Mens rea, a fundamental concept in criminal law, refers to the mental state or intention behind committing a crime, distinguishing between intentional acts and accidents. Understanding mens rea is crucial for determining criminal liability and the severity of charges in cases involving negligence, recklessness, or purposeful wrongdoing. Explore the rest of this article to learn how mens rea influences legal outcomes and your rights within the justice system.
Table of Comparison
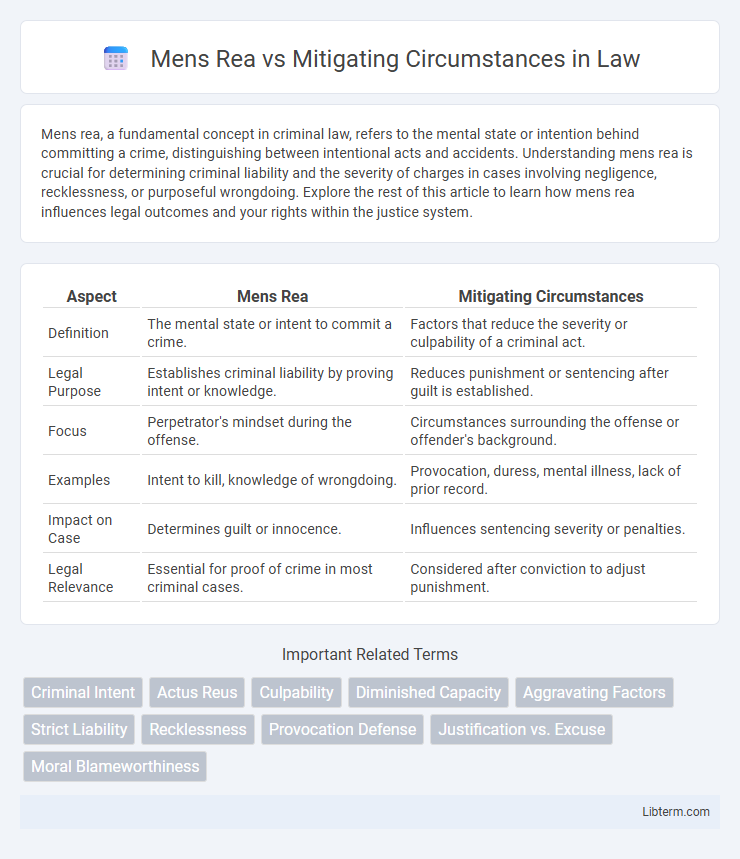
| Aspect | Mens Rea | Mitigating Circumstances |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The mental state or intent to commit a crime. | Factors that reduce the severity or culpability of a criminal act. |
| Legal Purpose | Establishes criminal liability by proving intent or knowledge. | Reduces punishment or sentencing after guilt is established. |
| Focus | Perpetrator's mindset during the offense. | Circumstances surrounding the offense or offender's background. |
| Examples | Intent to kill, knowledge of wrongdoing. | Provocation, duress, mental illness, lack of prior record. |
| Impact on Case | Determines guilt or innocence. | Influences sentencing severity or penalties. |
| Legal Relevance | Essential for proof of crime in most criminal cases. | Considered after conviction to adjust punishment. |
Introduction to Mens Rea and Mitigating Circumstances
Mens Rea, a fundamental concept in criminal law, refers to the defendant's mental state or intent at the time of committing a crime, which is crucial for establishing guilt. Mitigating circumstances are factors that do not excuse the offense but may reduce the severity of the punishment by providing context about the defendant's behavior or situation. Understanding the distinction between mens rea and mitigating circumstances is essential for accurately assessing criminal liability and sentencing.
Defining Mens Rea: The Mental Element of Crime
Mens rea represents the defendant's mental state at the time of committing a crime, encompassing intent, knowledge, recklessness, or negligence. This crucial element distinguishes a deliberate act from an accidental occurrence, directly impacting criminal liability. Understanding mens rea is essential for determining culpability, as it establishes whether the accused possessed the requisite mindset to commit the offense.
Types and Degrees of Mens Rea in Criminal Law
Types and degrees of mens rea in criminal law include intent, knowledge, recklessness, and negligence, each representing varying levels of culpability. Intent signifies a purposeful desire to commit a crime, while knowledge involves awareness that one's actions will likely cause a criminal outcome. Recklessness represents conscious disregard of a substantial risk, and negligence entails failure to exercise reasonable care, which differs fundamentally from mitigating circumstances that seek to reduce but not negate criminal responsibility.
What Are Mitigating Circumstances?
Mitigating circumstances refer to factors or conditions that do not excuse or justify a criminal act but may reduce the defendant's culpability or the severity of the punishment. These circumstances can include mental illness, lack of prior criminal history, duress, or minor involvement in the crime. Unlike mens rea, which concerns the defendant's intent or state of mind when committing the offense, mitigating circumstances focus on external or personal factors that influence sentencing decisions.
Distinguishing Between Mens Rea and Mitigating Circumstances
Mens rea refers to the defendant's mental state or intent at the time of committing a crime, which is crucial for establishing criminal liability. Mitigating circumstances, on the other hand, are factors that do not negate mens rea but reduce the severity of the offense or the offender's culpability during sentencing. Distinguishing between mens rea and mitigating circumstances is essential because mens rea affects the determination of guilt, whereas mitigating circumstances influence the punishment severity after guilt is established.
Legal Significance of Mens Rea in Criminal Proceedings
Mens rea, the mental state or intent behind a criminal act, is crucial in establishing criminal liability and differentiating between types of offenses such as intentional, reckless, or negligent actions. It determines the defendant's culpability and influences the severity of charges and sentencing in criminal proceedings. While mitigating circumstances may lessen punishment, mens rea fundamentally underpins the legal basis for conviction and the application of justice.
Role of Mitigating Circumstances in Sentencing
Mitigating circumstances play a crucial role in sentencing by providing context that may reduce the defendant's culpability linked to mens rea, such as diminished intent or impaired judgment. Courts consider factors like mental illness, coercion, or lack of premeditation to adjust sentences, often resulting in lighter penalties or alternative rehabilitation-focused measures. This nuanced approach balances legal responsibility with individualized justice, ensuring that the defendant's mens rea is assessed alongside external influences.
Case Law Illustrations: Mens Rea vs. Mitigating Factors
In *R v Cunningham* (1957), the court emphasized mens rea by establishing recklessness as a sufficient mental state for liability, while *R v Woollin* (1999) refined intent through indirect intention criteria. Conversely, *R v Brown* (1993) illustrated the role of mitigating circumstances, where consent reduced culpability despite the presence of mens rea. These cases demonstrate the judicial balance between proving mens rea and considering mitigating factors to determine appropriate sentencing.
Impact on Verdicts: How Courts Weigh Each Concept
Mens rea, the defendant's mental state during the crime, directly influences the establishment of criminal liability by proving intent or recklessness, thereby shaping the court's determination of guilt. Mitigating circumstances, such as mental illness or duress, do not negate guilt but serve to reduce the severity of the sentence by providing context that lessens moral culpability. Courts weigh mens rea as a foundational element for conviction, while mitigating circumstances primarily affect sentencing decisions, balancing accountability with fairness in punishment.
Conclusion: The Interplay of Intent and Circumstance in Justice
The interplay between mens rea and mitigating circumstances shapes the foundation of criminal justice by balancing intent with situational context. Mens rea establishes the defendant's mental state, while mitigating circumstances provide a nuanced understanding that can reduce culpability. This dynamic ensures that legal outcomes reflect both the defendant's intent and the complexities of their actions, promoting fair and just verdicts.
Mens Rea Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com