Polarization intensifies divisions within societies, leading to heightened conflicts and reduced opportunities for consensus. Understanding its causes and effects is essential for navigating social and political landscapes effectively. Explore the rest of the article to learn how polarization impacts your community and strategies to bridge divides.
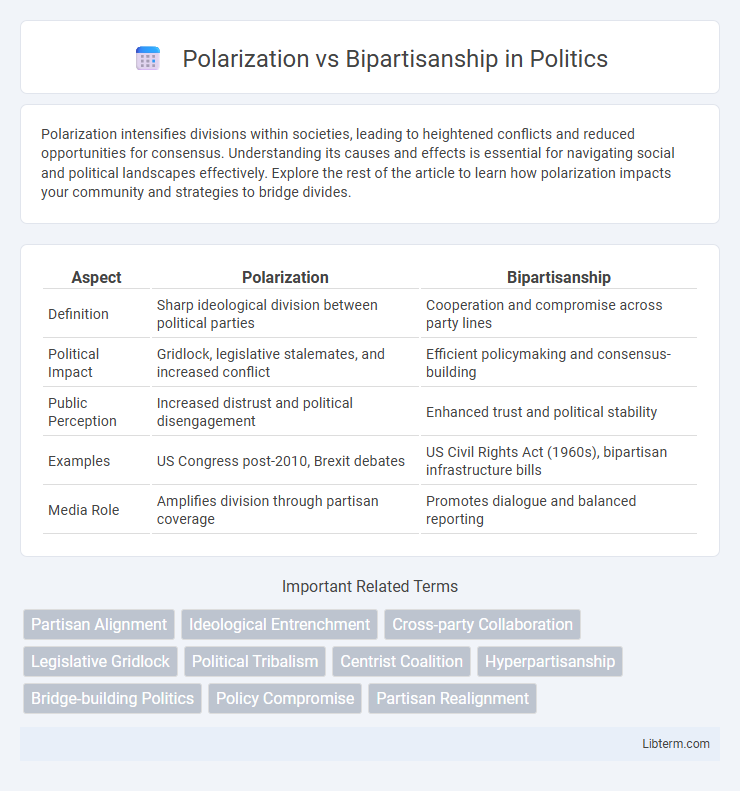
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Polarization | Bipartisanship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sharp ideological division between political parties | Cooperation and compromise across party lines |
| Political Impact | Gridlock, legislative stalemates, and increased conflict | Efficient policymaking and consensus-building |
| Public Perception | Increased distrust and political disengagement | Enhanced trust and political stability |
| Examples | US Congress post-2010, Brexit debates | US Civil Rights Act (1960s), bipartisan infrastructure bills |
| Media Role | Amplifies division through partisan coverage | Promotes dialogue and balanced reporting |
Understanding Polarization in Modern Politics
Polarization in modern politics refers to the growing ideological divide between political parties, often resulting in decreased cooperation and increased partisanship. This phenomenon intensifies political conflicts and reduces the likelihood of bipartisan solutions that address complex societal issues. Understanding these divisions requires analyzing factors such as media influence, social identity, and legislative gridlock that reinforce partisan attitudes.
The Core Principles of Bipartisanship
Bipartisanship centers on collaboration between opposing political parties to achieve common goals through compromise and mutual respect. It prioritizes understanding diverse perspectives, fostering dialogue, and pursuing policies that reflect shared values rather than partisan interests. Core principles include transparency, cooperation, and a commitment to the public good, which contrast sharply with the divisiveness often seen in polarization.
Historical Shifts: From Unity to Division
Historical shifts in U.S. politics reveal a transition from eras of bipartisanship, marked by collaborative policymaking and cross-party alliances, to increasing polarization characterized by ideological division and partisan gridlock. Key periods such as the New Deal and post-World War II era showcased bipartisan efforts that addressed national crises, while recent decades exhibit intensified party loyalty and reduced legislative compromise. This evolution reflects changes in media influence, electoral dynamics, and social identity politics fostering political fragmentation.
Causes Behind Political Polarization
Political polarization stems primarily from ideological sorting, where voters and politicians increasingly align within homogenous political parties, reinforcing partisan identities. Social media algorithms amplify echo chambers by curating content that supports users' existing beliefs, intensifying divisions. Economic inequality and geographic segregation further deepen polarization by fostering disparate experiences and priorities across different demographic groups.
The Role of Media in Deepening Divides
Media outlets often amplify political polarization by emphasizing sensationalism and partisan rhetoric, which deepens societal divides. Algorithms on social media platforms curate content that reinforces existing beliefs, creating echo chambers and reducing exposure to opposing viewpoints. This selective exposure diminishes opportunities for bipartisanship, undermining collaborative decision-making in democratic processes.
Bipartisanship in Practice: Success Stories
Bipartisanship in practice has led to significant legislative successes, such as the 1994 Crime Bill and the 2018 First Step Act, where cooperation across party lines achieved meaningful reforms. Collaborative efforts on immigration reform and infrastructure investment demonstrate the potential for bipartisan solutions to address complex national challenges. These examples highlight how mutual compromise can foster effective governance and policy stability.
The Impact of Polarization on Governance
Polarization significantly impedes effective governance by fostering gridlock and reducing lawmakers' willingness to compromise on critical issues. This ideological division often results in legislative stalemates, delaying essential policy decisions and undermining public trust in democratic institutions. Bipartisanship, in contrast, enables collaborative problem-solving and enhances governmental stability by bridging partisan divides, facilitating the passage of comprehensive legislation.
Challenges to Restoring Bipartisanship
Polarization in contemporary politics intensifies ideological divisions, making bipartisanship increasingly challenging to achieve due to entrenched party loyalties and media echo chambers. Legislative gridlock often results from heightened partisanship, obstructing policy compromise and collaborative governance. Overcoming these obstacles requires structural reforms and incentives that encourage cross-party dialogue and mutual concessions.
Strategies for Bridging Political Divides
Effective strategies for bridging political divides emphasize fostering open dialogue and promoting empathy between opposing groups to reduce polarization. Implementing bipartisan initiatives and collaborative policymaking encourages shared goals and mutual understanding, which strengthens cooperation across party lines. Educational programs that enhance critical thinking and media literacy help citizens recognize bias and build more constructive political engagement.
The Future: Can Bipartisanship Survive Polarization?
Bipartisanship faces significant challenges in the future due to increasing political polarization marked by ideological divides and media echo chambers. Persistent polarization reduces opportunities for compromise, making bipartisan legislation harder to achieve in Congress. However, fostering cross-party dialogue and prioritizing common goals could help bipartisanship endure despite entrenched partisan conflicts.
Polarization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com