Procedural learning involves acquiring skills and habits through repeated practice, allowing tasks to become automatic without conscious thought. This type of learning is crucial for mastering activities such as riding a bike, typing, or playing an instrument. Explore the rest of the article to understand how procedural learning shapes your everyday abilities.
Table of Comparison
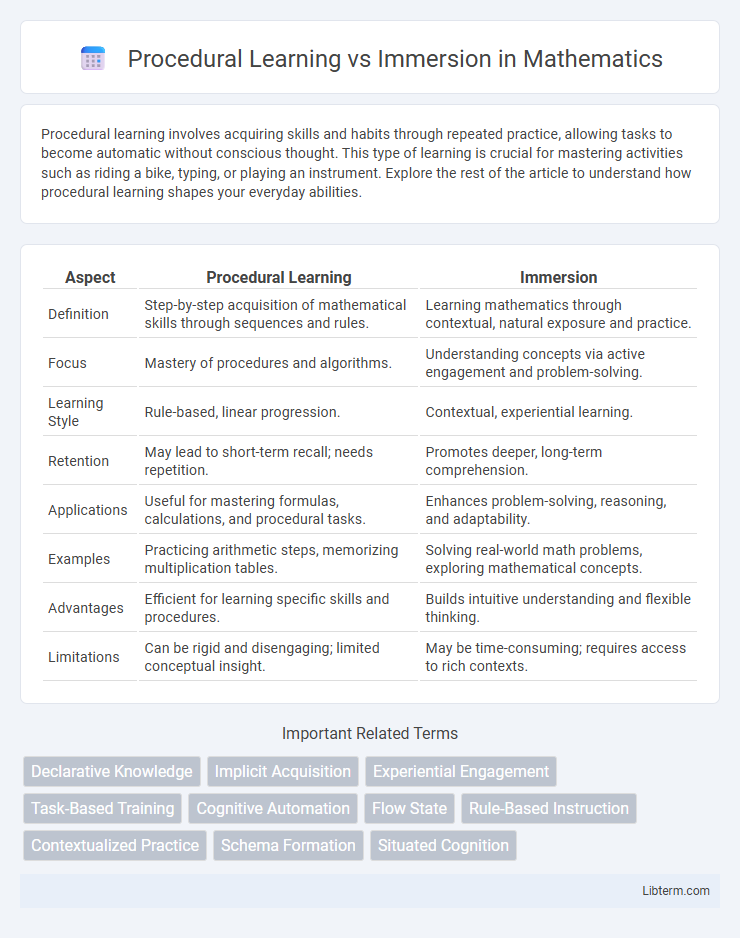
| Aspect | Procedural Learning | Immersion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Step-by-step acquisition of mathematical skills through sequences and rules. | Learning mathematics through contextual, natural exposure and practice. |
| Focus | Mastery of procedures and algorithms. | Understanding concepts via active engagement and problem-solving. |
| Learning Style | Rule-based, linear progression. | Contextual, experiential learning. |
| Retention | May lead to short-term recall; needs repetition. | Promotes deeper, long-term comprehension. |
| Applications | Useful for mastering formulas, calculations, and procedural tasks. | Enhances problem-solving, reasoning, and adaptability. |
| Examples | Practicing arithmetic steps, memorizing multiplication tables. | Solving real-world math problems, exploring mathematical concepts. |
| Advantages | Efficient for learning specific skills and procedures. | Builds intuitive understanding and flexible thinking. |
| Limitations | Can be rigid and disengaging; limited conceptual insight. | May be time-consuming; requires access to rich contexts. |
Understanding Procedural Learning
Procedural learning involves acquiring skills through repeated practice, enabling automatic execution of tasks without conscious thought, which is crucial for mastering motor skills, language syntax, and problem-solving procedures. Unlike immersion, which emphasizes contextual and experiential learning in natural environments, procedural learning relies on structured repetition and feedback to solidify neural pathways. Research in cognitive neuroscience highlights the basal ganglia's role in procedural memory formation, distinguishing it from declarative learning systems.
Defining Immersive Learning Approaches
Immersive learning approaches engage learners through realistic, interactive environments that simulate real-world scenarios, enhancing skill acquisition and retention. These methods often utilize virtual reality, augmented reality, or gamified simulations to create context-rich experiences that promote active participation and deeper cognitive processing. Unlike procedural learning, which focuses on repetitive practice of specific tasks, immersive learning emphasizes holistic understanding through experiential engagement.
Key Differences Between Procedural and Immersion Methods
Procedural learning emphasizes step-by-step mastery of skills through repetitive practice and structured guidance, enhancing specific task execution and memory retention. Immersion methods foster language acquisition or skill development by surrounding learners in rich, real-world contexts, promoting intuitive understanding and natural usage without explicit instructions. Key differences include procedural learning's focus on sequential, rule-based processing versus immersion's holistic, context-driven experience that encourages adaptive problem-solving and fluency.
Cognitive Mechanisms Behind Each Approach
Procedural learning relies on repetitive practice to engrain skills into implicit memory through the gradual strengthening of neural pathways associated with habit formation. Immersion engages multiple cognitive faculties including contextual inference, pattern recognition, and episodic memory, facilitating rapid language acquisition by mimicking naturalistic environments. The distinct neural substrates involved highlight procedural learning's dependence on the basal ganglia, whereas immersion heavily activates the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex for active encoding and retrieval.
Advantages of Procedural Learning
Procedural learning enhances skill acquisition by enabling the brain to develop automaticity through repetition and practice, making tasks more efficient and less cognitively demanding. It supports long-term retention and transferability of skills across contexts, particularly in motor and cognitive domains. This method is advantageous for fostering consistency and precision, as it relies on ingrained neural pathways rather than conscious effort.
Benefits of Immersive Learning
Immersive learning enhances retention by engaging multiple senses and creating realistic contexts, which accelerates skill acquisition and deep understanding. Unlike procedural learning that follows step-by-step instructions, immersion promotes active problem-solving and adaptability through experiential interaction. This method fosters intrinsic motivation and long-term memory consolidation by simulating real-world challenges and scenarios.
Challenges and Limitations of Procedural Learning
Procedural learning often faces challenges such as limited adaptability to novel contexts and slow acquisition speed due to repetitive practice requirements. Its dependence on step-by-step skill acquisition can hinder the development of deeper conceptual understanding compared to immersive methods that provide contextual learning. Furthermore, retention may be less robust as procedural learning frequently lacks engaging, real-world scenarios that boost motivation and long-term memory consolidation.
Obstacles in Implementing Immersion Techniques
Implementing immersion techniques in language learning faces obstacles such as the high resource demand for native-level interaction and authentic environment creation, which can be costly and time-consuming. Learners often struggle with initial comprehension difficulties that reduce motivation and hinder progress without sufficient scaffolded support. Additionally, procedural learning methods offer structured skill acquisition, making immersion challenging to adapt for diverse learner proficiency levels and cognitive styles.
Best Use Cases: When to Choose Each Method
Procedural learning excels in environments requiring step-by-step mastery of complex skills, such as surgical training or programming, where systematic repetition builds competence. Immersion is ideal for language acquisition and cultural adaptation, enabling learners to internalize nuances through contextual and experiential engagement. Selecting between procedural learning and immersion depends on the goal: structured skill development favors procedural methods, while naturalistic understanding benefits from immersive experiences.
Integrating Procedural Learning and Immersion for Optimal Results
Integrating procedural learning and immersion enhances skill acquisition by combining hands-on practice with contextual experience, allowing learners to internalize complex tasks effectively. Immersion provides realistic environments that reinforce procedural memory through active engagement, increasing retention and transferability of skills. This synergy accelerates mastery by aligning cognitive processes with authentic application scenarios, optimizing overall learning outcomes.
Procedural Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com