Stanza is a powerful natural language processing library designed to provide efficient and accurate text analysis including tokenization, part-of-speech tagging, and named entity recognition. Its ability to handle multiple languages and integrate smoothly with machine learning workflows makes it an essential tool for developers and data scientists working on language understanding. Discover how Stanza can enhance your projects by exploring the full capabilities detailed in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
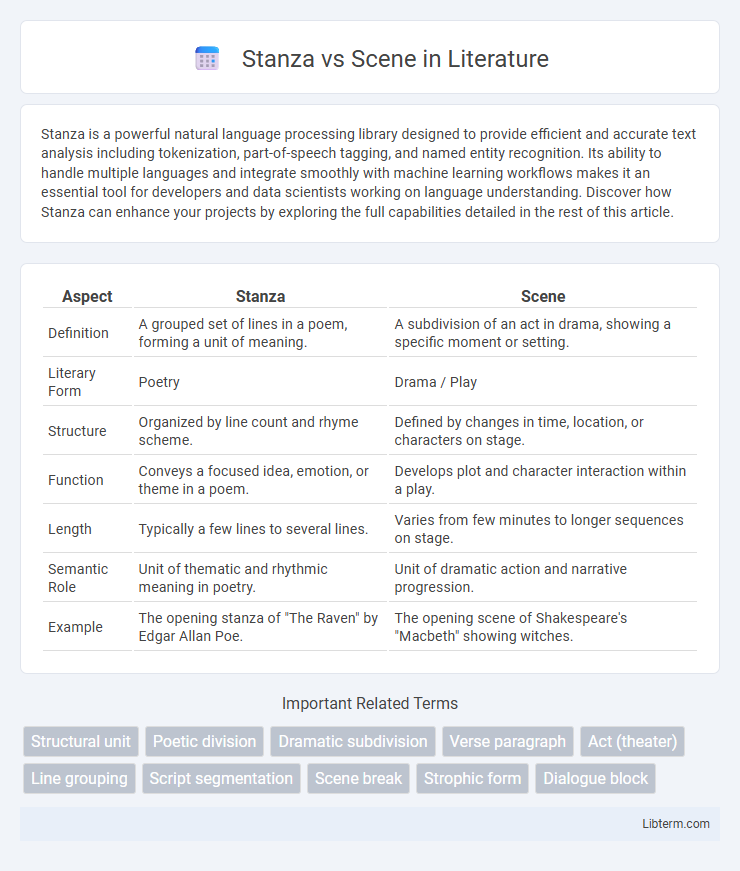
| Aspect | Stanza | Scene |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A grouped set of lines in a poem, forming a unit of meaning. | A subdivision of an act in drama, showing a specific moment or setting. |
| Literary Form | Poetry | Drama / Play |
| Structure | Organized by line count and rhyme scheme. | Defined by changes in time, location, or characters on stage. |
| Function | Conveys a focused idea, emotion, or theme in a poem. | Develops plot and character interaction within a play. |
| Length | Typically a few lines to several lines. | Varies from few minutes to longer sequences on stage. |
| Semantic Role | Unit of thematic and rhythmic meaning in poetry. | Unit of dramatic action and narrative progression. |
| Example | The opening stanza of "The Raven" by Edgar Allan Poe. | The opening scene of Shakespeare's "Macbeth" showing witches. |
Understanding Stanzas and Scenes
Understanding stanzas involves recognizing them as grouped lines of poetry that create a unit of thought, rhythm, or rhyme, often distinguished by a specific pattern or meter. Scenes, in contrast, are divisions within a play or narrative that mark changes in setting, time, or action, helping to structure the plot and guide audience engagement. Both stanzas and scenes serve as fundamental organizational tools in their respective literary forms, enhancing clarity and emotional impact.
Definition of Stanza in Literature
A stanza in literature is a grouped set of lines within a poem, often sharing a common rhyme scheme or rhythmic pattern, functioning similarly to a paragraph in prose. Each stanza serves as a structural unit that organizes ideas, emotions, or themes, enhancing the poem's overall coherence and artistic expression. Unlike scenes in drama, which depict specific actions or events in a narrative, stanzas primarily emphasize poetic form and imagery.
Definition of Scene in Drama and Prose
A scene in drama refers to a subdivision of an act where the setting remains constant and characters engage in continuous action or dialogue, driving the plot forward and revealing conflicts or emotions. In prose, a scene functions as a segment of the narrative that captures a specific moment or event, combining detailed description, character interaction, and setting to immerse readers in the unfolding story. Unlike a stanza, which is a grouped set of lines in poetry, a scene serves as a structural unit essential for pacing and developing the storyline in both theatrical scripts and prose narratives.
Key Structural Differences
A stanza is a grouped set of lines within a poem, typically sharing a consistent meter and rhyme scheme, serving as a unit of poetic structure. A scene is a subdivision of a play or narrative, representing a specific event or moment in the storyline, often defined by changes in time or location. The key structural difference lies in their function: stanzas organize thematic and rhythmic elements in poetry, while scenes organize dramatic action and narrative progression in theater or prose.
Purpose and Function in Narrative
A stanza structures poetry by grouping lines to convey specific emotions or ideas, creating rhythm and enhancing thematic emphasis. A scene organizes narrative action in drama or prose, advancing plot and revealing character interactions through time and setting changes. Both serve distinct narrative functions: stanzas provide lyrical coherence and mood, while scenes drive story progression and dramatic tension.
Usage in Poetry vs. Drama
A stanza serves as a fundamental structural unit in poetry, grouping lines that share a specific rhyme scheme or rhythm to convey a cohesive idea or emotion within a poem. In contrast, a scene functions as a division in drama, segmenting the narrative into discrete parts where particular actions or events unfold, often marked by changes in time or setting. While stanzas organize poetic expression, scenes drive the progression of a play by framing interactions and developments among characters.
Common Examples in Literature
Stanzas and scenes serve distinct purposes in literary structures; stanzas group lines in poetry to create rhythm and thematic unity, exemplified by Robert Frost's quatrains in "Stopping by Woods on a Snowy Evening." Scenes function in drama and prose to mark shifts in time, place, or action, as seen in Shakespeare's "Macbeth," where each scene advances the plot and reveals character development. Both elements organize content, with stanzas highlighting poetic form and scenes driving narrative progression.
Impact on Pacing and Flow
Stanzas create structured pauses and rhythm in poetry, enhancing deliberate pacing and focusing the reader's attention on specific emotions or ideas. Scenes drive the narrative forward in prose or drama, controlling tempo through actions, dialogue, and setting changes, which maintain dynamic movement and engagement. The use of stanzas slows down the reading experience for reflection, while scenes accelerate pacing to propel the plot and maintain momentum.
Reader Engagement and Interpretation
Stanzas in poetry create rhythmic pauses and emphasize emotional nuances, enhancing reader engagement through structured patterns and sound devices. Scenes in drama or prose provide dynamic settings and character interactions that immerse readers in vivid narratives, fostering deeper interpretation of plot and motivation. Both stanzas and scenes guide readers' emotional responses, with stanzas shaping mood through language and form, while scenes drive plot development and character understanding.
Choosing Between Stanza and Scene
Choosing between stanza and scene depends on the literary form and purpose; stanzas structure poetry into thematic units enhancing rhythm and mood, while scenes organize drama or prose to advance plot and develop characters. In poetry, stanzas create visual and rhythmic breaks that emphasize certain emotions or ideas, making them essential for lyrical or narrative depth. For playwrights and novelists, scenes provide a sequential framework that shapes the narrative flow and interaction, guiding the audience or readers through time and setting changes.
Stanza Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com