An ode is a lyrical poem that expresses deep admiration or praise for a person, object, or event with elevated language and stylistic devices. This poetic form often employs rich imagery and complex metaphors to evoke strong emotions and highlight the subject's significance. Explore the rest of the article to discover how odes can enrich your appreciation of poetry.
Table of Comparison
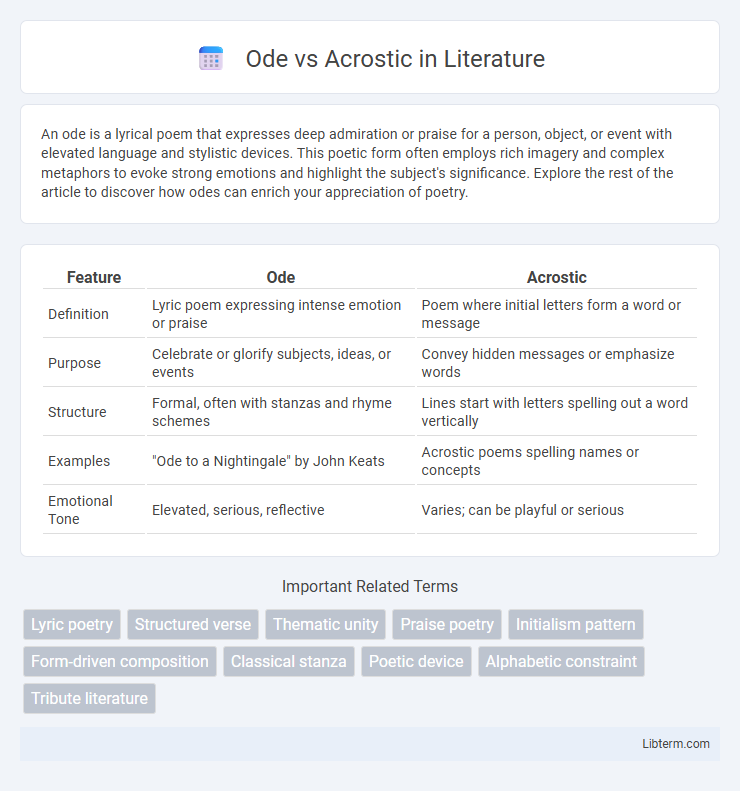
| Feature | Ode | Acrostic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lyric poem expressing intense emotion or praise | Poem where initial letters form a word or message |
| Purpose | Celebrate or glorify subjects, ideas, or events | Convey hidden messages or emphasize words |
| Structure | Formal, often with stanzas and rhyme schemes | Lines start with letters spelling out a word vertically |
| Examples | "Ode to a Nightingale" by John Keats | Acrostic poems spelling names or concepts |
| Emotional Tone | Elevated, serious, reflective | Varies; can be playful or serious |
Understanding Ode and Acrostic Poetry
Ode and acrostic poems are distinct poetic forms that serve different expressive purposes. An ode is a lyrical poem that praises or glorifies a person, event, or idea, often characterized by elevated language and formal structure. Acrostic poetry spells out a word or message vertically with the first letters of each line, combining creative wordplay with hidden meanings to engage readers visually and intellectually.
Definition and Origins of the Ode
An ode is a lyrical poem that expresses deep emotion, often celebrating a person, event, or abstract idea, originating from Ancient Greece where it was performed with musical accompaniment. This poetic form is characterized by formal structure and elevated style, traditionally used by poets like Pindar and Horace to convey praise and solemn reflection. In contrast, an acrostic arranges the first letters of each line or stanza to spell words or messages, emphasizing puzzle-like creativity rather than emotional celebration.
Definition and Origins of the Acrostic
An acrostic is a poetic form where the first letter of each line spells out a word or message, originating from ancient Greek and Latin literature used as mnemonic devices or hidden messages. Odes, by contrast, are formal, often lyrical poems expressing praise or admiration, rooted in classical Greek tradition. While odes emphasize structured elevation of themes, acrostics focus on letter-based patterns to convey layered meanings.
Structural Differences Between Ode and Acrostic
Odes typically follow a formal structure with stanzas of consistent meter and rhyme schemes, often organized into triads or quatrains that emphasize lyrical expression and elevated themes. Acrostics are distinguished by their unique structural feature where the first letter of each line or stanza spells out a word, phrase, or message, prioritizing the hidden textual pattern over fixed meter or rhyme. This fundamental difference highlights how odes focus on sonic and rhythmic harmony, while acrostics emphasize visual and semantic arrangement within the poem's lines.
Language and Tone: Ode vs Acrostic
Odes employ elevated, formal language often rich in metaphor and passion to convey deep admiration or emotion, creating a tone that is reflective and solemn. Acrostics use straightforward, clear language centered on spelling out a word or message vertically, resulting in a tone that is playful, structured, or instructional. The language of odes emphasizes lyrical beauty and thematic depth, whereas acrostics prioritize clarity and creativity within a rigid format.
Popular Themes in Ode and Acrostic Poems
Ode poems often explore themes of admiration, celebration, and profound emotion, commonly focusing on nature, love, heroism, or abstract concepts like beauty and truth. Acrostic poems frequently center around personal names, seasons, holidays, and virtues, using the initial letters of each line to spell a word closely tied to the poem's subject. Both forms emphasize thematic consistency, but odes typically delve deeper into expressive and reflective content, while acrostics highlight structural creativity linked to thematic representation.
Examples of Famous Odes
Famous odes such as John Keats' "Ode to a Nightingale" and Percy Bysshe Shelley's "Ode to the West Wind" exemplify the lyrical and elevated style characteristic of odes. In contrast, acrostic poems like Edgar Allan Poe's "An Acrostic" use the first letters of each line to spell a word or message, highlighting a structural rather than thematic focus. Odes celebrate subjects with rich imagery and emotional depth, while acrostics emphasize hidden textual patterns.
Examples of Notable Acrostics
Notable acrostics include Edgar Allan Poe's "A Valentine," where the first letters of each line spell the name of the recipient, and Lewis Carroll's "A Boat Beneath a Sunny Sky," which reveals a hidden message about Alice Liddell. Other famous examples include the hymn "All Creatures of Our God and King" by St. Francis of Assisi, where initial letters form phrases or names integral to the text's meaning. These examples showcase the acrostic's unique ability to convey layered messages within a structured poetic form.
Creative Uses for Ode and Acrostic in Modern Writing
Odes offer a rich, expressive format for praising ideas, emotions, or subjects, making them ideal for meditative poetry and personalized tributes in modern writing. Acrostics creatively encode messages or themes by aligning letters vertically, enhancing engagement and adding layers of meaning in educational content, branding, and interactive literature. Both forms uniquely foster emotional resonance and memorability, adapting traditional structures for contemporary artistic and communicative purposes.
Choosing Between Ode and Acrostic for Your Poem
Choosing between an ode and an acrostic poem depends on the desired tone and structure; odes are formal, expressive poems celebrating a subject, ideal for conveying deep admiration, while acrostic poems use the first letters of each line to spell a word, making them perfect for playful, creative expression or thematic emphasis. Odes often require more elaborate language and rhyme schemes, appealing to those seeking to elevate their subject with lyrical beauty. Acrostics suit beginners or poets looking for a concise, visually engaging format that highlights specific words or messages within the poem.
Ode Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com