De Interpretatione explores the fundamental principles of language, logic, and meaning, focusing on how words relate to concepts and reality. It delves into the intricacies of propositions, their truth values, and the relationship between language and thought. Discover how these insights can deepen Your understanding of communication by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
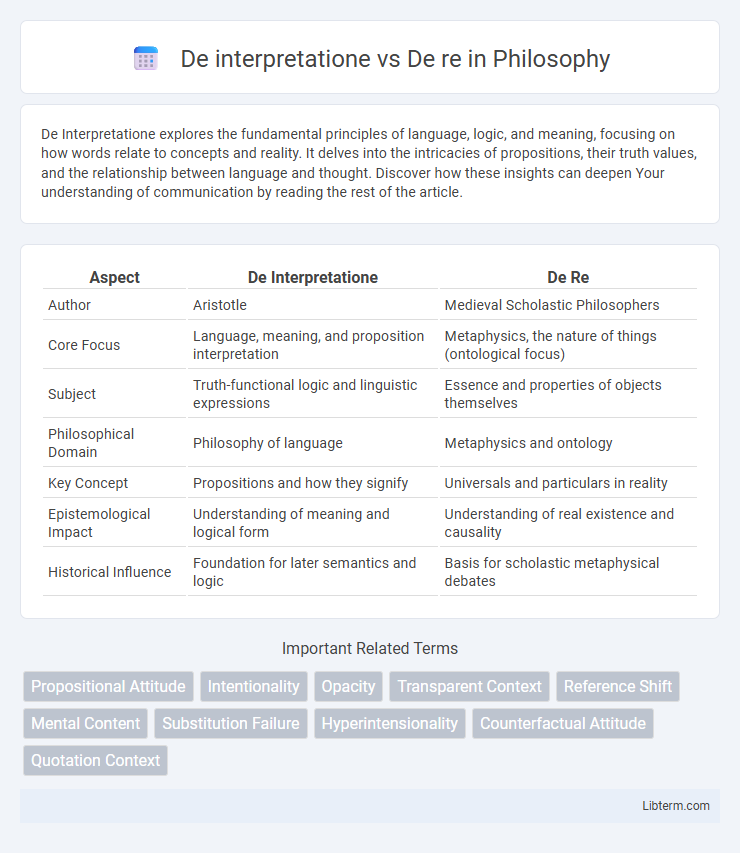
| Aspect | De Interpretatione | De Re |
|---|---|---|
| Author | Aristotle | Medieval Scholastic Philosophers |
| Core Focus | Language, meaning, and proposition interpretation | Metaphysics, the nature of things (ontological focus) |
| Subject | Truth-functional logic and linguistic expressions | Essence and properties of objects themselves |
| Philosophical Domain | Philosophy of language | Metaphysics and ontology |
| Key Concept | Propositions and how they signify | Universals and particulars in reality |
| Epistemological Impact | Understanding of meaning and logical form | Understanding of real existence and causality |
| Historical Influence | Foundation for later semantics and logic | Basis for scholastic metaphysical debates |
Introduction to De Interpretatione and De Re
Aristotle's *De Interpretatione* examines the principles of language, logic, and meaning by analyzing propositions, their components, and truth values. In contrast, *De Re* focuses on the relationship between language and the objects or things (res) that language signifies, addressing issues in semantics and metaphysics. The introduction to *De Interpretatione* establishes fundamental distinctions between terms, ideas, and sentences, forming the basis for understanding linguistic representation and logical inference.
Historical Context and Philosophical Background
De Interpretatione, written by Aristotle in the 4th century BCE, serves as a foundational text in the study of logic and language, particularly concerning the relationship between words and their meanings. It addresses the nature of propositions, categorizing statements as either simple or complex and explores the concepts of affirmation, negation, and contradiction within an early framework of semantic theory. De Re, rooted in medieval scholastic philosophy, contrasts with De Interpretatione by focusing on things (res) themselves, emphasizing the metaphysical aspects of reference and predication in relation to objects, which influenced later developments in ontology and the theory of reference.
Defining "De Interpretatione
De Interpretatione, a foundational text by Aristotle, examines the principles of language, logic, and meaning, focusing on the relationship between words and things. It introduces key concepts such as affirmation, negation, contradiction, and the analysis of propositions, which are fundamental to understanding semantic interpretation. In contrast, De Re centers on discussions about things themselves (objects or entities), emphasizing the ontological aspects rather than linguistic or propositional structures.
Defining "De Re
De Re, in philosophical and logical contexts, refers to statements or beliefs concerning things themselves rather than their descriptions or properties, emphasizing direct reference to objects. Unlike De Interpretatione, which deals with the interpretation and meaning of language or propositions, De Re focuses on the metaphysical and semantic relationship to the actual entities. This distinction is crucial in modal logic, where De Re modality pertains to necessity or possibility attributed to objects rather than to propositions or concepts.
Key Differences Between De Interpretatione and De Re
De Interpretatione centers on the theory of language and meaning, exploring how propositions express truth conditions through linguistic constructs such as terms and syllogisms. De Re, by contrast, focuses on attitudes or beliefs about objects themselves rather than their descriptions, addressing the semantics of reference and necessity in modal contexts. The key difference lies in De Interpretatione analyzing language structure and truth-value, whereas De Re emphasizes the ontological relationship between words and things in philosophical semantics.
Philosophical Implications of Both Concepts
De interpretatione explores the relationship between language and meaning, emphasizing how propositions express thoughts and the conditions under which statements are true or false. De re focuses on objects or things themselves, addressing the ontological status and reference of terms beyond mere linguistic expressions. Together, these concepts shape the philosophical discourse on reference, truth, and the interplay between language, thought, and reality.
Applications in Contemporary Linguistics
De interpretatione, centered on the theory of meaning and propositions, underpins modern semantics by distinguishing between linguistic expressions and their truth conditions, critical for analyzing sentence meaning in natural language processing. De re focuses on reference and the relationship between language and objects in the world, influencing contemporary studies on indexicals, definite descriptions, and context-dependent expressions. Together, these works inform computational linguistics in developing algorithms for sense disambiguation, reference resolution, and pragmatic inference.
De Re and De Dicto: Related Distinctions
De re and de dicto distinctions are central to the interpretation of modal and intensional contexts, with de re referring to statements about things themselves and de dicto focusing on the propositions or expressions containing those things. In De Interpretatione, Aristotle explores how meaning relates to truth and reference, which underpins the semantic difference between de re (about the object) and de dicto (about the statement). This contrast influences contemporary philosophy of language by clarifying ambiguity in propositional attitudes and modal logic.
Case Studies and Practical Examples
De Interpretatione primarily explores the nature of propositions and their truth conditions through abstract logical analysis, while De Re focuses on the reference of terms in specific contexts, emphasizing how objects are discussed. Case studies illustrating De Interpretatione include analyses of ambiguous statements and their logical validity, whereas De Re is exemplified by practical examples in legal reasoning, where the precise reference of terms affects judgments. These practical distinctions highlight how De Interpretatione aids formal semantic theory development, while De Re informs applied semantics in real-world contexts.
Conclusion: Significance in Philosophy and Linguistics
De Interpretatione emphasizes the foundational role of language and logic in understanding meaning and truth, highlighting how propositions convey knowledge. De Re focuses on the relationship between terms and actual objects, stressing reference and ontology in philosophical inquiry. Together, these works significantly influence contemporary philosophy of language and linguistics by shaping theories on semantics, reference, and the interplay between language and reality.
De interpretatione Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com