A legatee is an individual who receives assets or property through a will after someone's death. Understanding the rights and responsibilities of a legatee is crucial for managing inherited estates effectively. Explore the article to learn more about your role and benefits as a legatee in estate planning.
Table of Comparison
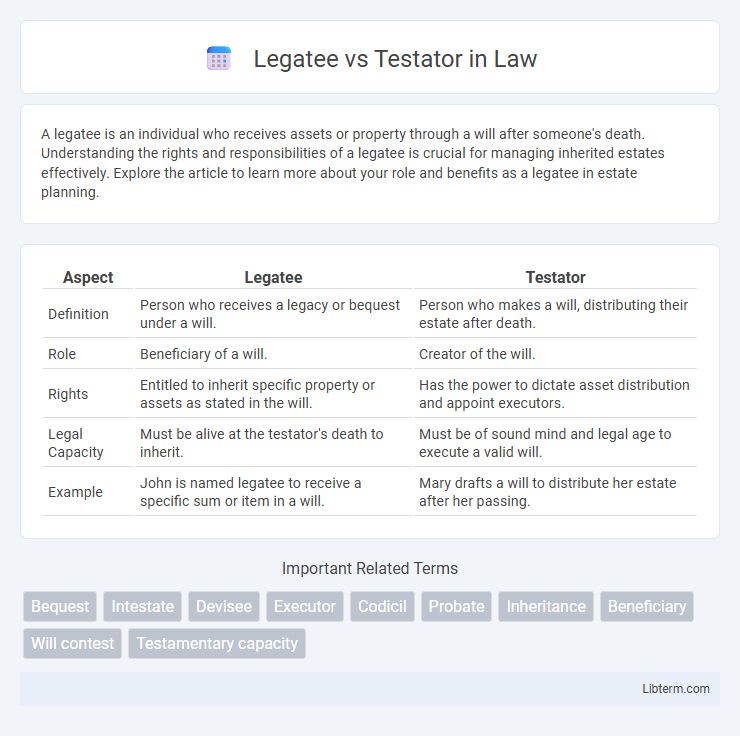
| Aspect | Legatee | Testator |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Person who receives a legacy or bequest under a will. | Person who makes a will, distributing their estate after death. |
| Role | Beneficiary of a will. | Creator of the will. |
| Rights | Entitled to inherit specific property or assets as stated in the will. | Has the power to dictate asset distribution and appoint executors. |
| Legal Capacity | Must be alive at the testator's death to inherit. | Must be of sound mind and legal age to execute a valid will. |
| Example | John is named legatee to receive a specific sum or item in a will. | Mary drafts a will to distribute her estate after her passing. |
Understanding the Roles: Legatee and Testator
A testator is the individual who creates a will, outlining the distribution of their estate after death, while a legatee is the person or entity designated to receive assets or benefits from that will. The testator holds the legal authority to specify legacy terms and beneficiaries, ensuring their intentions are fulfilled through probate. Understanding these distinct roles is crucial for executing wills accurately and protecting estate rights.
Definition of Legatee
A legatee is an individual or entity designated in a will to receive a legacy, which typically consists of personal property or assets bequeathed by the testator. The testator is the person who creates and executes a will, outlining how their estate and possessions should be distributed upon their death. Unlike the testator who formulates the will, the legatee is the recipient named to inherit specific assets or benefits from that will.
Definition of Testator
A testator is an individual who creates and executes a valid will to distribute their estate after death. This person holds the legal capacity to specify how assets, properties, and obligations are managed and allocated among beneficiaries. In contrast, a legatee is a recipient designated in the will to inherit specific property or assets from the testator.
Legal Differences Between Legatee and Testator
The testator is the individual who creates and signs a valid will, specifying how their estate should be distributed upon death, while the legatee is the person or entity designated to receive specific property or assets under the will. Legally, the testator holds the authority to alter or revoke the will during their lifetime, whereas the legatee holds no legal rights to the property until the testator's death and the will is executed. The testator's responsibilities include ensuring the will complies with local probate laws, whereas the legatee's role is passive, becoming effective only upon lawful transfer after probate.
Rights and Responsibilities of a Legatee
A legatee holds the right to receive specific assets or property as designated in a will, while the testator is the individual who creates the will and outlines these bequests. The legatee's responsibilities include accepting the inheritance as stipulated, complying with any conditions set by the testator, and working through the probate process to secure their entitlement. Unlike the testator, who manages and directs estate distribution, the legatee's role is primarily passive but crucial in upholding the terms of the testamentary document.
Duties and Powers of a Testator
The testator holds the primary responsibility of drafting and executing a valid will, clearly articulating the distribution of assets and appointing legatees or beneficiaries. Duties include ensuring the will complies with legal requirements, such as testamentary capacity and proper witness attestation. The testator possesses the power to revoke or amend the will at any time prior to death, reflecting changes in intentions or circumstances.
How Legatees Are Named in a Will
Legatees are specifically named individuals or entities designated in a will to receive particular assets or property from the testator's estate. The testator identifies legatees by clearly stating their full names and the exact items or amounts allocated to them, ensuring precise distribution of the estate. Legal terminology in the will must unambiguously link each legatee to their respective bequests to prevent disputes during probate.
Testator’s Intentions and Their Legal Impact
A testator is the individual who creates a will, expressing clear intentions about the distribution of their estate after death, which forms the legal foundation for asset allocation. The testator's intentions dictate how their assets are distributed, and courts prioritize these expressed wishes to ensure the will's execution aligns with their desired outcomes. Any ambiguity or lack of clarity in the testator's intentions can lead to legal disputes or challenges, impacting the legatee's rights and the overall administration of the estate.
Common Scenarios: Legatee vs Testator
A testator is the individual who creates a will, outlining the distribution of their estate after death, while a legatee is a person or entity designated to receive assets from that will. Common scenarios involve the testator appointing legatees such as family members, friends, or charitable organizations to inherit specific property or sums of money. Disputes often arise when legatees challenge the validity of the will or the testator's intentions, especially in cases of ambiguous language or potential undue influence.
Frequently Asked Questions on Legatees and Testators
A testator is an individual who creates a will outlining how their assets should be distributed after death, while a legatee is a person or entity designated in the will to receive specific assets or benefits. Frequently asked questions include how a legatee's inheritance differs from that of an heir, the legal rights of legatees if the will is contested, and what happens if a legatee predeceases the testator. Understanding the roles and legal distinctions between testators and legatees is essential for estate planning and probate processes.
Legatee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com