Suspension plays a critical role in vehicle dynamics by absorbing shocks from uneven road surfaces to ensure a smooth and comfortable ride. Effective suspension systems improve handling, stability, and tire contact with the road, enhancing both safety and performance. Explore the rest of the article to understand how different suspension types impact your driving experience.
Table of Comparison
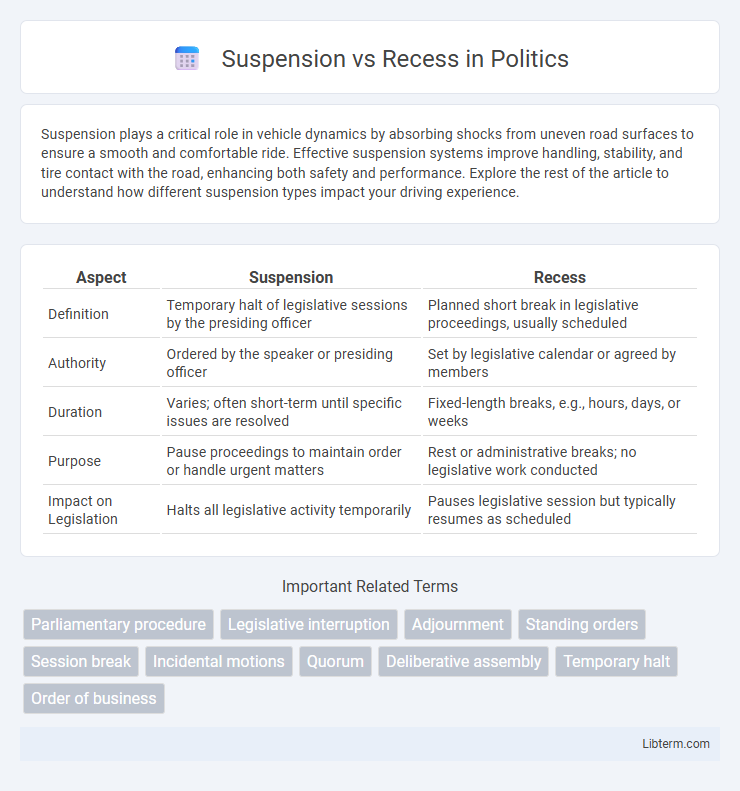
| Aspect | Suspension | Recess |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary halt of legislative sessions by the presiding officer | Planned short break in legislative proceedings, usually scheduled |
| Authority | Ordered by the speaker or presiding officer | Set by legislative calendar or agreed by members |
| Duration | Varies; often short-term until specific issues are resolved | Fixed-length breaks, e.g., hours, days, or weeks |
| Purpose | Pause proceedings to maintain order or handle urgent matters | Rest or administrative breaks; no legislative work conducted |
| Impact on Legislation | Halts all legislative activity temporarily | Pauses legislative session but typically resumes as scheduled |
Understanding Suspension and Recess: Key Definitions
Suspension refers to the temporary removal of a student from school as a disciplinary measure, often lasting from one to ten days, during which the student is prohibited from attending classes and school activities. Recess is a scheduled break period within the school day designed to provide students with time for relaxation, physical activity, and social interaction in a less structured environment. Understanding these key definitions highlights that suspension serves as a punishment for behavioral issues, while recess functions as a restorative and developmental break for all students.
Core Differences Between Suspension and Recess
Suspension temporarily halts a process or activity, often as a disciplinary measure or system pause, while recess refers to a scheduled break or interruption within a routine, such as a school day or legislative session. Suspension usually implies an external enforcement due to violation or issue, whereas recess is planned and regular, designed for rest or transition. Core differences lie in intent, duration, and causality: suspension is punitive and indefinite until conditions are met, recess is restorative and time-bound within normal operations.
Legal Foundations of Suspension vs Recess
Suspension is a formal disciplinary action grounded in statutory laws and school district policies, often requiring due process protections such as notice and a hearing. Recess, by contrast, is a routine break period established through educational guidelines and is not governed by disciplinary legal frameworks. Legal interpretations emphasize that suspension impacts student rights and educational access, while recess serves developmental and social purposes without invoking legal restrictions.
Impact on Parliamentary Proceedings
Suspension of parliamentary sessions halts all legislative activities temporarily, leading to delays in bill discussions and decision-making processes. Recess, while pausing formal sessions, allows committees and members to engage in constituency work and internal planning, maintaining some level of parliamentary function. The distinction affects the continuity and efficiency of legislative workflows, with suspension causing more abrupt interruptions compared to recess.
Triggers and Authority for Suspension
Suspension is typically triggered by severe violations of school policies such as violence, drug possession, or repeated misconduct, warranting immediate removal to maintain safety and order. Authority to impose suspension generally resides with school principals or designated administrative officials who assess the severity of the incident and its impact on the school environment. Recess, by contrast, is a scheduled break in the school day providing students with unstructured outdoor or indoor playtime, not related to disciplinary actions.
Common Reasons for Calling a Recess
Common reasons for calling a recess include the need for participants to rest, consult privately, or gather additional information before continuing the proceedings. Recesses allow time for resolving procedural issues, managing emotions, or addressing technical difficulties without concluding the session. This temporary pause helps maintain order and ensures that decisions are made with full consideration of all relevant facts.
Duration and Frequency: Suspension vs Recess
Suspensions typically last from one day to several weeks depending on the severity of the infraction, while recess periods are short, regular breaks usually lasting 15 to 30 minutes multiple times daily. Suspensions occur infrequently and are disciplinary actions taken for significant behavioral issues, whereas recesses happen routinely as part of the school day to provide students with physical activity and mental rest. The frequency and duration of suspensions vary greatly among schools, contrasting with the consistent, scheduled timing of recess sessions.
Procedural Implications and Limitations
Suspension pauses legal proceedings temporarily, allowing parties to address specific issues or await further developments, but it may extend case timelines and impact judicial efficiency. Recess refers to a short break during court sessions for rest or administrative purposes, typically without affecting the overall schedule or procedural deadlines. Procedurally, suspension can alter filing deadlines and hearing dates, whereas recess maintains existing timelines, limiting its effect on case progression.
Case Studies: Suspension and Recess in Practice
Case studies on suspension reveal a pattern of disproportionate impact on minority students, often leading to increased dropout rates and academic setbacks. Recess-focused case studies highlight improved student behavior, social skills, and cognitive function when adequate recess time is maintained in school schedules. Evidence from schools implementing recess shows a notable decrease in behavioral issues compared to those relying heavily on suspension as disciplinary action.
Choosing the Right Approach: Best Practices and Recommendations
Choosing the right approach between suspension and recess depends on the desired outcome, with suspension offering a stronger disciplinary action for serious infractions, while recess provides a brief break to help manage minor behavioral issues and improve focus. Best practices recommend assessing the context and severity of the behavior, prioritizing interventions that promote restorative justice and minimize negative educational impact. Schools should implement clear policies that balance safety and student development by combining suspension with supportive measures and using recess strategically to reinforce positive behavior.
Suspension Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com