Pluralism embraces the coexistence of diverse beliefs, cultures, and values within a society, fostering mutual respect and open dialogue. This approach enhances social cohesion and innovation by encouraging multiple perspectives to shape decisions and policies. Explore the rest of the article to understand how pluralism can positively impact your community and worldview.
Table of Comparison
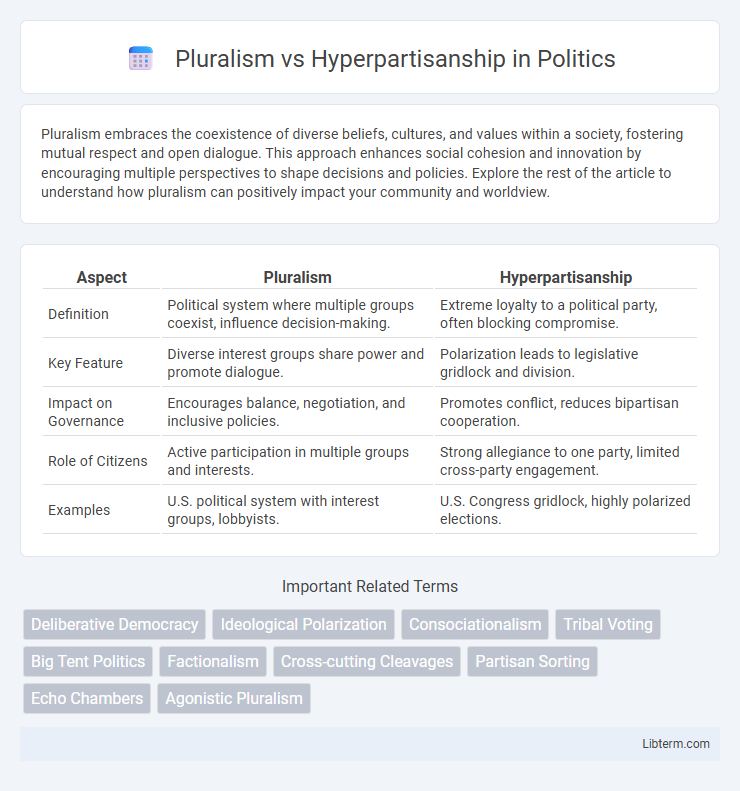
| Aspect | Pluralism | Hyperpartisanship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political system where multiple groups coexist, influence decision-making. | Extreme loyalty to a political party, often blocking compromise. |
| Key Feature | Diverse interest groups share power and promote dialogue. | Polarization leads to legislative gridlock and division. |
| Impact on Governance | Encourages balance, negotiation, and inclusive policies. | Promotes conflict, reduces bipartisan cooperation. |
| Role of Citizens | Active participation in multiple groups and interests. | Strong allegiance to one party, limited cross-party engagement. |
| Examples | U.S. political system with interest groups, lobbyists. | U.S. Congress gridlock, highly polarized elections. |
Understanding Pluralism: Foundations and Principles
Pluralism is grounded in the recognition of diverse and competing interests within society, emphasizing the peaceful coexistence and negotiation among multiple social groups and political parties. Its core principles include inclusive participation, respect for minority rights, and the protection of civil liberties to ensure balanced representation in governance. Unlike hyperpartisanship, which fractures political dialogue, pluralism fosters collaboration and deliberative democracy.
Defining Hyperpartisanship in Modern Politics
Hyperpartisanship in modern politics refers to an extreme, polarized loyalty to a political party, often resulting in an unwillingness to compromise or engage with opposing viewpoints. This phenomenon intensifies political divisions and disrupts democratic processes by prioritizing party agendas over national interests. Increasing social media influence and ideological echo chambers contribute significantly to the rise of hyperpartisan behavior among politicians and voters alike.
Historical Evolution: Pluralism vs Hyperpartisanship
Pluralism historically emerged as a democratic ideal promoting diverse interest groups and balanced power distribution, fostering negotiation and compromise in governance. Throughout the 20th century, increasing political polarization and media fragmentation fueled hyperpartisanship, characterized by extreme loyalty to partisan identities and reduced willingness for cross-party collaboration. This shift challenges pluralist principles by amplifying ideological divides and undermining institutional mechanisms designed for consensus-building.
The Role of Pluralism in Democratic Societies
Pluralism in democratic societies fosters a political environment where diverse groups and interests coexist, encouraging inclusive dialogue and compromise essential for policy-making. It supports the representation of multiple perspectives, preventing any single group from dominating the political discourse, thereby strengthening democratic legitimacy and social cohesion. Hyperpartisanship, by contrast, fractures this balance, leading to polarization, legislative gridlock, and diminished public trust in democratic institutions.
How Hyperpartisanship Erodes Civil Discourse
Hyperpartisanship erodes civil discourse by intensifying polarization and reducing willingness to engage in open, respectful dialogue across political divides. This deepened ideological entrenchment fosters echo chambers where misinformation thrives, undermining mutual understanding and democratic deliberation. The resulting breakdown in communication hinders policy compromise and weakens institutions dependent on collaborative governance.
Media Influence: Fueling Pluralism or Hyperpartisanship?
Media influence significantly shapes political discourse by either fostering pluralism or intensifying hyperpartisanship. Diverse media outlets that present multiple perspectives contribute to a pluralistic society by encouraging informed debate and critical thinking. Conversely, echo chambers and biased news sources amplify hyperpartisanship by promoting polarized views, reducing exposure to opposing opinions, and deepening societal divides.
Governance Outcomes: Cooperation vs Polarization
Governance outcomes under pluralism typically demonstrate higher levels of cooperation, as diverse political groups engage in dialogue and negotiate compromises that address multiple interests. In contrast, hyperpartisanship tends to exacerbate polarization, leading to legislative gridlock and reduced policy effectiveness due to rigid party loyalty and opposition. Empirical studies reveal that pluralistic systems correlate with enhanced policymaking efficiency and social stability, whereas hyperpartisan environments often witness increased public distrust and governance dysfunction.
Societal Impacts: Inclusivity and Exclusion
Pluralism fosters societal inclusivity by encouraging diverse perspectives, promoting dialogue, and enabling collaborative decision-making across different groups. Hyperpartisanship intensifies societal exclusion by deepening divisions, reinforcing echo chambers, and marginalizing opposing viewpoints. These contrasting dynamics shape social cohesion, influencing political stability and public trust in democratic institutions.
Case Studies: Pluralistic vs Hyperpartisan Systems
Case studies of pluralistic political systems, such as Switzerland and India, demonstrate diverse representation with multiple competing parties fostering compromise and policy moderation. In contrast, hyperpartisan systems like the United States and Brazil show extreme ideological polarization, leading to legislative gridlock and reduced public trust in governance. Analysis of voting patterns, media influence, and institutional design highlights the impact of pluralism in promoting political stability versus hyperpartisanship's role in deepening social divisions.
Navigating the Future: Balancing Pluralism and Partisan Interests
Navigating the future requires balancing pluralism's inclusive dialogue with the rigid demands of hyperpartisanship, ensuring diverse perspectives shape policy without gridlock. Emphasizing collaboration among ideological groups fosters democratic resilience and mitigates extreme polarization's impact on governance. Strategic engagement in bipartisan efforts promotes sustainable decision-making aligned with the broader public interest.
Pluralism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com