A faction represents a smaller, organized group within a larger entity, often united by shared interests or goals. These groups can influence decision-making and impact the overall dynamics of organizations, communities, or political parties. Discover how understanding factions can help you navigate complex social structures in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
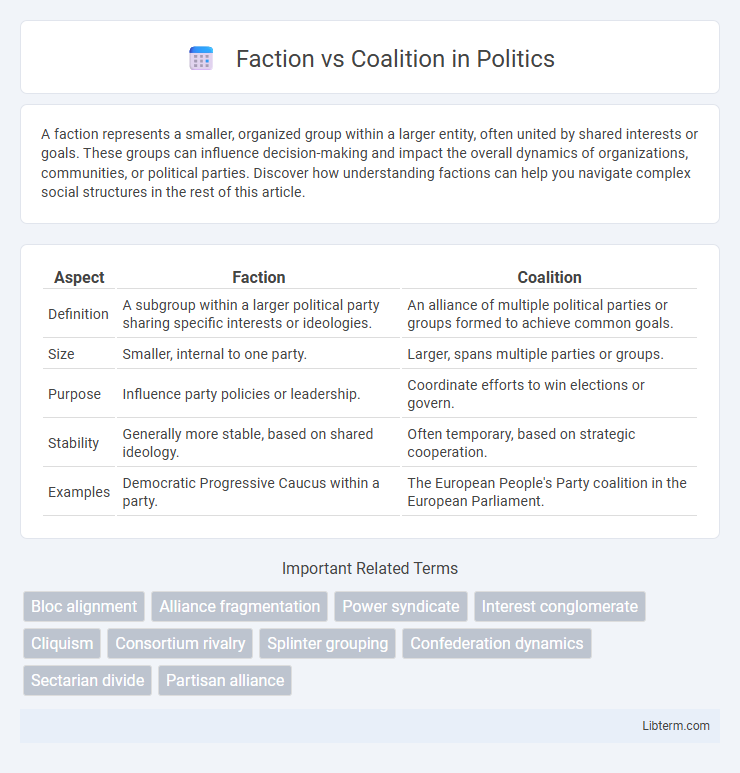
| Aspect | Faction | Coalition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A subgroup within a larger political party sharing specific interests or ideologies. | An alliance of multiple political parties or groups formed to achieve common goals. |
| Size | Smaller, internal to one party. | Larger, spans multiple parties or groups. |
| Purpose | Influence party policies or leadership. | Coordinate efforts to win elections or govern. |
| Stability | Generally more stable, based on shared ideology. | Often temporary, based on strategic cooperation. |
| Examples | Democratic Progressive Caucus within a party. | The European People's Party coalition in the European Parliament. |
Defining Factions and Coalitions
Factions are smaller, organized groups within a larger entity that pursue specific interests or agendas, often leading to internal divisions. Coalitions consist of multiple factions or parties that temporarily unite to achieve common goals despite differing individual agendas. Understanding the distinction between factions and coalitions is crucial for analyzing group dynamics and power structures in political and organizational contexts.
Historical Origins of Factions and Coalitions
Factions originated as informal groups within larger political parties or social movements, often driven by shared interests or ideological differences dating back to ancient civilizations like Greece and Rome. Coalitions emerged as strategic alliances formed between distinct political parties or groups to achieve common goals, particularly prominent during parliamentary systems in the 18th and 19th centuries. The historical evolution of factions highlights internal dissent and power struggles, while coalitions reflect pragmatic cooperation and power-sharing arrangements among diverse entities.
Key Characteristics: Faction vs Coalition
Factions are smaller groups within a larger organization or society that share specific interests or goals, often operating independently with a distinct identity and agenda. Coalitions consist of multiple factions or groups that temporarily unite to achieve a common objective, emphasizing collaboration and shared resources. While factions prioritize internal cohesion and particularistic aims, coalitions focus on broader alliance-building and strategic partnerships for collective impact.
Motivations Behind Formation
Factions form primarily from internal disagreements within a larger group, driven by differing ideologies, goals, or leadership disputes seeking to assert more influence or control. Coalitions emerge as strategic alliances between distinct groups or parties aiming to combine resources and power to achieve common objectives or respond to external threats. Understanding these motivations highlights factions' emphasis on internal differentiation versus coalitions' focus on external collaboration.
Power Dynamics and Leadership Structures
Factions typically operate as smaller, more centralized groups where leadership is concentrated and power is exercised through direct control or influence over members. Coalitions, on the other hand, consist of multiple distinct groups that collaborate while maintaining their own leadership structures, resulting in a more decentralized power dynamic. The stability of factions often depends on strong, singular leadership, whereas coalitions rely on negotiation and shared authority among the participating entities.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Factions typically operate with centralized decision-making, where a small group of leaders or a dominant figure makes strategic choices rapidly to maintain tight control and enforce unified goals. Coalitions emphasize collaborative decision-making, involving multiple independent groups or parties that negotiate and build consensus to balance diverse interests and ensure collective agreement. The faction model prioritizes agility and uniformity, while coalition processes focus on inclusivity and shared power dynamics.
Influence on Political Stability
Factions often create internal divisions within political parties, undermining cohesion and destabilizing governance by promoting competing agendas and power struggles. Coalitions, formed through alliances between different parties or groups, can enhance political stability by fostering collaboration and consensus-building among diverse interests. The success of coalitions in maintaining stability depends on effective negotiation and the ability to manage conflicting priorities without fragmenting the governing structure.
Real-World Examples Across Sectors
Factions and coalitions differ in structure and purpose, as factions represent internal groups within an organization or political party with distinct agendas, whereas coalitions are alliances formed between separate entities to achieve common goals. In politics, the Democratic Party's progressive and moderate factions often compete internally, while the NATO coalition unites multiple countries for collective security. In business, Google's various product teams may act as factions pushing different strategies, contrasted with the airline industry's Star Alliance coalition, where competitors collaborate for shared benefits.
Benefits and Challenges of Each
Factions often provide a strong sense of identity and loyalty, enabling swift decision-making and cohesive action, but they can struggle with internal disagreements and limited perspectives that hinder broader cooperation. Coalitions bring together diverse groups to pool resources and expertise, enhancing influence and problem-solving capabilities, yet face challenges such as conflicting interests, slower consensus-building, and difficulties in maintaining unity over time. Understanding the trade-offs between the focused commitment of factions and the inclusive collaboration of coalitions is crucial for effective political or organizational strategy.
The Future of Alliances: Faction or Coalition?
The future of alliances hinges on whether factions or coalitions will dominate strategic partnerships, with factions offering tightly knit groups united by common ideology or goals, fostering deep loyalty and streamlined decision-making. Coalitions, however, are broader alliances of diverse entities cooperating for mutual benefit, emphasizing flexibility and the pooling of resources to address complex challenges. As geopolitical dynamics evolve, the adaptability and resource-sharing capacity of coalitions may prove more advantageous, while factions retain strength in focused, mission-driven efforts.
Faction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com