Indefinite articles play a crucial role in English by introducing nonspecific nouns, helping to clarify meaning without limiting scope. Understanding how to properly use "a" and "an" enhances your communication skills and makes your writing more natural and engaging. Explore the full article to master the use of indefinite articles in various contexts.
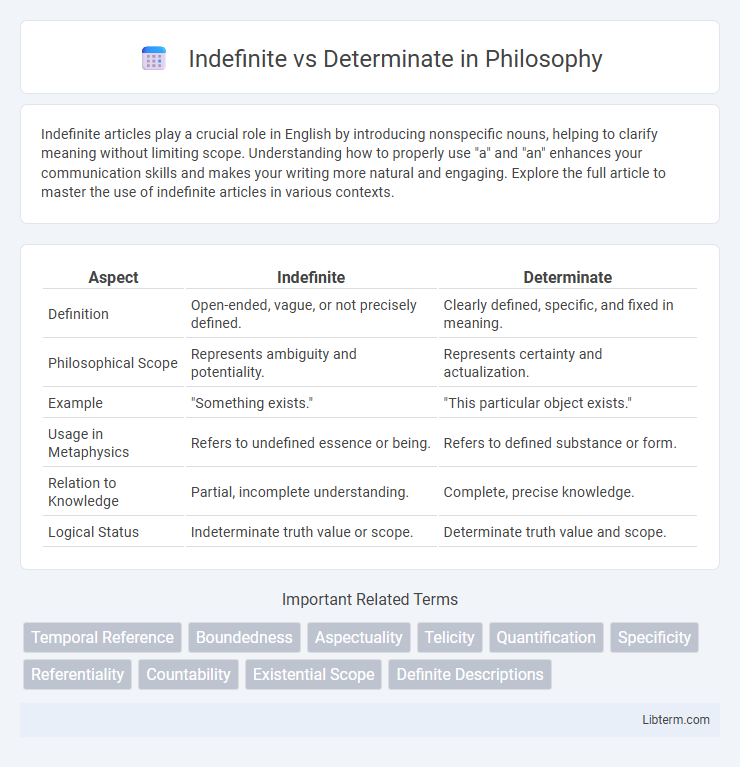
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Indefinite | Determinate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Open-ended, vague, or not precisely defined. | Clearly defined, specific, and fixed in meaning. |
| Philosophical Scope | Represents ambiguity and potentiality. | Represents certainty and actualization. |
| Example | "Something exists." | "This particular object exists." |
| Usage in Metaphysics | Refers to undefined essence or being. | Refers to defined substance or form. |
| Relation to Knowledge | Partial, incomplete understanding. | Complete, precise knowledge. |
| Logical Status | Indeterminate truth value or scope. | Determinate truth value and scope. |
Understanding Indefinite and Determinate: Key Definitions
Indefinite refers to a state or condition without a fixed limit or precise boundary, often used to describe time, quantity, or duration that is not specifically defined. Determinate, in contrast, denotes something clearly defined, fixed, or having exact limits, commonly applied in contexts such as legal terms, contracts, or biological growth where specific endpoints are established. Understanding these key definitions is crucial for interpreting contexts in law, linguistics, and sciences, where the distinction influences meaning, obligations, and processes.
Core Differences Between Indefinite and Determinate
Indefinite and determinate forms differ primarily in specificity and definiteness; indefinite refers to non-specific entities without a clear boundary, while determinate denotes specific, clearly identified objects or concepts. In grammar and legal contexts, indefinite indicates uncertain duration or amount, whereas determinate implies fixed, measurable limits. This distinction impacts interpretation, clarity, and application across languages, contracts, and classifications.
Examples of Indefinite Concepts in Context
Indefinite concepts include terms like "some," "few," and "many," which refer to unspecified quantities or entities within a category. For example, in the sentence "Some students arrived late," the exact number remains unknown and variable. These indefinite expressions allow for flexibility and generalization in communication, emphasizing quantity or identity without precision.
Examples of Determinate Uses in Practice
Determinate uses in practice include legal contracts specifying exact deadlines for performance, project management timelines with fixed milestones, and employment agreements that outline a definite term of service. For instance, a lease agreement may state a tenancy duration from January 1 to December 31, ensuring clarity and enforceability. Business plans often rely on determinate goals and deadlines to measure progress and allocate resources efficiently.
Relevance in Legal Terminology: Indefinite vs Determinate
In legal terminology, the distinction between indefinite and determinate terms carries significant relevance, as indefinite terms create flexibility and ambiguity, potentially leading to broader judicial interpretation. Determinate terms, by contrast, provide clear, precise definitions essential for enforceability and predictability in legal contracts and statutes. Courts prioritize determinate terms to ensure clarity in obligations, rights, and penalties, minimizing disputes and facilitating consistent application of the law.
Role in Philosophy: Interpreting Indefinite and Determinate
Indefinite and determinate concepts in philosophy shape how existence and identity are understood, with indeterminate entities highlighting potentiality and open-endedness, while determinate entities emphasize specificity and fixed attributes. Philosophers use these distinctions to analyze the nature of objects, states, and properties, addressing questions of ontology and epistemology. The interplay between indefinite and determinate informs debates on reality, perception, and knowledge classification within metaphysical frameworks.
Application in Mathematics and Logic
Indefinite and determinate forms play crucial roles in mathematics and logic, where indefinite expressions often represent unknown or variable elements, such as in existential quantification (x) indicating there exists some element x. Determinate forms correspond to specific, well-defined values or objects, enabling precise reasoning and proofs, particularly in functions and equations where variables assume fixed values. These distinctions facilitate clarity in logical formulations and computational algorithms, underpinning theorem proving and algorithmic problem-solving.
Impact on Language and Communication
Indefinite and determinate forms shape clarity and context in language, influencing how information is processed and understood. Indefinite terms introduce new or non-specific concepts, promoting generalization and open interpretation, while determinate forms specify known entities, enhancing precision and reducing ambiguity. This distinction impacts communication effectiveness by guiding listener expectations and facilitating more accurate information exchange.
Choosing Between Indefinite and Determinate in Writing
Choosing between indefinite and determinate articles hinges on clarity and specificity in writing; indefinite articles ("a," "an") introduce nonspecific items, while determinate articles ("the") refer to particular, known entities. Writers enhance precision by using determinate articles when the reader is assumed to know the subject, improving comprehension and context. Indefinite articles foster a general or new introduction of concepts, which aids in engaging readers and avoiding unnecessary specificity.
Summary Table: Indefinite vs Determinate at a Glance
The summary table of Indefinite vs Determinate highlights key distinctions: indefinite concepts lack specific limits, quantities, or duration, often used for general or unspecified references, while determinate concepts specify exact quantities, limits, or time frames, ensuring precision and clarity in communication. Indefinite forms typically express openness or variability, whereas determinate forms emphasize definiteness and constraints, facilitating clear differentiation in grammatical and semantic contexts. This comparison aids in understanding usage patterns in language, logic, and legal documents where precision matters.
Indefinite Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com