Interpleader is a legal procedure designed to resolve disputes when multiple parties claim the same property or funds held by a third party, known as the stakeholder. This process protects the stakeholder from multiple liabilities by allowing the court to determine the rightful claimant. Discover how interpleader can safeguard your interests and simplify complex multi-claim disputes by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
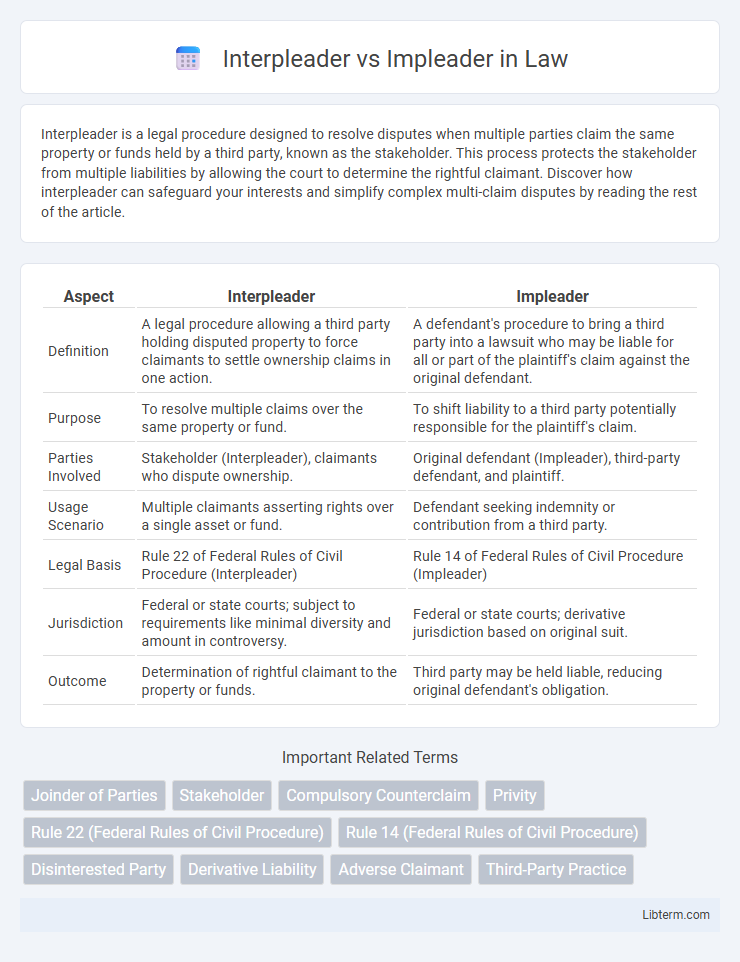
| Aspect | Interpleader | Impleader |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A legal procedure allowing a third party holding disputed property to force claimants to settle ownership claims in one action. | A defendant's procedure to bring a third party into a lawsuit who may be liable for all or part of the plaintiff's claim against the original defendant. |
| Purpose | To resolve multiple claims over the same property or fund. | To shift liability to a third party potentially responsible for the plaintiff's claim. |
| Parties Involved | Stakeholder (Interpleader), claimants who dispute ownership. | Original defendant (Impleader), third-party defendant, and plaintiff. |
| Usage Scenario | Multiple claimants asserting rights over a single asset or fund. | Defendant seeking indemnity or contribution from a third party. |
| Legal Basis | Rule 22 of Federal Rules of Civil Procedure (Interpleader) | Rule 14 of Federal Rules of Civil Procedure (Impleader) |
| Jurisdiction | Federal or state courts; subject to requirements like minimal diversity and amount in controversy. | Federal or state courts; derivative jurisdiction based on original suit. |
| Outcome | Determination of rightful claimant to the property or funds. | Third party may be held liable, reducing original defendant's obligation. |
Introduction to Interpleader and Impleader
Interpleader is a legal procedure allowing a party holding property or funds to initiate a lawsuit compelling claimants to litigate their entitlement, preventing multiple liabilities. Impleader enables a defendant to bring a third party into a lawsuit, asserting that the third party may be liable for all or part of the plaintiff's claim. These mechanisms streamline complex litigation by consolidating disputes involving multiple parties into a single proceeding.
Understanding Interpleader: Definition and Purpose
Interpleader is a legal procedure designed to resolve disputes involving multiple parties claiming the same property or funds, allowing the holder of the property to avoid multiple liabilities by initiating a single lawsuit. It serves to protect the stakeholder from conflicting claims by requiring claimants to litigate their entitlements among themselves. The primary purpose of interpleader is to ensure a fair and efficient resolution while preventing the stakeholder from facing double liability or multiple lawsuits.
Understanding Impleader: Definition and Purpose
Impleader is a procedural mechanism in civil litigation that allows a defendant to bring a third party into a lawsuit, claiming that this third party is liable for all or part of the plaintiff's claim. The primary purpose of impleader is to efficiently resolve related claims involving multiple parties in a single action, preventing multiple lawsuits and inconsistent judgments. Unlike interpleader, which addresses competing claims over the same property or fund, impleader focuses on shifting liability or indemnity to a third party.
Key Differences Between Interpleader and Impleader
Interpleader involves a party holding property or funds who initiates a lawsuit to compel multiple claimants to litigate their claims collectively, preventing multiple liabilities. Impleader allows a defendant to bring a third party into the lawsuit if that third party may be liable for all or part of the plaintiff's claim against the defendant. The key difference lies in interpleader resolving competing claims over the same property, while impleader shifts liability among parties connected by the original claim.
Legal Scenarios for Using Interpleader
Interpleader is primarily used in legal scenarios where multiple parties claim rights to the same property or funds, allowing the stakeholder to avoid multiple liabilities by consolidating all claimants into a single lawsuit. Common instances include disputes over insurance proceeds, escrow funds, or inheritance where a neutral party holds the contested asset. Unlike impleader, which brings a third-party defendant into an existing lawsuit to share liability, interpleader resolves conflicting claims among claimants to the same specific property or fund.
Legal Scenarios for Using Impleader
Impleader is primarily used in legal scenarios where a defendant seeks to bring a third party into a lawsuit who may be liable for all or part of the plaintiff's claim, such as in indemnity or contribution cases. This mechanism is common in contract disputes, construction litigation, and tort claims where a third party's involvement is essential to resolving the complete controversy. Courts facilitate impleader to streamline complex lawsuits by addressing related claims collectively, minimizing the risk of multiple lawsuits.
Procedural Requirements for Interpleader
Interpleader requires the plaintiff to deposit the disputed property or funds with the court and name all potential claimants as defendants to resolve conflicting claims in a single action. The procedural steps include filing a verified complaint, providing notice to all claimants, and securing the court's approval before disbursing the property. Compliance with these requirements ensures protection from multiple liability and promotes judicial efficiency in distributing the contested assets.
Procedural Requirements for Impleader
Impleader requires the defendant to file a third-party complaint within a specified time frame, typically 14 days after serving the original answer, to bring in a third party who may be liable for any judgment against the defendant. The third-party defendant must be properly served with the complaint and given the opportunity to respond. Procedural rules under Rule 14 of the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure govern the impleader process, including deadlines, service requirements, and judicial discretion to permit or deny impleader motions.
Advantages and Limitations of Interpleader and Impleader
Interpleader offers the advantage of protecting a stakeholder from multiple liabilities by consolidating competing claims into a single lawsuit, simplifying resolution and reducing legal costs, but it is limited to situations involving rival claimants to the same fund or property. Impleader allows a defendant to bring a third party into a lawsuit who may be liable for all or part of the plaintiff's claim, spreading liability and potentially minimizing the defendant's financial exposure; however, it complicates litigation, may prolong proceedings, and depends on timely court approval. Both mechanisms streamline disputes differently: interpleader efficiently resolves conflicting claims, while impleader reallocates liability, each with distinct procedural constraints and strategic implications.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Interpleader and Impleader
Choosing between interpleader and impleader depends on the nature of the dispute and the parties involved. Interpleader effectively resolves claims from multiple parties competing for the same property or funds, preventing duplicate litigation and inconsistent obligations. Impleader is optimal when a defendant seeks to bring a third party into a lawsuit to share liability or indemnify, streamlining the allocation of responsibility within a single case.
Interpleader Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com