A writ of habeas corpus is a legal instrument used to challenge unlawful detention or imprisonment, ensuring an individual's right to liberty is protected. It compels authorities to justify the legality of a person's detention before a court, preventing arbitrary incarceration. Explore the detailed procedures and important cases involving habeas corpus in the full article.
Table of Comparison
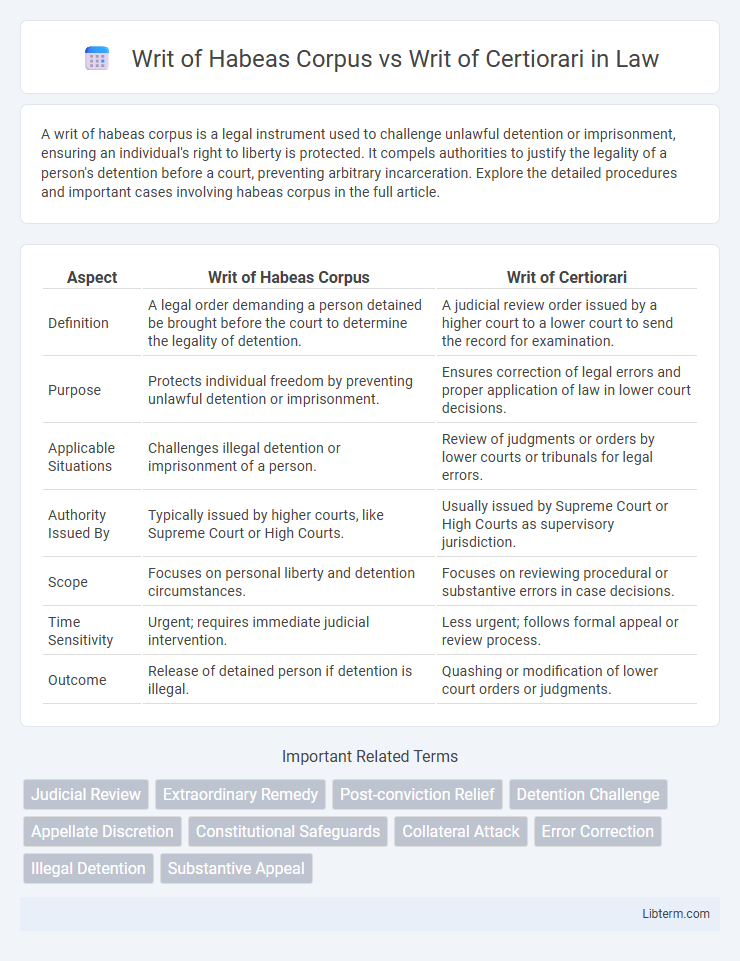
| Aspect | Writ of Habeas Corpus | Writ of Certiorari |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A legal order demanding a person detained be brought before the court to determine the legality of detention. | A judicial review order issued by a higher court to a lower court to send the record for examination. |
| Purpose | Protects individual freedom by preventing unlawful detention or imprisonment. | Ensures correction of legal errors and proper application of law in lower court decisions. |
| Applicable Situations | Challenges illegal detention or imprisonment of a person. | Review of judgments or orders by lower courts or tribunals for legal errors. |
| Authority Issued By | Typically issued by higher courts, like Supreme Court or High Courts. | Usually issued by Supreme Court or High Courts as supervisory jurisdiction. |
| Scope | Focuses on personal liberty and detention circumstances. | Focuses on reviewing procedural or substantive errors in case decisions. |
| Time Sensitivity | Urgent; requires immediate judicial intervention. | Less urgent; follows formal appeal or review process. |
| Outcome | Release of detained person if detention is illegal. | Quashing or modification of lower court orders or judgments. |
Introduction to Legal Writs
The writ of habeas corpus is a fundamental legal instrument used to challenge unlawful detention by compelling authorities to present the detained individual before the court. The writ of certiorari serves as a supervisory tool for higher courts to review and correct errors in lower court decisions, ensuring proper judicial process. Both writs are critical components of judicial review, safeguarding individual rights and maintaining the rule of law.
Defining Habeas Corpus
A Writ of Habeas Corpus is a legal order requiring a person under arrest to be brought before a court to determine if their detention is lawful, serving as a fundamental safeguard against unlawful imprisonment. In contrast, a Writ of Certiorari is an order by a higher court to review the decision and proceedings of a lower court. Habeas Corpus protects individual freedom by ensuring that imprisonment does not occur without just cause.
Defining Certiorari
The writ of certiorari is a legal order issued by a higher court directing a lower court to deliver its record in a case for review, primarily used to correct errors of jurisdiction or law. Unlike the writ of habeas corpus, which is focused on challenging unlawful detention or imprisonment, certiorari serves to ensure the proper application of law by enabling appellate courts to oversee lower court decisions. This discretionary remedy plays a critical role in the judicial system by maintaining consistency and legality in court rulings.
Historical Origins and Development
The Writ of Habeas Corpus originated in English common law during the 12th century as a remedy to challenge unlawful detention, establishing a fundamental safeguard for individual liberty. The Writ of Certiorari emerged later in the 14th century as a supervisory writ allowing higher courts to review and correct lower court decisions, enhancing judicial oversight. Both writs evolved to balance state authority and personal rights, influencing modern legal systems worldwide.
Core Purpose and Objectives
The Writ of Habeas Corpus serves the core purpose of safeguarding individual freedom by requiring a person under arrest to be brought before a judge to review the legality of detention. The Writ of Certiorari primarily functions to supervise lower courts or administrative bodies by ordering the record of a case for review, ensuring proper jurisdiction and adherence to legal procedures. Both writs aim to uphold justice--Habeas Corpus by preventing unlawful imprisonment, and Certiorari by maintaining legal order through appellate oversight.
Legal Grounds for Issuance
The Writ of Habeas Corpus is issued to determine the legality of a person's detention, ensuring protection against unlawful imprisonment by requiring the custodian to justify the detainee's confinement. The Writ of Certiorari is granted by higher courts to review and correct errors of jurisdiction or grave abuse of discretion in lower court decisions, ensuring proper legal procedure and fairness. Both writs serve as essential judicial tools but differ in purpose, with Habeas Corpus focusing on personal liberty and Certiorari addressing procedural or jurisdictional errors in judicial acts.
Procedural Differences
The Writ of Habeas Corpus demands the release of a person unlawfully detained, requiring the custodian to justify the legality of the detention before the court, often initiated by the detainee or their representative. The Writ of Certiorari is an appellate tool used by higher courts to review and correct lower court decisions, focusing on legal errors or jurisdictional issues rather than on detainment. Habeas Corpus proceedings are typically expedited to prevent unlawful imprisonment, while Certiorari follows a discretionary review process based on petitions filed after final judgments.
Impact on Judicial Review
The Writ of Habeas Corpus directly influences judicial review by safeguarding individual freedom from unlawful detention, compelling courts to examine the legality of imprisonment. In contrast, the Writ of Certiorari impacts judicial review by enabling higher courts, particularly the Supreme Court, to selectively review and correct errors in lower court decisions, thus ensuring consistency and adherence to legal standards. Both writs play crucial roles in the judicial system by affirming the authority of courts to oversee governmental and lower court actions, but they operate through distinct procedural mechanisms.
Key Case Examples
The writ of habeas corpus is exemplified by the landmark case *Boumediene v. Bush* (2008), where the Supreme Court affirmed detainees' constitutional right to challenge unlawful imprisonment. In contrast, the writ of certiorari is highlighted in *Roe v. Wade* (1973), where the Supreme Court granted certiorari to review and ultimately decide on abortion rights. These cases demonstrate habeas corpus as a protection against wrongful detention, while certiorari functions as a discretionary tool for the Court to select cases of significant legal importance.
Comparative Analysis and Practical Implications
The Writ of Habeas Corpus serves as a fundamental legal remedy to challenge unlawful detention, ensuring an individual's right to personal liberty, while the Writ of Certiorari functions as a supervisory order by a higher court to review and correct lower court decisions for jurisdictional or procedural errors. In comparative analysis, Habeas Corpus directly addresses the legality of detention, offering immediate relief, whereas Certiorari provides appellate oversight primarily focused on legal error correction rather than personal freedom. Practically, Habeas Corpus is pivotal in safeguarding constitutional rights against illegal imprisonment, while Certiorari maintains judicial consistency and uniformity in legal interpretations across cases.
Writ of Habeas Corpus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com