Whistleblower protection safeguards individuals who report misconduct, ensuring they face no retaliation or discrimination. These legal frameworks empower you to expose fraud, corruption, or unethical behavior with confidence. Discover how these protections work and why they are vital in the full article.
Table of Comparison
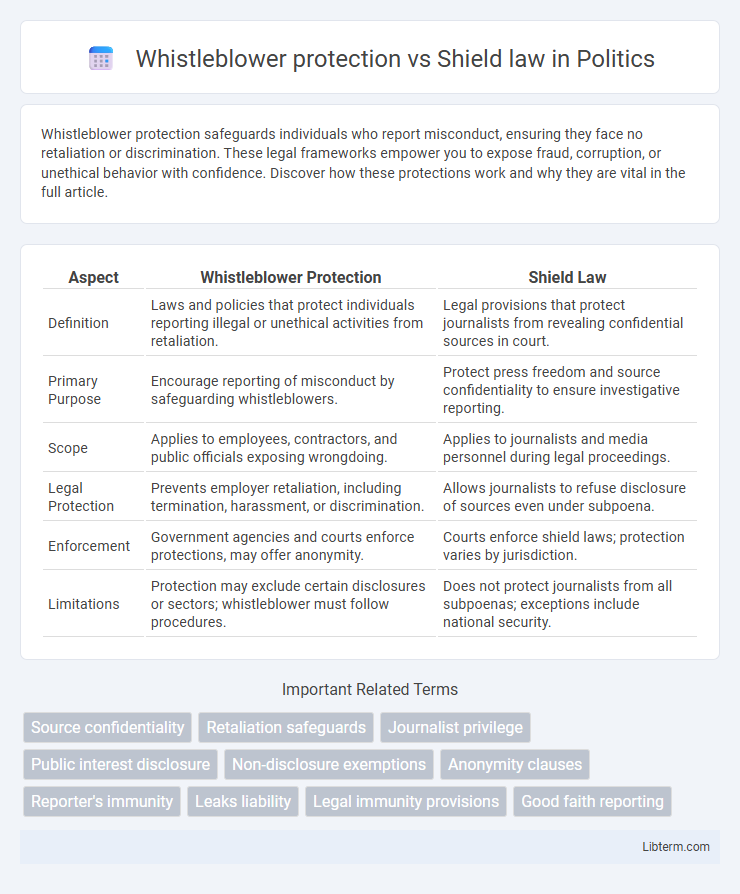
| Aspect | Whistleblower Protection | Shield Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Laws and policies that protect individuals reporting illegal or unethical activities from retaliation. | Legal provisions that protect journalists from revealing confidential sources in court. |
| Primary Purpose | Encourage reporting of misconduct by safeguarding whistleblowers. | Protect press freedom and source confidentiality to ensure investigative reporting. |
| Scope | Applies to employees, contractors, and public officials exposing wrongdoing. | Applies to journalists and media personnel during legal proceedings. |
| Legal Protection | Prevents employer retaliation, including termination, harassment, or discrimination. | Allows journalists to refuse disclosure of sources even under subpoena. |
| Enforcement | Government agencies and courts enforce protections, may offer anonymity. | Courts enforce shield laws; protection varies by jurisdiction. |
| Limitations | Protection may exclude certain disclosures or sectors; whistleblower must follow procedures. | Does not protect journalists from all subpoenas; exceptions include national security. |
Introduction to Whistleblower Protection and Shield Laws
Whistleblower protection laws safeguard employees who report misconduct, ensuring they are shielded from retaliation such as termination or harassment. Shield laws provide legal immunity to whistleblowers, particularly in revealing confidential or proprietary information, allowing them to disclose wrongdoing without fearing civil or criminal liability. Together, these legal frameworks promote transparency and accountability by encouraging the disclosure of illegal or unethical activities within organizations.
Defining Whistleblower Protection
Whistleblower protection refers to legal safeguards that shield employees from retaliation when they report misconduct, fraud, or violations within an organization. These protections often include confidentiality provisions, anti-retaliation measures, and legal remedies for whistleblowers facing adverse actions such as termination or harassment. Shield laws specifically provide journalists and certain professionals with the right to refuse disclosure of confidential sources, complementing whistleblower protection by safeguarding the flow of information to the public.
What Are Shield Laws?
Shield laws provide journalists with legal protections that prevent them from being compelled to reveal confidential sources or unpublished information in court. These laws vary by jurisdiction but are designed to preserve the freedom of the press and encourage the flow of information vital to public interest. Unlike whistleblower protection statutes, which safeguard employees exposing illegal activities from retaliation, shield laws specifically focus on protecting journalistic activities and sources.
Key Differences Between Whistleblower Protection and Shield Laws
Whistleblower protection laws specifically safeguard employees who report illegal or unethical activities within organizations, ensuring they are not retaliated against by employers. Shield laws offer journalists and media professionals legal immunity from being compelled to reveal confidential sources or unpublished information during legal proceedings. The key difference lies in the scope: whistleblower protections focus on employee rights against employer retaliation, while shield laws concentrate on preserving press freedom and source confidentiality.
Legal Frameworks Governing Whistleblowers
Whistleblower protection encompasses a broad range of legal frameworks designed to safeguard individuals who report misconduct, including federal laws like the Whistleblower Protection Act (WPA) and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX). Shield laws, typically enacted at the state level, provide specific protections primarily for journalists and their sources, often extending to whistleblowers by protecting confidentiality and preventing compelled disclosure. These legal frameworks collectively aim to encourage transparency and accountability by mitigating retaliation risks against whistleblowers in various sectors.
Journalistic Privilege Under Shield Laws
Journalistic privilege under shield laws provides reporters legal protection to refuse revealing confidential sources or unpublished information during legal proceedings, ensuring freedom of the press and integrity in investigative journalism. Unlike whistleblower protection laws, which safeguard individuals who expose wrongdoing from retaliation, shield laws specifically focus on shielding journalists to maintain source confidentiality. These laws vary by jurisdiction but are crucial for enabling journalists to report on corruption, misconduct, or other sensitive issues without fear of legal compulsion to disclose sensitive information.
Challenges Faced by Whistleblowers
Whistleblowers frequently encounter retaliation such as job termination, harassment, and legal repercussions despite existing whistleblower protection laws and shield laws designed to offer confidentiality and legal immunity. Challenges include inconsistent application of these laws across jurisdictions, limited scope that often excludes certain sectors or issues, and delays in legal processes that leave whistleblowers vulnerable during investigations. Many whistleblowers also face difficulty proving retaliation or maintaining anonymity, which undermines the effectiveness of both whistleblower protection statutes and shield laws.
The Role of the Media in Whistleblower Cases
The role of the media in whistleblower cases is crucial for amplifying protected disclosures under whistleblower protection laws and shield laws. Media outlets serve as intermediaries that bring unethical or illegal activities to public attention while shield laws protect journalists from revealing confidential sources, ensuring whistleblowers can share sensitive information without fear of exposure. This dynamic fosters transparency, accountability, and the enforcement of legal safeguards designed to protect whistleblowers from retaliation.
Case Studies: Whistleblowers vs. Journalistic Sources
Whistleblower protection laws safeguard individuals who expose illegal or unethical activities within organizations, often granting them immunity from retaliation, while shield laws specifically protect journalists from being compelled to reveal confidential sources. In landmark cases like *United States v. Sterling* and *In re Grand Jury Subpoena*, courts have highlighted the tension between safeguarding whistleblowers and protecting journalistic sources, underscoring the legal nuances in their distinct protections. These case studies reveal the critical balance courts strike between encouraging whistleblowing for transparency and preserving press freedom through shield laws.
Striking a Balance: Enhancing Legal Safeguards
Whistleblower protection laws and shield laws play crucial roles in safeguarding individuals who expose wrongdoing, with whistleblower protections focusing on preventing retaliation and shield laws offering confidentiality for sources. Striking a balance involves enhancing these legal safeguards to ensure transparency while protecting whistleblowers' identities and rights, fostering an environment where ethical disclosures are encouraged without fear of reprisal. Legal frameworks must evolve to address both personal security and public interest, harmonizing protection mechanisms to strengthen accountability in various sectors.
Whistleblower protection Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com