Eviction occurs when a landlord legally removes a tenant from rental property due to lease violations or nonpayment of rent. Understanding the eviction process, your rights, and possible defenses is crucial to navigate this stressful situation effectively. Discover more about eviction procedures and how to protect your housing in the full article.
Table of Comparison
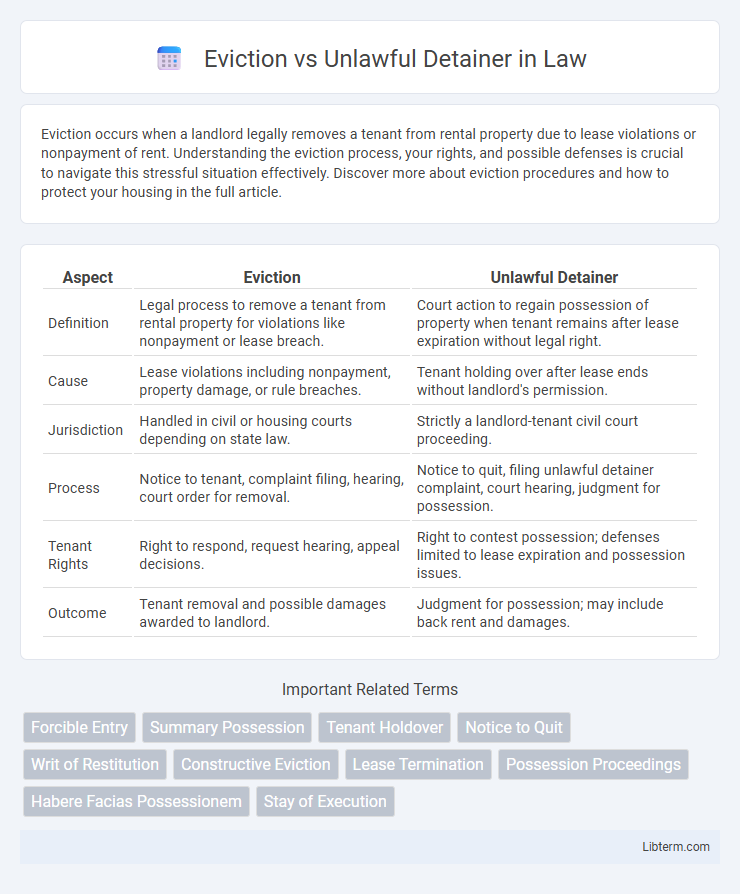
| Aspect | Eviction | Unlawful Detainer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal process to remove a tenant from rental property for violations like nonpayment or lease breach. | Court action to regain possession of property when tenant remains after lease expiration without legal right. |
| Cause | Lease violations including nonpayment, property damage, or rule breaches. | Tenant holding over after lease ends without landlord's permission. |
| Jurisdiction | Handled in civil or housing courts depending on state law. | Strictly a landlord-tenant civil court proceeding. |
| Process | Notice to tenant, complaint filing, hearing, court order for removal. | Notice to quit, filing unlawful detainer complaint, court hearing, judgment for possession. |
| Tenant Rights | Right to respond, request hearing, appeal decisions. | Right to contest possession; defenses limited to lease expiration and possession issues. |
| Outcome | Tenant removal and possible damages awarded to landlord. | Judgment for possession; may include back rent and damages. |
Understanding Eviction and Unlawful Detainer: Key Differences
Eviction is a legal process initiated by landlords to remove tenants who fail to comply with lease terms, typically due to non-payment or violation of rules. Unlawful detainer specifically refers to the tenant's refusal to vacate the property after the lease has ended or eviction notice has been served, forming the basis for a formal court action. Understanding these distinctions allows landlords and tenants to navigate rights and responsibilities within housing law more effectively.
Legal Definitions: Eviction vs. Unlawful Detainer
Eviction is the legal process by which a landlord removes a tenant from a rental property, often due to lease violations or nonpayment of rent. Unlawful detainer is a specific legal action filed by the landlord to regain possession of the property when a tenant refuses to vacate after the lease expires or is terminated. Understanding the distinction between eviction as a broader concept and unlawful detainer as the formal court proceeding is essential in landlord-tenant law.
Grounds for Eviction Compared to Unlawful Detainer
Grounds for eviction typically include non-payment of rent, lease violations, property damage, or unauthorized occupants, which form the legal basis for initiating removal proceedings. Unlawful detainer specifically refers to the legal action taken after a tenant unlawfully remains on the property post-eviction notice or lease expiration. Understanding that eviction grounds establish why a tenant must leave while unlawful detainer addresses the process to recover possession clarifies the distinction in landlord-tenant disputes.
The Eviction Process Explained
The eviction process involves a legal procedure initiated by landlords to remove tenants who fail to comply with lease terms, such as nonpayment of rent or property damage. It begins with a formal notice to the tenant, followed by filing an unlawful detainer lawsuit if the tenant does not vacate the property within the specified time. Courts review the case, and if the landlord prevails, a writ of possession is issued, allowing law enforcement to remove the tenant and restore the property.
Unlawful Detainer Proceedings: What to Expect
Unlawful detainer proceedings occur when a landlord seeks to regain possession of a property after a tenant has violated lease terms, typically by failing to pay rent or overstaying the lease duration. These legal actions involve filing a complaint in court, attending a hearing where both parties present evidence, and obtaining a judgment that may lead to eviction by law enforcement if the tenant does not comply. Understanding local laws and timelines, such as notice requirements and court processes, is crucial for both landlords and tenants facing unlawful detainer cases.
Rights of Tenants During Eviction and Unlawful Detainer Cases
Tenants facing eviction or unlawful detainer actions maintain the right to receive proper legal notice, typically a written eviction notice specifying the reason and timeframe to remedy the violation. During eviction proceedings, tenants can present defenses such as improper notice, landlord retaliation, or failure to maintain habitable premises, ensuring due process rights are respected. Courts often require landlords to prove lawful grounds for eviction, while tenants retain the right to contest claims and request reasonable time to relocate or cure lease breaches under local tenant protection laws.
Landlord Obligations Under Both Processes
Landlords must follow specific legal procedures in both eviction and unlawful detainer actions, including providing proper notice and filing required court documents. In eviction cases, landlords are obligated to ensure tenant's due process rights are protected before regaining possession of the property. During unlawful detainer proceedings, landlords must strictly adhere to statutory timelines and evidence requirements to lawfully remove tenants.
Court Procedures: Eviction vs. Unlawful Detainer
Court procedures for eviction involve the landlord serving a formal notice to the tenant, followed by filing a lawsuit if the tenant fails to comply. An unlawful detainer action specifically refers to the legal process landlords use to regain possession of property when a tenant remains after the lease expires or after eviction notice dismissal. Both procedures require a court hearing where evidence is presented, and the judge determines whether to issue a writ of possession allowing the landlord to reclaim the property.
Frequently Asked Questions: Eviction and Unlawful Detainer
Eviction is the legal process by which a landlord removes a tenant from rental property, while unlawful detainer refers specifically to the tenant's wrongful refusal to vacate after the lease ends or eviction notice is served. Common questions include the timeline for filing eviction, the difference in legal procedures between eviction and unlawful detainer, and tenant rights during each process. Understanding state-specific laws, required notices, and court procedures is crucial for both landlords and tenants in resolving disputes efficiently.
Preventing Disputes: Best Practices for Landlords and Tenants
Preventing disputes between landlords and tenants requires clear communication, adherence to lease terms, and timely resolution of conflicts related to eviction and unlawful detainer. Landlords should provide written notices aligned with local laws, maintain accurate documentation, and conduct regular property inspections to address issues proactively. Tenants benefit from understanding their rights, responding promptly to notices, and seeking mediation or legal advice to resolve disagreements before escalation to unlawful detainer proceedings.
Eviction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com