Sanad represents reliability and trustworthiness in various contexts, often serving as a certificate or endorsement in Islamic scholarship and legal documents. Its usage ensures authenticity and preserves the credibility of information or transactions. Discover how Sanad can impact your understanding of historical and contemporary records in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
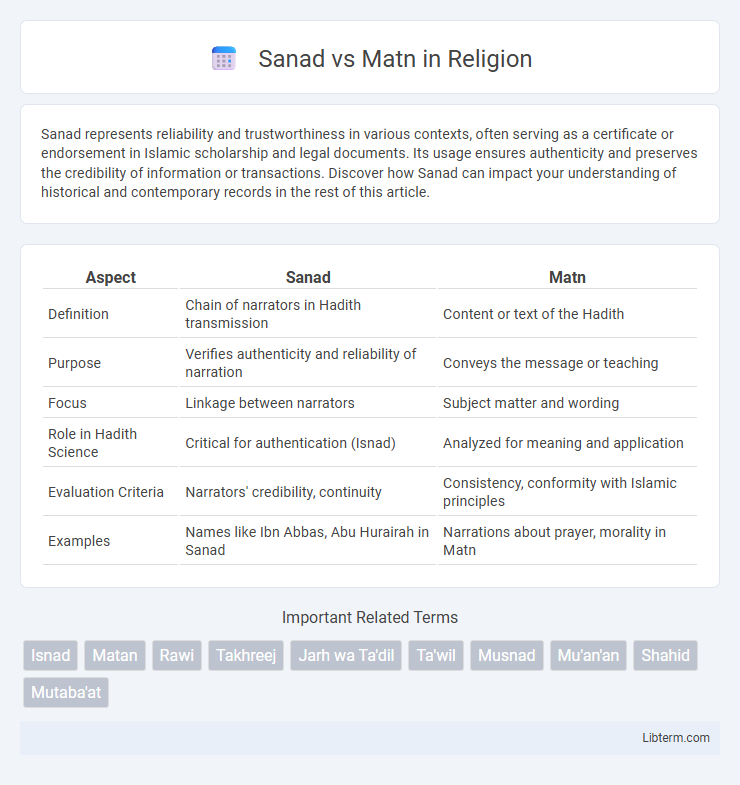
| Aspect | Sanad | Matn |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chain of narrators in Hadith transmission | Content or text of the Hadith |
| Purpose | Verifies authenticity and reliability of narration | Conveys the message or teaching |
| Focus | Linkage between narrators | Subject matter and wording |
| Role in Hadith Science | Critical for authentication (Isnad) | Analyzed for meaning and application |
| Evaluation Criteria | Narrators' credibility, continuity | Consistency, conformity with Islamic principles |
| Examples | Names like Ibn Abbas, Abu Hurairah in Sanad | Narrations about prayer, morality in Matn |
Introduction to Sanad and Matn
Sanad refers to the chain of narrators who transmit a hadith, ensuring the credibility and authenticity of the report, while Matn is the actual content or text of the hadith itself. The Sanad serves as a critical tool in Islamic scholarship for verifying the reliability of each narrator, thus preserving the integrity of prophetic traditions. Understanding the Sanad alongside the Matn enables scholars to critically assess the authenticity and interpret the meanings within the hadith accurately.
Defining Sanad: Chain of Narrators
Sanad refers to the chain of narrators transmitting a hadith, serving as a critical tool for verifying the authenticity and reliability of Islamic traditions. Each narrator in the sanad must meet strict criteria in terms of memory, integrity, and moral character to ensure the accuracy and preservation of the original message. Scholars rigorously examine the sanad to authenticate hadiths, distinguishing genuine reports from fabricated or weak ones.
Exploring Matn: The Text of Hadith
Matn refers to the actual text or content of a hadith, encompassing the words, actions, or tacit approvals of the Prophet Muhammad as recorded in Islamic tradition. Scholars analyze the matn to ensure its consistency with established theological principles, historical context, and linguistic authenticity to validate the hadith's message. This examination complements the sanad, or chain of narrators, by focusing on the substance and reliability of the text itself within the framework of hadith studies.
Historical Development of Sanad and Matn
The historical development of Sanad and Matn is rooted in early Islamic scholarship, where Sanad refers to the chain of narrators verifying the authenticity of a Hadith, and Matn denotes the actual text or content of the Hadith itself. Over the centuries, scholars meticulously analyzed Sanads to ensure reliable transmission, while critical examination of Matn helped identify textual consistency and authenticity. This dual focus shaped the foundations of Hadith sciences, influencing Islamic jurisprudence and historical documentation.
Importance of Sanad in Hadith Authentication
Sanad plays a critical role in Hadith authentication by providing a reliable chain of narrators that ensures the text's credibility and traceability to the Prophet Muhammad. The integrity and memory of each narrator in the sanad directly affect the hadith's authenticity, distinguishing sahih (authentic) hadiths from forged or weak ones. Scholars rigorously analyze the sanad to maintain the preservation of Islamic teachings and uphold the accuracy of prophetic traditions.
Role of Matn in Understanding Hadith Content
Matn is the core text of a hadith that conveys the Prophet Muhammad's sayings, actions, or approvals, making it essential for understanding the content and message of the narration. While Sanad verifies the chain of transmission, Matn provides the substantive guidance and legal rulings derived from the hadith. Scholars closely analyze Matn to interpret Islamic teachings accurately and assess the authenticity based on the coherence and consistency of its message.
Criteria for Evaluating Sanad
The criteria for evaluating Sanad in Islamic scholarship include the unbroken chain of narrators, the reliability and trustworthiness of each narrator, and the precise transmission of the narrated text without alteration. Scholars assess the narrator's memory, moral integrity, and consistency across different hadith reports to ensure authenticity. A strong Sanad must demonstrate continuity stemming from the Prophet Muhammad, enabling the Matn to be deemed credible and authoritative.
Methods for Analyzing Matn
Methods for analyzing Matn in Islamic jurisprudence include linguistic analysis, contextual examination, and thematic interpretation to evaluate the text's authenticity and coherence. Scholars assess grammar, vocabulary, and semantic consistency to detect anomalies or errors indicative of fabrication or alteration. Cross-referencing with reliable chains of transmission (Sanad) supports validation and aids in understanding legal and theological implications embedded within the Matn.
Common Issues in Differentiating Sanad and Matn
Common issues in differentiating Sanad and Matn often arise due to the overlapping content where both contain key textual elements. Sanad, the chain of narration, sometimes includes phrases or words that resemble the narrative style of Matn, causing ambiguity. Scholars frequently face challenges distinguishing the authoritative source of the Hadith text versus the reliability of its transmitters, leading to complexities in Hadith authentication.
Conclusion: The Interdependence of Sanad and Matn
Sanad and Matn are inseparable components of hadith, with Sanad ensuring the authenticity while Matn conveys the content. The reliability of the Sanad directly impacts the credibility of the Matn, emphasizing their mutual dependence in Islamic scholarship. Understanding hadith requires analyzing both chains of transmission and textual substance to preserve the integrity of prophetic teachings.
Sanad Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com