A statute is a formal written law enacted by a legislative body that governs behavior within a specific jurisdiction. These laws provide clear rules and guidelines to ensure order and justice in society. Explore the rest of this article to understand how statutes impact your legal rights and responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
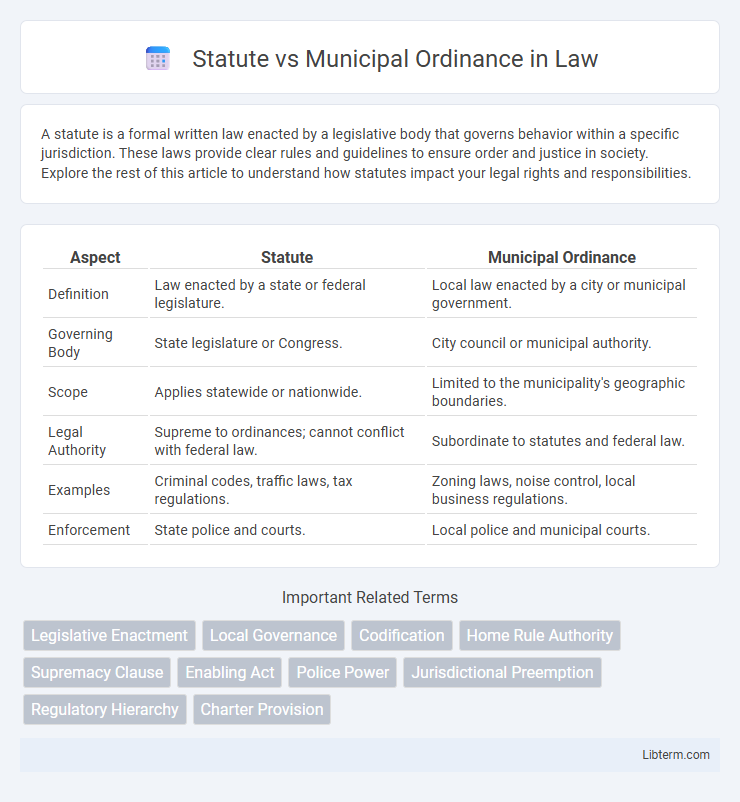
| Aspect | Statute | Municipal Ordinance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Law enacted by a state or federal legislature. | Local law enacted by a city or municipal government. |
| Governing Body | State legislature or Congress. | City council or municipal authority. |
| Scope | Applies statewide or nationwide. | Limited to the municipality's geographic boundaries. |
| Legal Authority | Supreme to ordinances; cannot conflict with federal law. | Subordinate to statutes and federal law. |
| Examples | Criminal codes, traffic laws, tax regulations. | Zoning laws, noise control, local business regulations. |
| Enforcement | State police and courts. | Local police and municipal courts. |
Definition of Statute
A statute is a formal written law enacted by a legislative body, such as a state or federal legislature, establishing specific legal standards and regulations applicable to a broad jurisdiction. Statutes carry the force of law and are codified into legal codes, distinguishing them from municipal ordinances, which are local laws passed by city or town governments governing more localized issues. Statutes often address wide-ranging matters including criminal law, civil rights, and public policy, providing a structured legal framework enforceable across entire states or countries.
Definition of Municipal Ordinance
A municipal ordinance is a law or regulation enacted by a local government authority, such as a city or town council, to address issues within its jurisdiction. Unlike statutes, which are laws passed by state or federal legislatures and typically have broader application, municipal ordinances specifically govern local matters like zoning, public safety, and sanitation. These ordinances must comply with state and federal laws while catering to the unique needs of the community.
Key Differences Between Statutes and Municipal Ordinances
Statutes are laws enacted by state legislatures or the federal government, possessing broader jurisdiction and authority, whereas municipal ordinances are local laws passed by city or town councils with limited jurisdiction confined to their municipality. Statutes generally address wide-ranging legal issues, including criminal, civil, and administrative matters, while municipal ordinances typically regulate local concerns such as zoning, public safety, and sanitation. Violations of statutes can result in state or federal penalties, whereas ordinance violations usually incur fines or local penalties specific to the municipality.
Authority and Jurisdiction
Statutes are laws enacted by state or federal legislatures, holding authority over broad geographic areas and addressing statewide or national issues. Municipal ordinances are local laws passed by city or town councils, possessing jurisdiction limited to their specific municipalities and addressing community-level matters. Authority of statutes supersedes municipal ordinances when conflicts arise, ensuring uniform application of higher-level laws.
Legislative Process: Statutes vs Ordinances
Statutes are laws enacted by state legislatures through a formal legislative process involving committee reviews, debates, and votes in both legislative chambers before receiving gubernatorial approval. Municipal ordinances are created by city or town councils following a simpler legislative procedure, usually including public hearings and council votes without state-level involvement. The statute process is more complex and standardized, reflecting broader jurisdictions, while ordinances address local issues with more flexible, localized enactments.
Scope of Application
Statutes are laws enacted by state or federal legislatures that apply broadly across an entire state or country, governing wide-ranging legal matters such as criminal law, civil rights, and taxation. Municipal ordinances are local laws passed by city or town governments, specifically regulating issues within the municipality like zoning, noise control, and local business operations. The scope of application for statutes is broad and uniform across the jurisdiction, whereas municipal ordinances have a limited scope, affecting only residents and activities within the specific locality.
Enforcement Mechanisms
Statutes are laws enacted by legislative bodies at the state or federal level and typically carry enforcement through state or federal agencies, courts, and law enforcement authorities. Municipal ordinances, established by local governments, are enforced by local agencies such as city police, code enforcement officers, or municipal courts, often focusing on community-specific regulations. The scope of enforcement varies, with statutes addressing broader legal frameworks and ordinances targeting localized compliance within municipalities.
Examples of Statutes and Municipal Ordinances
Statutes such as the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Clean Air Act establish broad federal legal standards applicable nationwide, addressing issues like discrimination and environmental protection. Municipal ordinances include local regulations such as noise control laws, zoning requirements, and curfews enacted by city councils to manage community-specific concerns. These local ordinances complement statutes by targeting neighborhood safety, property use, and public health within a municipality's jurisdiction.
Legal Hierarchy and Conflict Resolution
Statutes are laws enacted by state legislatures or Congress and hold higher authority than municipal ordinances, which are local laws passed by city or county governments. When a conflict arises, statutes preempt ordinances under the legal principle of preemption, invalidating any local law that contradicts or interferes with state or federal statutes. Courts resolve conflicts by assessing whether the ordinance falls within the municipality's authority and ensures consistency with overarching statutory law to maintain legal hierarchy.
Impact on Citizens and Communities
Statutes, enacted by state legislatures, create broad legal frameworks that directly affect citizens' rights and responsibilities, shaping statewide policies and standards. Municipal ordinances, established by local governments, address specific community needs by regulating behaviors and services at a neighborhood or city level, allowing tailored responses to local issues. The impact on communities varies as statutes provide uniformity across the state, while ordinances enable localized governance that can quickly adapt to unique social, economic, and environmental conditions.
Statute Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com