Warranty coverage protects your purchase by ensuring repairs or replacements for defects within a specified period. Understanding the terms and conditions helps you make informed decisions about product maintenance and potential claims. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to maximize your warranty benefits and safeguard your investment.
Table of Comparison
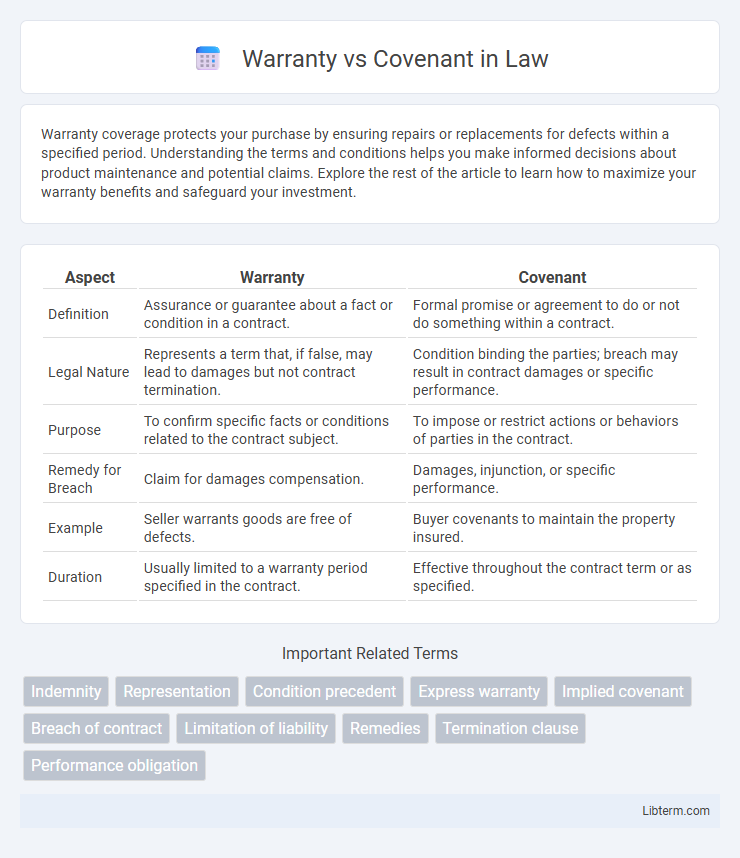
| Aspect | Warranty | Covenant |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assurance or guarantee about a fact or condition in a contract. | Formal promise or agreement to do or not do something within a contract. |
| Legal Nature | Represents a term that, if false, may lead to damages but not contract termination. | Condition binding the parties; breach may result in contract damages or specific performance. |
| Purpose | To confirm specific facts or conditions related to the contract subject. | To impose or restrict actions or behaviors of parties in the contract. |
| Remedy for Breach | Claim for damages compensation. | Damages, injunction, or specific performance. |
| Example | Seller warrants goods are free of defects. | Buyer covenants to maintain the property insured. |
| Duration | Usually limited to a warranty period specified in the contract. | Effective throughout the contract term or as specified. |
Understanding Warranties: Definition and Scope
Warranties are legally binding assurances given by one party to another, guaranteeing specific facts or conditions about a product or service, often covering quality, performance, or title. They provide a basis for legal recourse if the promised conditions are not met, defining the scope of liability and remedies available. Understanding warranties involves analyzing their express or implied nature, duration, and the precise obligations they impose within contractual agreements.
What Is a Covenant? Key Features Explained
A covenant is a legally binding promise or agreement between parties in a contract, often relating to property or real estate transactions. Key features include enforceability against successors, specificity in obligations, and the creation of obligations or restrictions on the use of land or behavior. Unlike warranties, covenants focus on ongoing duties or restrictions rather than guarantees of fact or condition.
Core Differences Between Warranty and Covenant
Warranty guarantees the truth of certain facts at the time a contract is made, providing the injured party with the right to claim damages if the warranty is breached. Covenant involves a promise or agreement that a party will do or refrain from doing something in the future, with breach entitling the non-breaching party to seek specific performance or damages. The core difference lies in warranties addressing present or past facts, while covenants focus on future conduct or obligations.
Legal Implications: Warranty vs Covenant
Warranties in legal contracts provide assurances or promises about the truth of certain facts, allowing the injured party to claim damages if a warranty is breached without necessarily terminating the contract. Covenants involve promises to perform or refrain from specific actions, and breach may entitle the non-breaching party to seek remedies including contract termination or specific performance. Understanding the distinct legal implications of warranties versus covenants is crucial for drafting enforceable agreements that clearly outline rights, obligations, and available remedies.
Types of Warranties in Contracts
Types of warranties in contracts include express warranties, which are explicitly stated promises about the quality or performance of goods or services, and implied warranties, which arise by law, such as the implied warranty of merchantability ensuring goods are fit for ordinary use. There are also warranty of title guaranteeing the seller's right to transfer ownership, and warranty against encumbrances protecting the buyer from undisclosed claims or liens. Understanding these warranties is crucial for defining the obligations and protections for parties within contract law.
Common Types of Covenants
Common types of covenants in real estate include affirmative covenants requiring specific actions like property maintenance, and restrictive covenants limiting property use, such as prohibiting commercial activities or imposing architectural guidelines. Warranty differs as it guarantees certain conditions or facts about the property, such as clear title or undisclosed defects, whereas covenants are ongoing obligations or restrictions tied to the property deed. Understanding these distinctions is critical in negotiating property agreements and ensuring compliance with contractual obligations.
Breach of Warranty: Consequences and Remedies
Breach of warranty in contract law occurs when a party fails to fulfill a specific guarantee or promise, leading to potential damages or compensation claims. Remedies for breach of warranty typically include monetary damages to cover losses but do not usually permit contract termination, distinguishing it from breach of covenant or condition. Courts assess the extent of harm caused by the breach and award damages proportionate to the losses directly resulting from the unmet warranty.
Breach of Covenant: Legal Recourse
When a breach of covenant occurs, the harmed party typically seeks legal recourse through damages or specific performance to enforce the agreement. Unlike warranties, covenants are promises within a contract whose violation can lead to claims for injunctive relief or contract termination. Courts assess the nature of the breach and related contract terms to determine appropriate remedies under contract law principles.
Real-World Examples: Warranty and Covenant in Practice
In real estate transactions, a warranty typically guarantees the condition of the property, such as a home inspector providing a warranty on structural elements, offering homeowners peace of mind against future defects. Covenants often appear in homeowners' associations, where property owners agree to abide by community rules like maintaining lawn appearance or prohibiting certain exterior modifications to preserve neighborhood aesthetics. Understanding these practical distinctions helps buyers recognize that warranties protect against existing issues, while covenants impose ongoing obligations affecting property use.
Choosing the Right Clause: Warranty or Covenant?
Choosing the right clause between warranty and covenant depends on the obligations and remedies desired in a contract. A warranty provides a promise that certain facts or conditions are true, allowing for damages if breached, while a covenant is a binding agreement to perform or refrain from specific actions, often enforceable through injunctions or specific performance. Assessing the purpose, scope, and enforcement mechanisms of each clause ensures selecting the appropriate legal tool for risk management and contractual compliance.
Warranty Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com