Specific performance is a legal remedy that compels a party to fulfill their contractual obligations exactly as agreed, rather than providing monetary damages. This remedy is typically granted when monetary compensation is inadequate, such as in real estate transactions or unique goods contracts. Explore the article to understand how specific performance can impact your contractual agreements and when it may be applied.
Table of Comparison
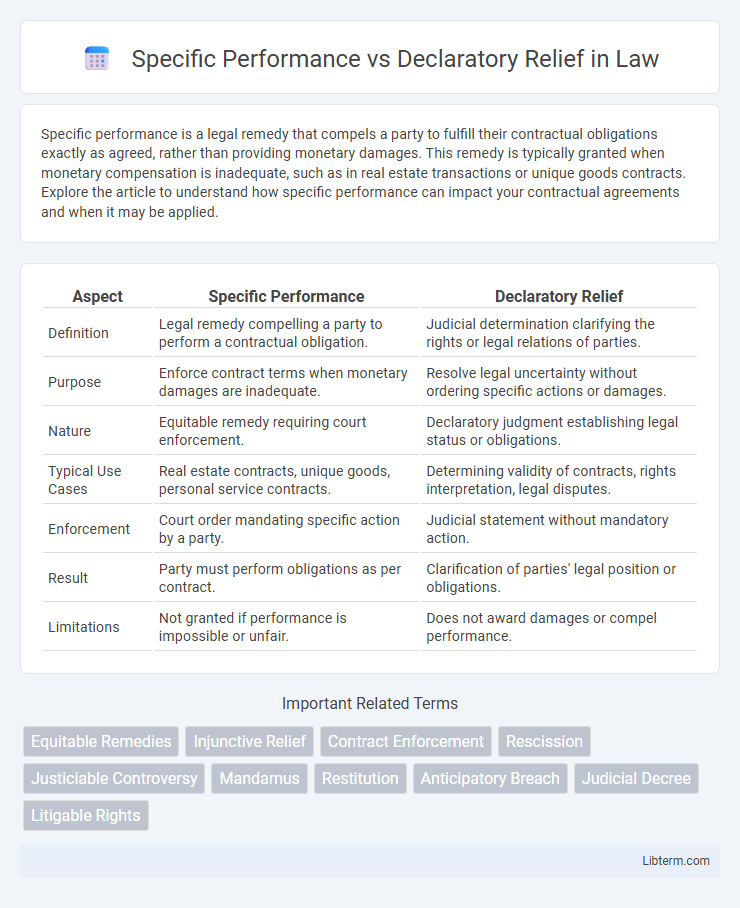
| Aspect | Specific Performance | Declaratory Relief |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal remedy compelling a party to perform a contractual obligation. | Judicial determination clarifying the rights or legal relations of parties. |
| Purpose | Enforce contract terms when monetary damages are inadequate. | Resolve legal uncertainty without ordering specific actions or damages. |
| Nature | Equitable remedy requiring court enforcement. | Declaratory judgment establishing legal status or obligations. |
| Typical Use Cases | Real estate contracts, unique goods, personal service contracts. | Determining validity of contracts, rights interpretation, legal disputes. |
| Enforcement | Court order mandating specific action by a party. | Judicial statement without mandatory action. |
| Result | Party must perform obligations as per contract. | Clarification of parties' legal position or obligations. |
| Limitations | Not granted if performance is impossible or unfair. | Does not award damages or compel performance. |
Understanding Specific Performance
Specific performance is an equitable remedy compelling a party to fulfill their contractual obligations when monetary damages are inadequate, commonly applied in real estate transactions and unique goods contracts. It ensures the aggrieved party receives the exact performance promised, emphasizing the uniqueness or irreplaceability of the subject matter. Understanding specific performance involves recognizing its limitations, such as impracticality in personal service contracts or where continuous supervision by courts is necessary.
Defining Declaratory Relief
Declaratory relief is a judicial determination that clarifies the rights, duties, or obligations of parties without ordering any specific action or awarding damages. This form of equitable remedy resolves legal uncertainty by establishing the legal status or interpretation of contracts, statutes, or legal relationships. Unlike specific performance, which compels parties to fulfill contractual duties, declaratory relief provides certainty and guidance for future conduct without mandating performance.
Key Differences Between Specific Performance and Declaratory Relief
Specific performance compels a party to fulfill contractual obligations when monetary damages are inadequate, often used in real estate or unique goods cases. Declaratory relief, on the other hand, provides a court-issued statement clarifying parties' rights or legal relationships without ordering any action or awarding damages. The key difference lies in enforcement: specific performance mandates action, whereas declaratory relief resolves uncertainties without compelling conduct.
Legal Basis for Specific Performance
Specific performance is an equitable remedy grounded in contract law, compelling a party to fulfill their contractual obligations when monetary damages are inadequate. The legal basis for specific performance derives from principles established in landmark cases such as *Lumley v. Wagner* and codified within the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) for the sale of goods. Declaratory relief, in contrast, provides a judicial determination of rights or status without mandating action, serving as a preventive remedy rather than a coercive enforcement.
Legal Basis for Declaratory Relief
The legal basis for declaratory relief is rooted in statutes such as the Declaratory Judgment Act, which empowers courts to determine the rights, duties, or obligations of parties without ordering any specific action or awarding damages. This remedy is particularly valuable in resolving legal uncertainties and preventing future litigation by providing a binding judicial determination on the parties' legal relationship. Unlike specific performance, which mandates a party to fulfill contractual obligations, declaratory relief solely clarifies legal statuses or interpretations without coercive enforcement.
Situations Warranting Specific Performance
Specific performance is typically warranted in cases involving unique goods or real estate where monetary damages are inadequate to remedy the breach. Courts grant specific performance when the subject matter is irreplaceable, such as in contracts for the sale of land or rare items. This equitable remedy ensures that the party receives exactly what was agreed upon, rather than a financial substitute.
When to Seek Declaratory Relief
Declaratory relief is sought when a party needs a judicial determination to clarify their rights, obligations, or legal status without requesting coercive enforcement or damages. It is particularly useful in preventing future disputes by resolving uncertainties before contractual breaches or violations occur. Courts grant declaratory relief when there is a justiciable controversy that requires immediate resolution to guide future conduct.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Specific Performance
Specific performance compels a party to fulfill contractual obligations, providing a powerful remedy when monetary damages are inadequate, especially in unique goods or real estate transactions. Its advantages include ensuring contract enforcement and preventing unjust enrichment, but it poses challenges like difficulty in supervision, potential hardship on the breaching party, and limited applicability in personal service contracts. The disadvantages also involve delayed resolution and the risk of prolonged litigation, highlighting the importance of careful judicial discretion in ordering specific performance.
Pros and Cons of Declaratory Relief
Declaratory relief provides a court's official determination of parties' rights without ordering any specific action, offering clarity and preventing future disputes. Its pros include lower costs, faster resolution, and the ability to guide behavior without coercive enforcement. However, it lacks the power to compel action, may lead to continued litigation if parties ignore the declaration, and sometimes fails to provide immediate effective remedies.
Choosing the Right Remedy: Factors to Consider
Choosing between specific performance and declaratory relief depends on the nature of the contractual breach and the feasibility of enforcing the remedy. Specific performance is ideal when monetary damages are inadequate, often in transactions involving unique property or goods, ensuring actual fulfillment of contractual obligations. Declaratory relief serves as a proactive measure to clarify legal rights or obligations without compelling action, suitable when parties seek guidance to prevent future disputes or confirm contract terms.
Specific Performance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com