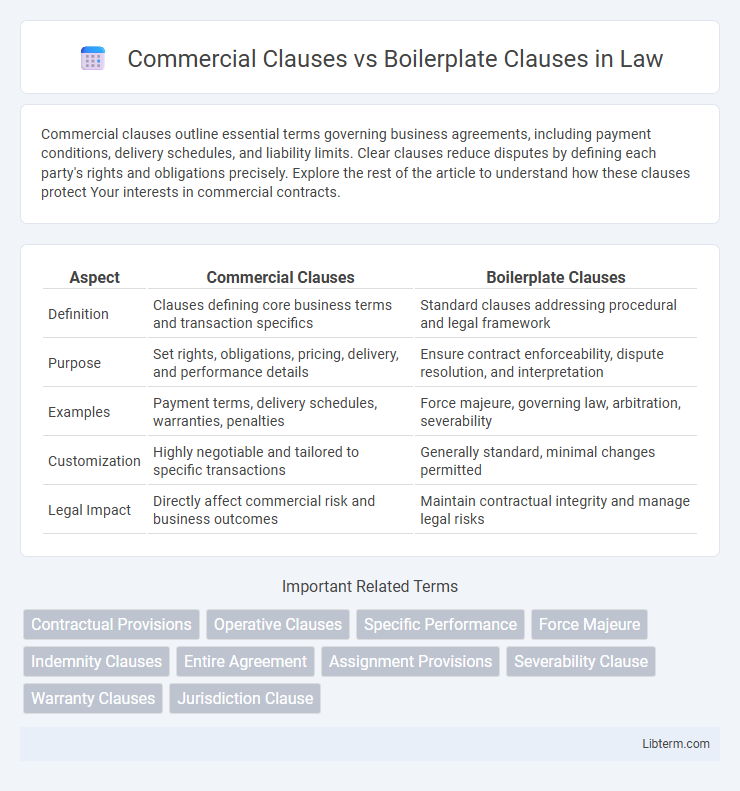
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Commercial Clauses | Boilerplate Clauses |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clauses defining core business terms and transaction specifics | Standard clauses addressing procedural and legal framework |
| Purpose | Set rights, obligations, pricing, delivery, and performance details | Ensure contract enforceability, dispute resolution, and interpretation |
| Examples | Payment terms, delivery schedules, warranties, penalties | Force majeure, governing law, arbitration, severability |
| Customization | Highly negotiable and tailored to specific transactions | Generally standard, minimal changes permitted |
| Legal Impact | Directly affect commercial risk and business outcomes | Maintain contractual integrity and manage legal risks |
Introduction to Contract Clauses
Commercial clauses in contracts specify key business terms such as pricing, delivery schedules, and payment conditions that directly impact the transaction's execution and commercial relationship between parties. Boilerplate clauses consist of standardized provisions like arbitration, governing law, and force majeure, ensuring legal consistency and risk allocation across various contracts. Distinguishing between these clauses is essential for drafting contracts that balance operational terms with overarching legal protections.
Defining Commercial Clauses
Commercial clauses define the specific rights, obligations, and conditions tailored to the core business transaction, such as payment terms, delivery schedules, warranties, and pricing structures. These clauses address the commercial risks and operational details unique to the contract's purpose, ensuring clarity in performance expectations. Distinct from boilerplate clauses, commercial clauses directly impact the economic and functional aspects of the agreement.
Understanding Boilerplate Clauses
Boilerplate clauses are standardized provisions found in contracts that address general terms such as jurisdiction, dispute resolution, and force majeure, ensuring consistency and legal clarity across agreements. These clauses typically do not focus on the primary commercial objectives but provide essential legal frameworks that support the enforceability of the contract. While commercial clauses customize the business-specific elements, boilerplate clauses create a foundational structure that mitigates risk and clarifies procedural obligations.
Key Differences Between Commercial and Boilerplate Clauses
Commercial clauses primarily address specific business terms such as payment conditions, delivery schedules, and product specifications, defining the operational framework of a contract. Boilerplate clauses consist of standard provisions like force majeure, jurisdiction, and dispute resolution, which provide a legal backbone ensuring contract stability across different agreements. The key difference lies in commercial clauses tailoring obligations and rights directly linked to transaction details, while boilerplate clauses manage overarching legal formalities and procedural guarantees.
Importance of Commercial Clauses in Agreements
Commercial clauses define the specific rights, obligations, and risks tailored to the unique business transaction, ensuring clarity and mutual understanding between parties. These clauses address critical elements such as payment terms, delivery schedules, and performance standards that directly impact the commercial success and legal enforceability of the agreement. Unlike boilerplate clauses, which provide standardized legal protections, commercial clauses are vital for aligning contractual terms with strategic business objectives and mitigating transaction-specific risks.
Role of Boilerplate Clauses in Contracts
Boilerplate clauses serve as essential contractual provisions that standardize the terms governing interpretation, dispute resolution, and enforcement, ensuring consistency and predictability across agreements. These clauses address issues such as governing law, jurisdiction, force majeure, and severability, which are critical for managing legal risks and operational uncertainties. By providing a legal framework applicable regardless of the specific commercial terms, boilerplate clauses complement commercial clauses and uphold the contract's overall integrity.
Examples of Common Commercial Clauses
Common commercial clauses in contracts include payment terms specifying currency, invoicing schedule, and due dates, delivery obligations outlining shipment methods and deadlines, and warranty provisions defining product standards and repair processes. Confidentiality agreements protect sensitive business information, while indemnity clauses allocate risk by detailing circumstances under which one party compensates the other for losses. Termination clauses often specify notice periods and conditions under which either party can end the agreement, ensuring clarity in commercial transactions.
Typical Boilerplate Clauses and Their Functions
Typical boilerplate clauses include force majeure, governing law, dispute resolution, indemnity, and entire agreement provisions, each serving to manage risks and clarify contractual obligations. Force majeure clauses protect parties from unforeseen events, while governing law and dispute resolution clauses specify jurisdiction and methods for handling conflicts. Indemnity clauses allocate liability, and entire agreement clauses confirm that the contract supersedes prior negotiations, ensuring legal clarity and enforceability.
Drafting Tips for Commercial and Boilerplate Clauses
Drafting commercial clauses requires precise language tailored to specific business transactions, such as payment terms, delivery schedules, and liability limitations, ensuring clear allocation of rights and obligations. Boilerplate clauses, covering jurisdiction, force majeure, and dispute resolution, must be carefully standardized yet adaptable to reflect the contract's context and avoid ambiguous or overly generic terms. Combining meticulous customization of commercial clauses with strategic integration of well-defined boilerplate provisions enhances contract enforceability and mitigates legal risks.
Conclusion: Balancing Commercial and Boilerplate Provisions
Balancing commercial clauses and boilerplate clauses is essential for creating effective contracts that protect parties' interests and ensure clarity. Commercial clauses address specific transaction terms, while boilerplate clauses provide standard legal protections and procedural rules. Harmonizing these provisions prevents conflicts, reduces ambiguities, and promotes enforceability, ultimately supporting smoother business relationships and risk management.
Commercial Clauses Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com