Estoppel prevents a person from asserting something contrary to what is implied by a previous action or statement, ensuring fairness and consistency in legal matters. This principle is crucial in contract and property law to avoid unjust outcomes. Discover how estoppel can impact your rights and legal decisions in the full article.
Table of Comparison
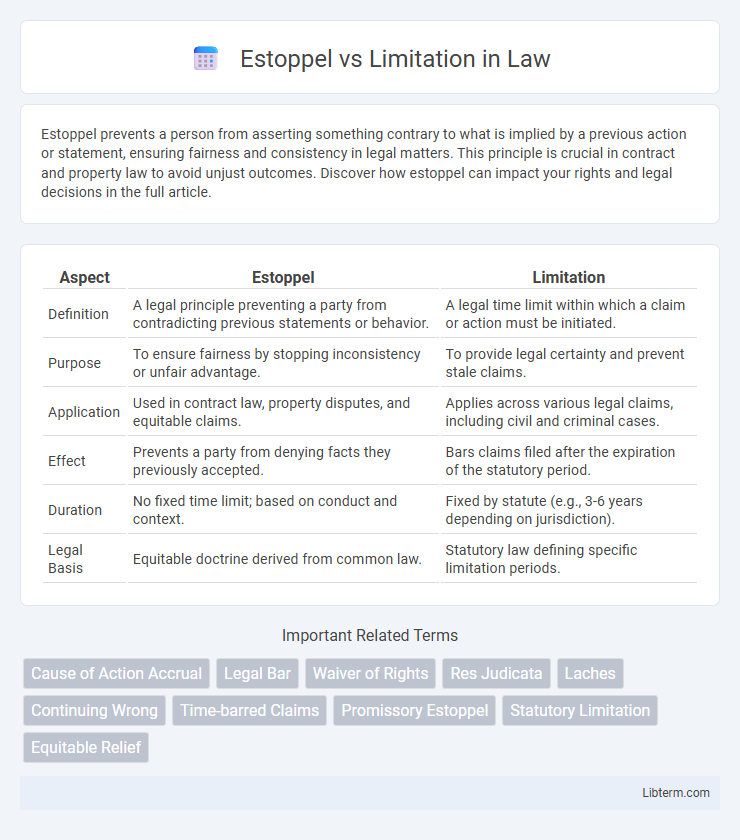
| Aspect | Estoppel | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A legal principle preventing a party from contradicting previous statements or behavior. | A legal time limit within which a claim or action must be initiated. |
| Purpose | To ensure fairness by stopping inconsistency or unfair advantage. | To provide legal certainty and prevent stale claims. |
| Application | Used in contract law, property disputes, and equitable claims. | Applies across various legal claims, including civil and criminal cases. |
| Effect | Prevents a party from denying facts they previously accepted. | Bars claims filed after the expiration of the statutory period. |
| Duration | No fixed time limit; based on conduct and context. | Fixed by statute (e.g., 3-6 years depending on jurisdiction). |
| Legal Basis | Equitable doctrine derived from common law. | Statutory law defining specific limitation periods. |
Introduction to Estoppel and Limitation
Estoppel prevents a party from asserting rights or facts that contradict their previous statements or behaviors, thereby ensuring fairness and consistency in legal relations. Limitation refers to the statutory period within which a legal claim must be initiated, after which the right to sue is barred to provide legal certainty and finality. Both doctrines play critical roles in dispute resolution by regulating the timing and admissibility of claims in courts.
Defining Estoppel: Key Concepts
Estoppel is a legal doctrine preventing a party from asserting something contrary to what is implied by their previous actions or statements, ensuring fairness and consistency in legal proceedings. Key concepts include representation, reliance, and detriment, where one party's misleading conduct causes another to act to their disadvantage. Estoppel differs from limitation periods, which restrict the time frame to bring a claim, as it focuses on preventing injustice due to inconsistent behavior rather than enforcing procedural deadlines.
Understanding the Law of Limitation
The law of limitation sets the maximum time period within which a legal claim can be initiated, ensuring timely resolution and preventing indefinite threats of litigation. Estoppel, on the other hand, prevents a party from asserting a right or defense that contradicts their previous conduct or statements, often serving as an equitable barrier when the limitation period has expired. Understanding the distinction clarifies that limitation laws impose statutory deadlines for claims, while estoppel operates as a defense to promote fairness and prevent injustice in legal proceedings.
Core Differences Between Estoppel and Limitation
Estoppel prevents a party from asserting a claim or right contradictory to their previous conduct or statements, ensuring fairness and reliance in legal relationships. Limitation, governed by statutes of limitations, restricts the time period within which a legal action can be initiated to promote legal certainty and finality. While estoppel addresses equitable fairness and behavior, limitation strictly concerns the temporal boundaries for bringing lawsuits.
Legal Principles Governing Estoppel
Estoppel operates as a legal principle preventing a party from asserting rights or facts contradictory to previous statements or behavior, ensuring fairness and consistency in judicial proceedings. It primarily functions to protect the reliance interests of others, preventing injustice caused by misleading conduct or silence when there is a duty to speak. Unlike limitation, which restricts the time within which legal claims can be made, estoppel bars claims based on equitable grounds regardless of time constraints.
Statutory Provisions for Limitation
Statutory provisions for limitation establish fixed time periods within which legal claims must be initiated, typically defined by specific legislation such as the Limitation Act 1980 in England and Wales. These statutory limits are designed to provide legal certainty and prevent the indefinite threat of litigation by barring claims after expiration of the prescribed period. Estoppel, in contrast, is an equitable doctrine that can prevent a party from relying on limitation defenses if their conduct has misled the opposing party, but it does not override or extend statutory limitation periods.
Applications of Estoppel in Legal Proceedings
Estoppel prevents a party from contradicting or denying previous statements or actions that were relied upon by others, ensuring fairness and consistency in legal proceedings. It is commonly applied in contract disputes to bar a party from reneging on agreements, in property law to uphold boundary agreements, and in preventing the assertion of legal defenses like limitation periods when such claims would be unjust. Courts use estoppel to enforce reliance interests, thereby complementing but not replacing statutory limitation rules that govern the time frame for bringing claims.
Impact of Limitation on Legal Rights
Limitation periods restrict the time frame within which legal claims can be initiated, directly impacting the enforceability of rights and the availability of remedies. Unlike estoppel, which prevents parties from asserting inconsistent positions to avoid injustice, limitation bars the right to sue once the statutory period expires, promoting legal certainty and finality. This means that failure to act within prescribed limitation periods can result in the permanent loss of legal rights regardless of the claim's merits.
Judicial Interpretations: Estoppel vs Limitation
Judicial interpretations differentiate estoppel and limitation by emphasizing estoppel's role in preventing a party from asserting claims contradictory to their previous conduct or statements, ensuring fairness and consistency in legal dealings. Limitation pertains strictly to statutory time frames within which claims or actions must be initiated, serving as a defense to bar stale claims and promote legal certainty. Courts consistently uphold estoppel as an equitable doctrine that may override strict limitation periods where justice demands, highlighting the nuanced balance between procedural deadlines and equitable relief.
Conclusion: Choosing the Appropriate Legal Doctrine
Selecting between estoppel and limitation requires evaluating the nature of the case and the specific legal elements involved. Estoppel is most effective where preventing unfairness or injustice is paramount, particularly in cases involving representations or assurances. Limitation statutes, however, strictly govern the timeframe for initiating claims, ensuring legal certainty and finality.
Estoppel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com