Completion technology enhances productivity by automating routine tasks and providing accurate suggestions in real-time. Its integration into various software platforms helps streamline workflows and minimize errors. Discover how completion tools can transform your daily operations by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
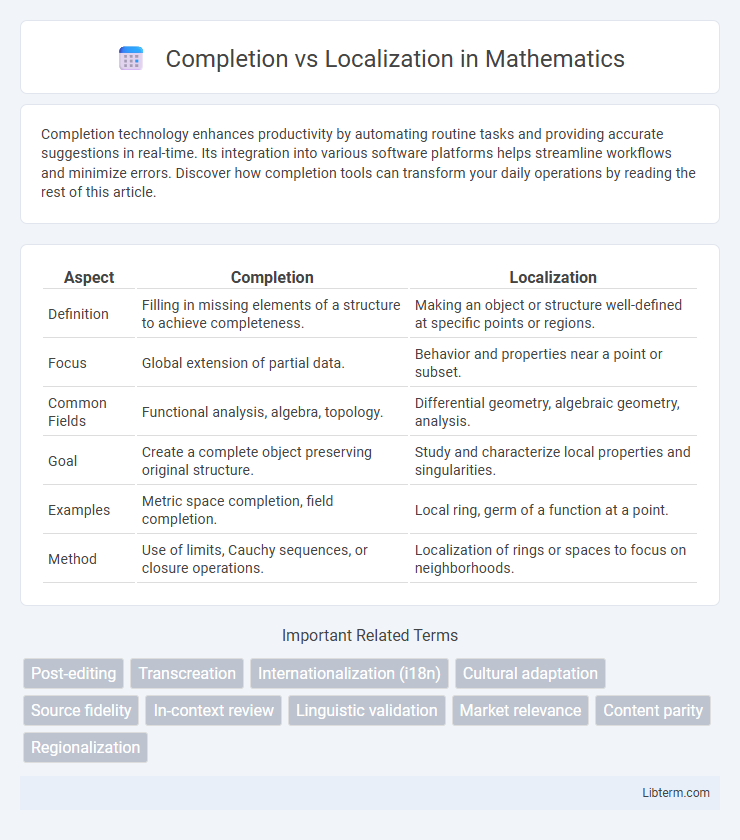
| Aspect | Completion | Localization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Filling in missing elements of a structure to achieve completeness. | Making an object or structure well-defined at specific points or regions. |
| Focus | Global extension of partial data. | Behavior and properties near a point or subset. |
| Common Fields | Functional analysis, algebra, topology. | Differential geometry, algebraic geometry, analysis. |
| Goal | Create a complete object preserving original structure. | Study and characterize local properties and singularities. |
| Examples | Metric space completion, field completion. | Local ring, germ of a function at a point. |
| Method | Use of limits, Cauchy sequences, or closure operations. | Localization of rings or spaces to focus on neighborhoods. |
Understanding Completion and Localization
Completion refers to the process of finalizing or fulfilling a task, project, or translation to ensure all components are accurately addressed. Localization involves adapting content or products to meet the cultural, linguistic, and regulatory requirements of a specific target market. Understanding completion ensures quality and accuracy, while mastering localization guarantees relevance and acceptance in diverse global contexts.
Key Differences Between Completion and Localization
Completion involves filling in missing information or text to create a coherent and contextually accurate output, primarily focusing on continuity and relevance within a single language. Localization adapts content to fit the cultural, linguistic, and regional specifics of a target audience, ensuring that the message resonates appropriately across different locales. Key differences include completion's emphasis on completeness and fluency in one language versus localization's focus on cultural adaptation, idiomatic expressions, and regional nuances.
The Role of Completion in Global Projects
Completion in global projects ensures the accurate fulfillment of all specified requirements, enabling seamless integration across diverse markets and regulatory environments. It validates that products or services meet international standards, which enhances consistency and reliability in localization efforts. Effective completion minimizes errors and rework, accelerating time-to-market and improving customer satisfaction worldwide.
Localization: Adapting Content for Target Audiences
Localization ensures content resonates by adapting language, cultural references, and user experience to specific regional preferences and norms. It involves modifying idioms, date formats, units of measure, and visuals to align with the target audience's expectations and enhance engagement. Effective localization increases relevance, boosts user satisfaction, and drives higher conversion rates in global markets.
Completion vs Localization: Use Cases
Completion excels in code generation, automating routine tasks, and boosting developer productivity by predicting and suggesting code snippets based on context. Localization specializes in adapting software to different languages and cultural norms, ensuring user interfaces, date formats, and content meet regional requirements. Use cases for Completion include accelerating software development and reducing errors, while Localization is essential for global market expansion and enhancing user experience across diverse demographics.
Impact on User Experience
Completion significantly enhances user experience by anticipating user needs and providing relevant suggestions, reducing input effort and accelerating task completion. Localization improves user experience by adapting interfaces to cultural and linguistic preferences, ensuring content relevance and increasing user comfort and engagement. Both strategies address different dimensions of usability, with completion streamlining interaction and localization fostering inclusivity and accessibility.
Challenges in Achieving Completion and Localization
Challenges in achieving completion include data quality issues, incomplete user inputs, and ambiguous queries that hinder accurate and relevant output generation. Localization faces challenges such as cultural nuances, language-specific idioms, and context adaptation that require more than direct translation to maintain meaning and user engagement. Both processes demand sophisticated algorithms and extensive datasets to effectively address variability and ensure precise, context-aware results.
Best Practices for Balancing Completion and Localization
Balancing completion and localization requires aligning translation goals with target audience expectations and cultural context to ensure content accuracy and relevance. Implementing iterative review cycles with native linguists enhances localization quality while maintaining the original message's completeness. Leveraging translation memory tools and glossaries promotes consistency and efficiency across both completion and localization phases.
Tools and Technologies for Efficient Processes
Completion tools often utilize AI-driven APIs and automation software to finalize projects quickly, enhancing accuracy through machine learning algorithms. Localization technologies focus on adapting content for specific regions using translation management systems, glossaries, and cultural adaptation tools like CAT software and Terminology Databases. Combining cloud-based platforms with real-time collaboration tools streamlines both completion and localization, reducing turnaround time and improving workflow efficiency.
Future Trends in Completion and Localization
Future trends in completion and localization emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance accuracy and efficiency. Advanced neural network models and automated workflows are expected to reduce turnaround times and improve context-aware translations. Growing demand for multilingual content across digital platforms drives innovation in real-time localization and completion solutions tailored for global markets.
Completion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com