A choice of law clause specifies which jurisdiction's laws will govern the interpretation and enforcement of a contract, providing clarity and predictability for all parties involved. This clause helps prevent legal disputes by establishing a predefined legal framework, ensuring your agreement is handled consistently regardless of where a dispute arises. Explore the rest of the article to understand how to draft an effective choice of law clause tailored to your needs.
Table of Comparison
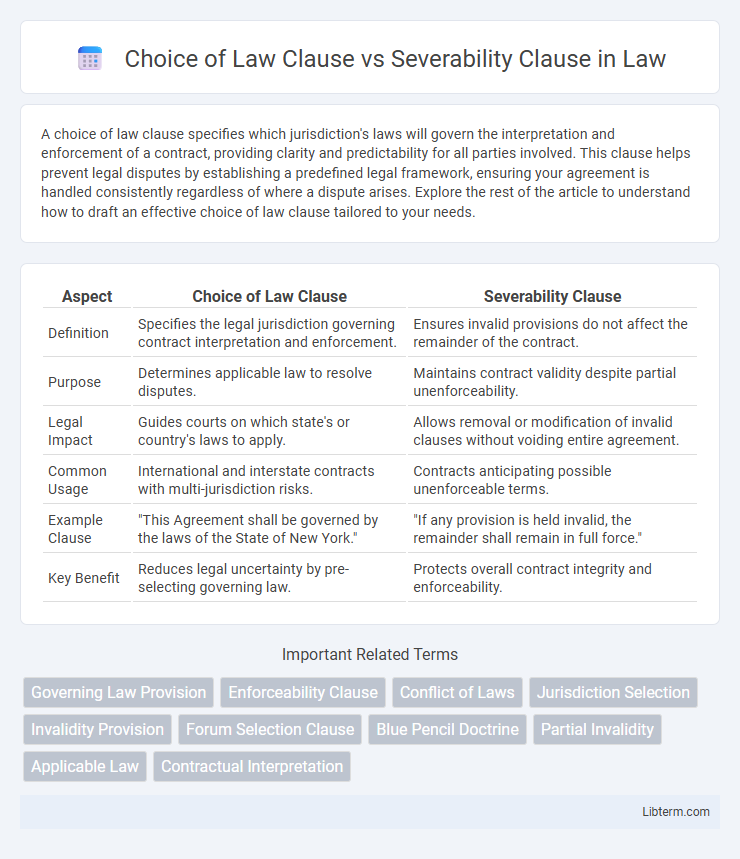
| Aspect | Choice of Law Clause | Severability Clause |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specifies the legal jurisdiction governing contract interpretation and enforcement. | Ensures invalid provisions do not affect the remainder of the contract. |
| Purpose | Determines applicable law to resolve disputes. | Maintains contract validity despite partial unenforceability. |
| Legal Impact | Guides courts on which state's or country's laws to apply. | Allows removal or modification of invalid clauses without voiding entire agreement. |
| Common Usage | International and interstate contracts with multi-jurisdiction risks. | Contracts anticipating possible unenforceable terms. |
| Example Clause | "This Agreement shall be governed by the laws of the State of New York." | "If any provision is held invalid, the remainder shall remain in full force." |
| Key Benefit | Reduces legal uncertainty by pre-selecting governing law. | Protects overall contract integrity and enforceability. |
Introduction to Contract Clauses
Choice of law clauses specify which jurisdiction's laws govern the interpretation and enforcement of a contract, providing clarity and predictability in cross-border agreements. Severability clauses ensure that if any provision of the contract is found invalid or unenforceable, the remaining terms remain effective and enforceable. Both clauses are fundamental in contract drafting to manage legal risks and uphold contractual stability.
What is a Choice of Law Clause?
A Choice of Law Clause specifies which jurisdiction's laws will govern the interpretation and enforcement of a contract, providing clarity and predictability in legal disputes. This clause ensures that parties understand which legal framework applies, reducing ambiguity and potential conflicts in cross-border agreements. It plays a crucial role in international contracts by designating a specific legal system to avoid uncertainty in case of litigation.
Key Functions of Choice of Law Clauses
Choice of law clauses determine the legal framework governing contract interpretation and dispute resolution, ensuring predictability and reducing jurisdictional conflicts. These clauses specify which jurisdiction's laws apply, facilitating clearer risk assessment and enforcement strategies. Severability clauses, conversely, protect contract validity by allowing unenforceable provisions to be removed without nullifying the entire agreement.
What is a Severability Clause?
A severability clause is a contractual provision that ensures if one part of the agreement is found to be invalid or unenforceable, the remainder of the contract remains effective and binding. This clause protects the contract's overall integrity by isolating problematic terms without voiding the entire agreement. In contrast, a choice of law clause designates which jurisdiction's laws will govern the contract, focusing on legal interpretation rather than contract validity.
Key Functions of Severability Clauses
Severability clauses ensure that if any part of a contract is found to be invalid or unenforceable, the remaining provisions continue to operate effectively, preserving the contract's overall integrity. These clauses safeguard against a contract being completely voided due to one problematic section, maintaining enforceability and stability in legal agreements. Unlike choice of law clauses, which designate the governing jurisdiction for interpreting the contract, severability clauses focus specifically on the operational durability of contract terms amid legal challenges.
Differences Between Choice of Law and Severability Clauses
Choice of law clauses determine which jurisdiction's laws will govern the interpretation and enforcement of a contract, ensuring predictability in legal disputes by specifying the applicable legal framework. Severability clauses, by contrast, ensure that if any provision of the contract is found to be invalid or unenforceable, the remainder of the agreement remains intact and effective. The primary difference lies in their function: choice of law clauses address legal jurisdiction and applicable law, while severability clauses preserve contract validity despite partial invalidity.
Legal Implications of Choice of Law Clauses
Choice of law clauses determine the jurisdiction whose laws will govern a contract, influencing dispute resolution, enforceability, and interpretation of contract terms, which is crucial for cross-border agreements. Legal implications include potential conflicts with mandatory local laws and variations in substantive legal rights, affecting risk allocation between parties. Severability clauses ensure that if a choice of law provision or any contract part is found unenforceable, the remainder of the contract remains effective, preserving contractual stability.
Legal Implications of Severability Clauses
Severability clauses play a critical role in contract law by ensuring that if one provision is found to be unenforceable or invalid, the remainder of the agreement remains effective and binding. This legal safeguard prevents entire contracts from being voided due to the failure of a single clause, thereby maintaining contractual stability and predictability. In contrast, choice of law clauses determine which jurisdiction's laws govern the contract, impacting the contract's interpretation and enforcement but not directly addressing the enforceability of individual provisions.
Practical Considerations for Drafting Both Clauses
When drafting Choice of Law and Severability Clauses, it is crucial to clearly specify the governing legal framework to avoid jurisdictional disputes and ensure enforceability across relevant courts. The Severability Clause should be tailored to preserve the contract's validity even if specific provisions are deemed unenforceable, preventing the entire agreement from being voided. Practical considerations include aligning these clauses with the contract's nature, applicable jurisdictional rules, and the parties' risk tolerance to minimize litigation risks and maintain contractual integrity.
Conclusion: Importance in Effective Contract Drafting
Choice of law clauses determine the legal framework governing a contract, ensuring predictability and reducing disputes over jurisdiction, while severability clauses preserve contract enforceability by allowing invalid provisions to be severed without voiding the entire agreement. Both clauses are essential in effective contract drafting to manage legal risks and maintain contractual stability. Incorporating these provisions strategically enhances clarity, protects parties' interests, and supports dispute resolution efficiency.
Choice of Law Clause Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com