Patronage plays a crucial role in the advancement of arts, culture, and innovation by providing financial and moral support to creators and institutions. Understanding how patronage influences your favorite works and cultural trends can reveal the hidden networks behind artistic success. Explore the rest of the article to discover how patronage shapes creative landscapes and impacts society.
Table of Comparison
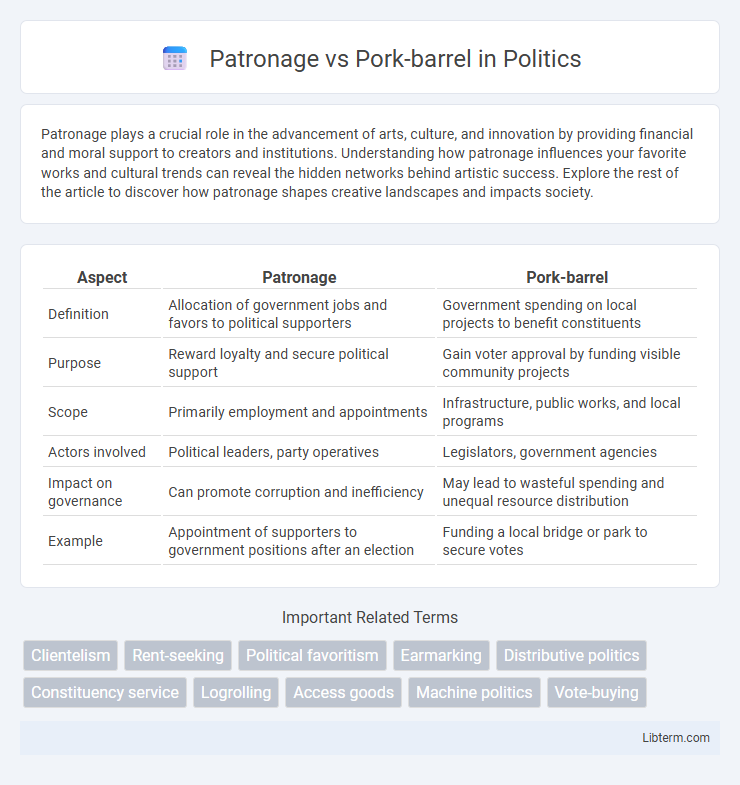
| Aspect | Patronage | Pork-barrel |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allocation of government jobs and favors to political supporters | Government spending on local projects to benefit constituents |
| Purpose | Reward loyalty and secure political support | Gain voter approval by funding visible community projects |
| Scope | Primarily employment and appointments | Infrastructure, public works, and local programs |
| Actors involved | Political leaders, party operatives | Legislators, government agencies |
| Impact on governance | Can promote corruption and inefficiency | May lead to wasteful spending and unequal resource distribution |
| Example | Appointment of supporters to government positions after an election | Funding a local bridge or park to secure votes |
Understanding Patronage: Definition and History
Patronage refers to the power of political leaders to appoint supporters to government positions or grant favors in exchange for loyalty, a practice deeply rooted in political history dating back to ancient civilizations like Rome. This system helped consolidate power by rewarding allies and ensuring continued support, influencing modern political structures worldwide. Unlike pork-barrel spending, which allocates funds to specific local projects, patronage primarily involves personnel appointments and direct political favors.
Pork-barrel Politics Explained
Pork-barrel politics refers to the allocation of government funds for localized projects designed to please voters or legislators and secure their support. Unlike patronage, which involves appointing supporters to government positions, pork-barrel spending emphasizes budgetary favors that directly benefit a specific constituency. This practice often leads to increased government expenditure and political bargaining focused on winning electoral advantages rather than broader public interest.
Key Differences Between Patronage and Pork-barrel
Patronage involves political leaders providing jobs and favors to supporters based on loyalty, whereas pork-barrel refers to government spending allocated for localized projects to benefit constituents. Patronage emphasizes personal relationships and political support, while pork-barrel focuses on tangible infrastructure or development benefits. The key difference lies in patronage's reliance on political favoritism versus pork-barrel's emphasis on resource distribution for electoral gain.
The Origins and Evolution of Patronage
Patronage originated in ancient political systems as a method for leaders to secure loyalty by granting favors, appointments, and resources to supporters, forming a basis for clientelism. Its evolution traces through European monarchies and early American politics, where it institutionalized as the "spoils system," allowing elected officials to distribute government jobs to political allies. Over time, patronage became a subject of reform efforts aiming to replace it with merit-based civil services to reduce corruption and enhance government efficiency.
How Pork-barrel Projects Are Allocated
Pork-barrel projects are allocated through targeted government spending aimed at benefiting specific local constituencies, often secured by legislators to gain political support and votes. These projects typically involve funding for localized infrastructure, public works, or community services that may not align with broader national priorities. The allocation process often relies on political bargaining, with legislators leveraging their influence over budget approvals to direct resources to their districts.
Political Impacts of Patronage Systems
Patronage systems significantly influence political stability by reinforcing loyalty among party members and ensuring electoral support through the allocation of jobs and resources. This practice often leads to entrenched clientelism, undermining meritocracy and increasing opportunities for corruption within government institutions. Consequently, patronage impacts policy decisions and governance quality by prioritizing political interests over public welfare and institutional efficiency.
Socioeconomic Effects of Pork-barrel Spending
Pork-barrel spending often channels government funds into localized projects, leading to uneven socioeconomic development and reinforcing regional disparities. This practice can stimulate short-term job creation but frequently overlooks long-term economic sustainability and equitable resource allocation. Unlike patronage, which centers on political loyalty, pork-barrel allocations predominantly impact public infrastructure and social services, influencing community welfare and local economic dynamics.
Public Perceptions: Patronage vs Pork-barrel
Public perceptions of patronage and pork-barrel politics often highlight perceptions of favoritism and misuse of public funds. Patronage is seen as the allocation of government jobs or favors to political supporters, which can undermine meritocracy and trust in institutions. Pork-barrel spending is typically viewed as the use of government funds for localized projects designed to curry favor with legislators' constituencies, often criticized for promoting inefficiency and corruption.
Case Studies: Examples from Around the World
Patronage systems often manifest in countries like India and Brazil, where political leaders allocate government jobs and resources to loyal supporters to consolidate power, impacting public sector efficiency. In contrast, pork-barrel politics is evident in the United States and the Philippines, where legislators secure localized government spending projects, such as infrastructure or community facilities, to gain voter support within their districts. Case studies from Nigeria reveal a blend of both practices, highlighting how patronage networks intersect with pork-barrel expenditures to shape electoral dynamics and governance outcomes.
Reform Efforts and Recommendations
Reform efforts addressing patronage and pork-barrel politics emphasize transparency, accountability, and merit-based systems to reduce corruption and misuse of public funds. Recommendations include establishing independent commissions for fair resource allocation and enforcing strict regulations on political donations and project approvals. Implementing digital platforms for monitoring public expenditures promotes citizen oversight and discourages favoritism in government spending.
Patronage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com