Policy continuity ensures stability and predictability in governance, fostering investor confidence and long-term economic growth. It minimizes disruptions caused by frequent changes in regulations, allowing businesses and citizens to plan effectively for the future. Discover how policy continuity can impact your environment by reading the rest of this article.
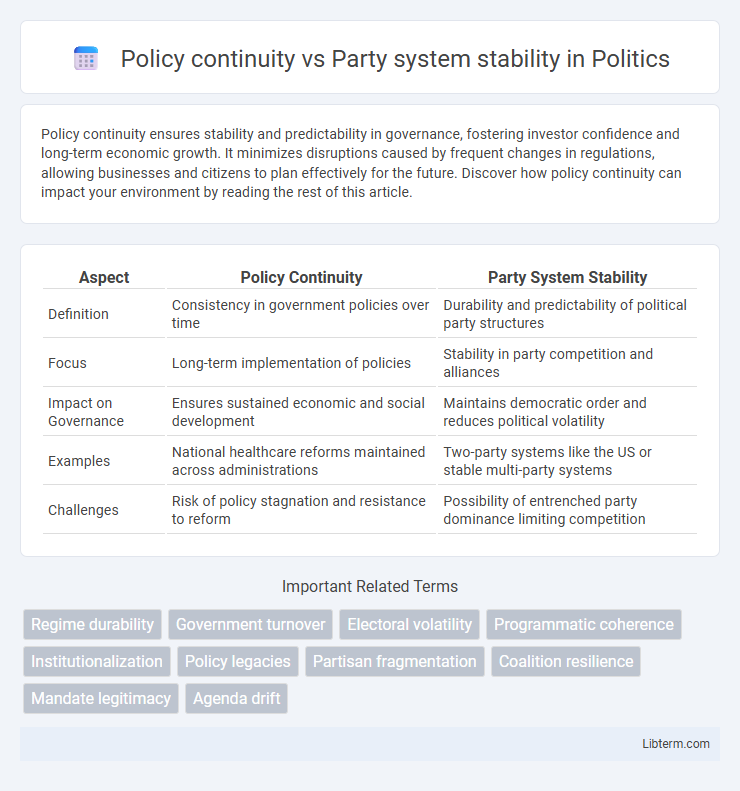
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Policy Continuity | Party System Stability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consistency in government policies over time | Durability and predictability of political party structures |
| Focus | Long-term implementation of policies | Stability in party competition and alliances |
| Impact on Governance | Ensures sustained economic and social development | Maintains democratic order and reduces political volatility |
| Examples | National healthcare reforms maintained across administrations | Two-party systems like the US or stable multi-party systems |
| Challenges | Risk of policy stagnation and resistance to reform | Possibility of entrenched party dominance limiting competition |
Introduction to Policy Continuity and Party System Stability
Policy continuity ensures stable governance by maintaining consistent government actions and regulations over time, which supports long-term economic growth and public trust. Party system stability refers to the persistence of existing political parties and structures, fostering predictability in political competition and representation. Both concepts are crucial for democratic consolidation, as continuous policies depend on stable party systems to implement and sustain them effectively.
Defining Policy Continuity in Political Systems
Policy continuity in political systems refers to the consistent implementation and maintenance of public policies over time, regardless of changes in government or political leadership. This stability ensures long-term development goals are met and enhances public trust by reducing uncertainty in governance. Policy continuity is often measured by the degree to which key programs, regulations, and strategic priorities remain unaltered across electoral cycles.
Understanding Party System Stability: Key Concepts
Party system stability refers to the consistency and predictability of political parties' presence, behavior, and voter support over time. It ensures effective governance by maintaining a balance between ideological diversity and institutional coherence within a democratic framework. Understanding key concepts such as party institutionalization, voter alignment, and electoral volatility is essential to analyze how stability influences policy continuity and political development.
Historical Context: Evolution of Party Systems
The historical context of party systems reveals how policy continuity often depends on the evolution and stability of these systems, with periods of major realignment marking significant shifts in political agendas. In established democracies, stable party systems have facilitated consistent policy frameworks, while times of instability or fragmentation correlate with frequent policy changes and uncertainty. The transition from one dominant party system to another typically reflects deep social and economic transformations influencing both institutional behavior and policy priorities.
The Role of Political Parties in Policy Making
Political parties shape policy continuity by promoting consistent platforms that guide legislative agendas and government priorities over time. Their stability within the party system ensures cohesive decision-making, reduces policy volatility, and facilitates long-term strategic planning. Disruptions in party system stability often lead to fragmented policy approaches, undermining sustained governance and effective policy implementation.
Factors Affecting Policy Continuity Across Governments
Policy continuity across governments is significantly influenced by institutional arrangements, including bureaucratic autonomy and legal frameworks that ensure the implementation of long-term strategies regardless of party changes. The degree of ideological similarity between successive parties within the party system affects stability, with greater congruence fostering consistent policy agendas. Public opinion and interest group pressures also shape the extent to which new governments maintain or alter existing policies, impacting overall policy continuity.
Party System Fragmentation and Its Impact on Governance
Party system fragmentation, characterized by an increase in the number of effective political parties, poses significant challenges to policy continuity and governance stability. Fragmented party systems often lead to coalition governments with diverse interests, resulting in policy gridlock, inconsistent legislation, and difficulties in long-term strategic planning. Empirical studies show that high fragmentation correlates with reduced government effectiveness, increased policy volatility, and weakened institutional capacity to implement reforms.
Comparative Analysis: Stable vs. Volatile Party Systems
Stable party systems tend to ensure greater policy continuity due to predictable legislative coalitions and coherent governance, facilitating long-term strategic planning and implementation. In contrast, volatile party systems often lead to frequent government changes and policy reversals, undermining consistency and creating uncertainty for investors and stakeholders. Comparative analysis reveals that countries with stable party systems typically exhibit stronger institutional frameworks and higher levels of political trust, contributing to sustained economic growth and social development.
Strategies for Enhancing Both Policy Continuity and Party Stability
Implementing clear institutional frameworks such as fixed legislative terms and robust policy evaluation mechanisms enhances policy continuity while reducing abrupt shifts driven by political changes. Strengthening intra-party democracy and fostering coalition governance promote party system stability through increased accountability and collaboration among diverse political actors. Integrating data-driven policy feedback loops ensures long-term strategic planning aligns with evolving public preferences, simultaneously supporting sustained policy agendas and stable party alliances.
Conclusion: Balancing Policy Consistency with Political Pluralism
Balancing policy consistency with political pluralism requires maintaining adaptable governance structures that accommodate diverse party interests while ensuring steady policy implementation. Effective institutions promote policy continuity by fostering cooperation across party lines without stifling political competition. Sustainable democracy hinges on this equilibrium, enabling long-term development alongside vibrant multiparty engagement.
Policy continuity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com