The Privacy Act establishes critical guidelines for protecting personal information collected by government agencies, ensuring your data is handled securely and transparently. It grants individuals rights to access and correct their information while restricting unauthorized disclosure. Explore the rest of the article to understand how the Privacy Act safeguards your privacy and what it means for you.
Table of Comparison
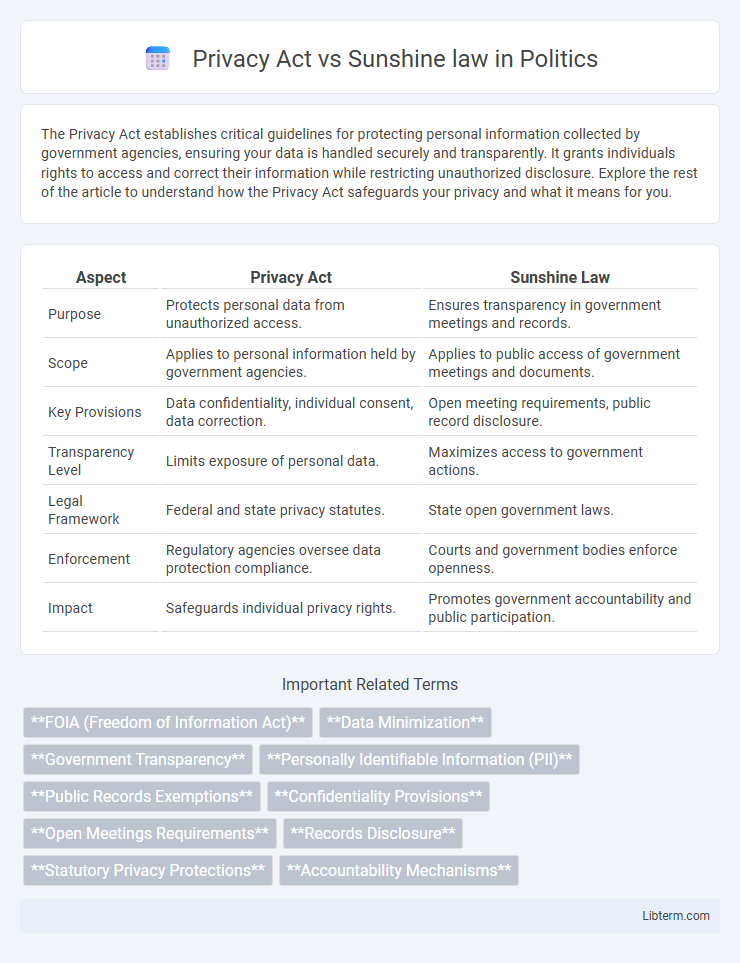
| Aspect | Privacy Act | Sunshine Law |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects personal data from unauthorized access. | Ensures transparency in government meetings and records. |
| Scope | Applies to personal information held by government agencies. | Applies to public access of government meetings and documents. |
| Key Provisions | Data confidentiality, individual consent, data correction. | Open meeting requirements, public record disclosure. |
| Transparency Level | Limits exposure of personal data. | Maximizes access to government actions. |
| Legal Framework | Federal and state privacy statutes. | State open government laws. |
| Enforcement | Regulatory agencies oversee data protection compliance. | Courts and government bodies enforce openness. |
| Impact | Safeguards individual privacy rights. | Promotes government accountability and public participation. |
Introduction to Privacy Act and Sunshine Law
The Privacy Act of 1974 establishes federal guidelines for handling personal information, protecting individuals' privacy by regulating how government agencies collect, use, and disclose data. The Sunshine Law, primarily applied at state levels, mandates transparency by requiring government meetings and records to be open to the public, promoting accountability and preventing secrecy. Both laws balance transparency and privacy, with the Privacy Act emphasizing data protection and the Sunshine Law enhancing governmental openness.
Historical Background and Legislative Intent
The Privacy Act of 1974 was enacted to safeguard individuals' personal information maintained by federal agencies, reflecting growing concerns over government misuse of data following the Watergate scandal. The Sunshine Law, originating in the early 20th century, was designed to promote transparency and accountability in government by mandating open meetings and public access to governmental decision-making processes. Both laws embody distinct legislative intents: the Privacy Act prioritizes protecting personal privacy, while the Sunshine Law emphasizes government openness and citizen oversight.
Key Definitions and Legal Framework
The Privacy Act governs the protection of personal information maintained by federal agencies, defining key terms such as "record," "individual," and "agency" to establish rights for individuals regarding access and amendment of their data. Sunshine laws, often referred to as Open Meeting Acts, mandate transparency by requiring government meetings to be open to the public, emphasizing terms like "meeting," "public body," and "quorum" to ensure accountability. Both legal frameworks promote transparency and privacy but operate within distinct scopes: the Privacy Act focuses on data protection, while Sunshine laws emphasize open governance.
Rights Protected Under the Privacy Act
The Privacy Act safeguards individuals' rights to control access to their personal information held by federal agencies, ensuring protections against unauthorized disclosure, correction of records, and access to one's own data. It establishes requirements for agencies to maintain data accuracy, relevance, and privacy, shielding citizens from government overreach. This contrasts with the Sunshine Law, which emphasizes transparency and public access to government proceedings rather than individual privacy rights.
Transparency Mandates of the Sunshine Law
The Sunshine Law enforces strict transparency mandates by requiring government agencies to conduct meetings openly, ensuring public access to discussions and decisions. Unlike the Privacy Act, which protects personal information from unauthorized disclosure, the Sunshine Law emphasizes accountability through real-time public participation and record availability. These transparency requirements foster governmental openness and public trust by promoting direct observation of official actions.
Major Differences Between the Two Laws
The Privacy Act primarily protects individuals' personal information held by federal agencies, ensuring controlled access and safeguarding data privacy. In contrast, the Sunshine Law mandates transparency and public access to government meetings and records at state and local levels, promoting open government practices. While the Privacy Act emphasizes confidentiality and data protection, the Sunshine Law focuses on accountability and public oversight.
Overlapping Areas and Legal Interactions
The Privacy Act and Sunshine Law both regulate government transparency and access to information, with overlapping areas in public records and government meetings. The Privacy Act primarily safeguards individual personal information from unauthorized disclosure, while the Sunshine Law mandates open meetings and access to public records, promoting governmental accountability. Legal interactions between these laws require balancing transparency obligations with privacy protections, ensuring that disclosure under the Sunshine Law does not violate the Privacy Act's confidentiality provisions.
Common Conflicts: Privacy vs. Public Access
The Privacy Act protects individual personal information from unauthorized disclosure, while the Sunshine Law mandates government transparency and public access to records and meetings. Common conflicts arise when sensitive personal data is embedded in public records, challenging officials to balance privacy rights with the public's right to know. Courts often weigh the necessity of disclosure against potential harm to privacy, applying exemptions to limit access without undermining government accountability.
Compliance Challenges for Organizations
Organizations face significant compliance challenges when navigating the Privacy Act and Sunshine Law due to their contrasting requirements; the Privacy Act emphasizes protecting personal information and limiting disclosure, while the Sunshine Law mandates transparency and public access to government records. Balancing these conflicting demands requires robust data management strategies, clear policies on information classification, and continuous employee training to avoid breaches and legal penalties. Implementing comprehensive compliance programs with regular audits and legal consultations helps organizations address the complexities of managing privacy and open records simultaneously.
Conclusion: Balancing Privacy and Transparency
The Privacy Act safeguards individuals' personal information by regulating government data collection and use, while the Sunshine Law promotes transparency by ensuring public access to government meetings and records. Effective governance requires a careful balance between respecting privacy rights and maintaining openness in public affairs. Striking this balance enhances public trust and accountability without compromising sensitive personal data.
Privacy Act Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com