Allocate resources efficiently to maximize productivity and achieve your project goals within budget constraints. Proper allocation ensures optimal use of time, manpower, and materials, preventing waste and delays. Discover practical strategies to improve allocation and drive success in your ventures by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
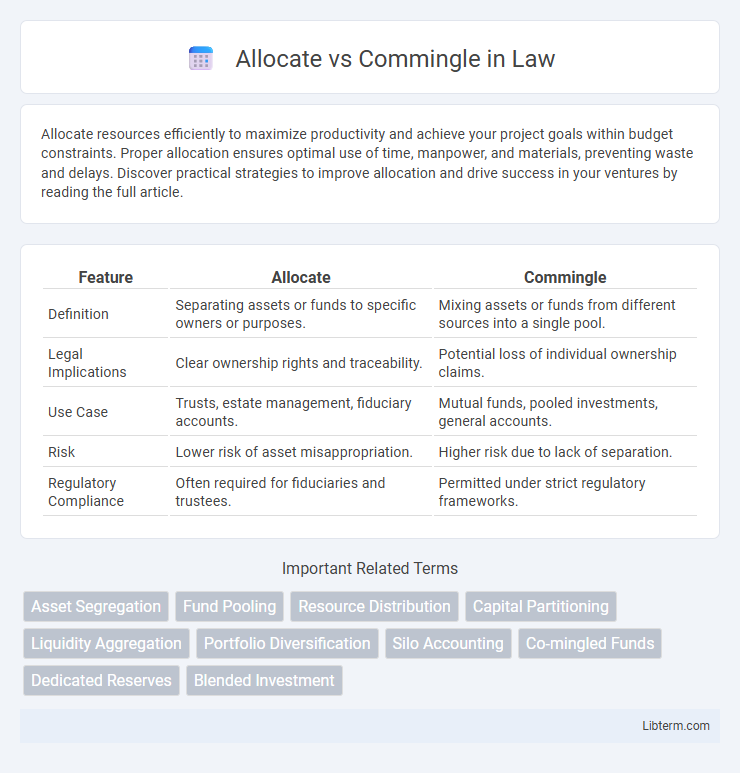
| Feature | Allocate | Commingle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Separating assets or funds to specific owners or purposes. | Mixing assets or funds from different sources into a single pool. |
| Legal Implications | Clear ownership rights and traceability. | Potential loss of individual ownership claims. |
| Use Case | Trusts, estate management, fiduciary accounts. | Mutual funds, pooled investments, general accounts. |
| Risk | Lower risk of asset misappropriation. | Higher risk due to lack of separation. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Often required for fiduciaries and trustees. | Permitted under strict regulatory frameworks. |
Understanding Asset Allocation
Understanding asset allocation involves deciding how to distribute investments across different asset classes, either by allocating specific portions to each category or commingling assets into pooled funds. Allocate strategies emphasize targeted distribution to balance risk and return, while commingle approaches pool resources for collective investment, potentially enhancing diversification and reducing costs. Effective asset management depends on aligning allocation choices with investment goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
Defining Commingling in Finance
Commingling in finance refers to the practice of combining client funds with the firm's own money, which can raise risks related to fiduciary responsibility and regulatory compliance. Unlike allocate methods where assets are distinctly separated and assigned to individual accounts, commingling merges resources, potentially compromising transparency and increasing the chance of misuse or misidentification of funds. Regulatory frameworks, such as those imposed by the SEC or FINRA, strictly govern commingling to protect investor interests and maintain financial integrity.
Key Differences Between Allocate and Commingle
Allocate involves assigning specific resources or funds to designated accounts or projects, ensuring clear tracking and accountability. Commingle refers to mixing resources, such as funds or assets, from multiple sources into a single pool without maintaining individual distinctions. Key differences include allocation's emphasis on segregation and accountability versus commingling's consolidation for simplified management or investment.
Benefits of Asset Allocation Strategies
Asset allocation strategies optimize investment portfolios by distributing assets across diverse categories such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, which reduces risk and enhances potential returns. Allocating funds according to an investor's risk tolerance and financial goals provides customized exposure to various market sectors, improving long-term growth prospects. In contrast to commingling funds, allocation maintains transparency and control over individual investments, ensuring better alignment with specific financial objectives.
Risks Associated with Commingling Funds
Commingling funds increases the risk of legal complications, such as breach of fiduciary duty and difficulty in tracing funds during audits or disputes. It can lead to financial mismanagement and potential loss of client trust due to the lack of transparency and accountability. Properly allocating funds mitigates these risks by ensuring clear segregation and accurate record-keeping, which facilitates compliance and protects all parties involved.
Legal Implications of Commingling Assets
Commingling assets can create significant legal risks by obscuring individual ownership and making it difficult to trace funds, potentially leading to claims of impropriety or breach of fiduciary duty. Courts often scrutinize commingled assets in divorce, bankruptcy, or estate disputes, increasing the likelihood of financial liability or loss of protection for personal or business assets. Properly allocating assets maintains clear records and ownership rights, minimizing legal exposure and ensuring compliance with fiduciary, contractual, and regulatory obligations.
Best Practices for Allocating Resources
Allocating resources involves assigning specific tasks, budgets, or materials to designated projects or departments to maximize efficiency and accountability. Best practices include setting clear objectives, using data-driven forecasts, and regularly reviewing allocations to adjust for changing priorities. In contrast, commingling resources blends assets across projects or functions, which can reduce transparency and complicate performance tracking.
How to Avoid Commingling Issues
To avoid commingling issues, maintain clear segregation of funds by using separate bank accounts for each client or project, ensuring accurate tracking and allocation of resources. Implement robust accounting software with detailed transaction categories and audit trails to monitor fund movements precisely. Regular reconciliation and transparent reporting enhance compliance and prevent legal complications associated with fund commingling.
Real-World Examples: Allocate vs Commingle
In real-world financial management, allocate refers to distributing funds or resources specifically to designated accounts or projects, ensuring clear tracking and accountability, such as a company assigning budget to different departments. Commingle involves mixing funds from different sources into a single account, commonly seen in investment or escrow accounts where client funds are pooled to simplify management but require strict compliance to prevent misuse. For instance, law firms often commingle client funds for operational efficiency, while nonprofits allocate donations to specific programs to maintain transparency and donor trust.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Portfolio
Choosing the right approach for your portfolio involves understanding the key differences between allocate and commingle strategies. Allocate strategies assign specific assets or securities to individual investors, offering greater control and customization, whereas commingle strategies pool assets from multiple investors, providing diversification and cost efficiency. Portfolio managers should evaluate factors such as investment objectives, risk tolerance, liquidity needs, and administrative complexity to determine whether allocation or commingling aligns best with their portfolio goals.
Allocate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com