Surface learning focuses on memorization and rote recall rather than understanding concepts deeply, often leading to short-term retention. This approach may limit your ability to apply knowledge effectively in practical situations or critical thinking. Explore the rest of this article to discover strategies for moving beyond surface learning and achieving deeper comprehension.
Table of Comparison
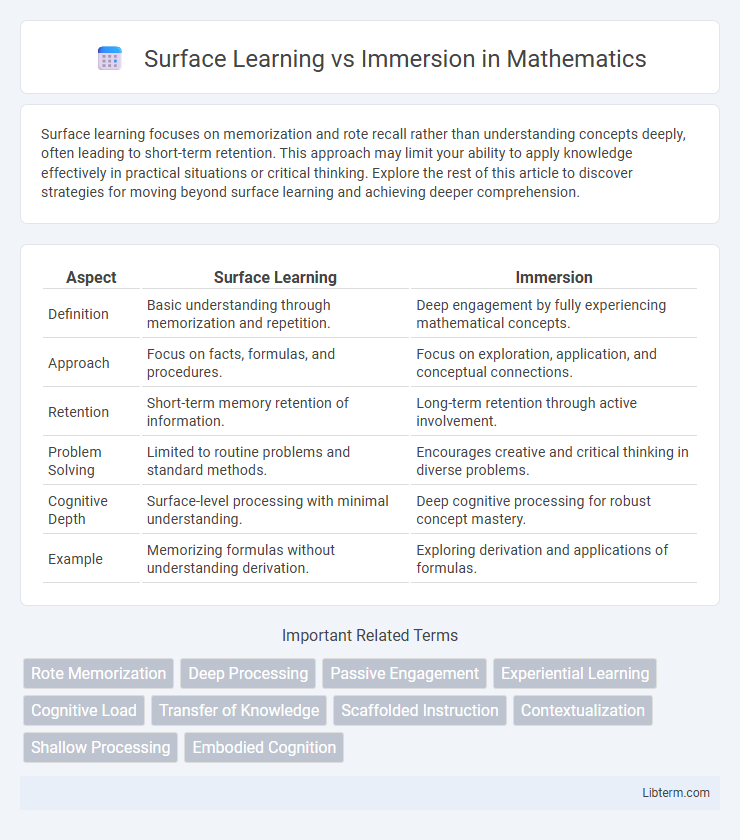
| Aspect | Surface Learning | Immersion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Basic understanding through memorization and repetition. | Deep engagement by fully experiencing mathematical concepts. |
| Approach | Focus on facts, formulas, and procedures. | Focus on exploration, application, and conceptual connections. |
| Retention | Short-term memory retention of information. | Long-term retention through active involvement. |
| Problem Solving | Limited to routine problems and standard methods. | Encourages creative and critical thinking in diverse problems. |
| Cognitive Depth | Surface-level processing with minimal understanding. | Deep cognitive processing for robust concept mastery. |
| Example | Memorizing formulas without understanding derivation. | Exploring derivation and applications of formulas. |
Introduction to Surface Learning and Immersion
Surface learning emphasizes memorization and rote repetition, often leading to short-term retention without deep understanding. Immersion involves engaging comprehensively with the subject, facilitating meaningful connections and long-lasting knowledge. Research shows immersion techniques improve critical thinking and application skills compared to surface learning strategies.
Defining Surface Learning
Surface learning involves rote memorization and superficial engagement with content, often aimed at passing exams rather than understanding. This approach prioritizes memorizing facts and details without connecting concepts or exploring deeper meanings. It contrasts with immersion, which emphasizes active, meaningful engagement and contextual understanding.
What Is Immersion Learning?
Immersion learning is an educational approach where learners are deeply engaged in a language or subject by being surrounded by it in authentic contexts, promoting natural acquisition through active use rather than rote memorization. This method emphasizes experiential learning, allowing students to develop fluency and comprehension by interacting in real-life situations, which contrasts with surface learning that often relies on passive memorization and repetition. Immersion environments boost cognitive engagement and long-term retention by integrating language or content into daily activities and meaningful communication.
Key Differences Between Surface and Immersion Approaches
Surface learning emphasizes memorization and rote repetition of facts, often resulting in shallow understanding and limited application. Immersion approaches engage learners deeply through context-rich environments, promoting meaningful comprehension and practical skill development. Key differences include the depth of cognitive engagement and the ability to transfer knowledge effectively beyond initial learning scenarios.
Advantages of Surface Learning
Surface learning enables quick acquisition of fundamental concepts, making it ideal for mastering extensive curricula efficiently. Its emphasis on memorization and repetition supports strong performance in standardized testing and assessments. This approach provides learners with a broad knowledge base, essential for building foundational skills before progressing to deeper contextual understanding.
Benefits of Immersion Learning
Immersion learning accelerates language acquisition by surrounding learners with authentic linguistic input, fostering natural communication skills and cultural understanding. It enhances retention and fluency through constant practice in real-life contexts, promoting deeper cognitive connections compared to surface learning. This approach also boosts confidence and adaptability, enabling learners to apply knowledge effectively across diverse situations.
Challenges in Surface and Immersion Learning
Surface learning faces challenges such as limited retention, shallow understanding, and difficulty applying concepts beyond rote memorization, often leading to fragmented knowledge. Immersion learning struggles with cognitive overload, cultural dissonance, and the need for high motivation and resilience to adapt effectively in unfamiliar environments. Both methods require tailored strategies to overcome barriers in engagement, comprehension, and long-term application of skills.
Choosing the Right Approach for Different Learners
Surface learning targets basic comprehension and rote memorization, ideal for learners needing quick recall of facts or foundational knowledge. Immersion facilitates deeper understanding through context-rich experiences, best suited for learners benefiting from active engagement and practical application. Selecting the right approach depends on individual learning styles, goals, and subject complexity to maximize retention and skill development.
Real-world Applications and Case Studies
Surface learning often involves memorization without deep understanding, limiting its effectiveness in real-world applications such as problem-solving or project execution. Immersion techniques, exemplified by case studies in language acquisition and medical training, enhance practical skills by providing contextual, hands-on experiences that replicate actual work environments. Case studies from industries like engineering and healthcare demonstrate that immersive learning leads to higher retention rates and better transfer of knowledge to workplace challenges.
Conclusion: Finding Balance Between Surface and Immersion
Striking a balance between surface learning and immersion optimizes knowledge retention and skill development by integrating quick access to broad concepts with deep, contextual understanding. Surface learning facilitates efficient overview and initial comprehension, while immersion fosters critical thinking and long-term mastery through active engagement. Effective learning strategies combine both approaches, tailoring depth and breadth to align with individual goals and subject complexity.
Surface Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com