Fiqh, the Islamic jurisprudence, governs ethical and legal aspects of Muslim life, offering comprehensive guidance derived from the Quran and Hadith. It covers rituals, family matters, and commercial transactions, ensuring adherence to divine principles. Explore how Fiqh can shape your understanding and practice by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
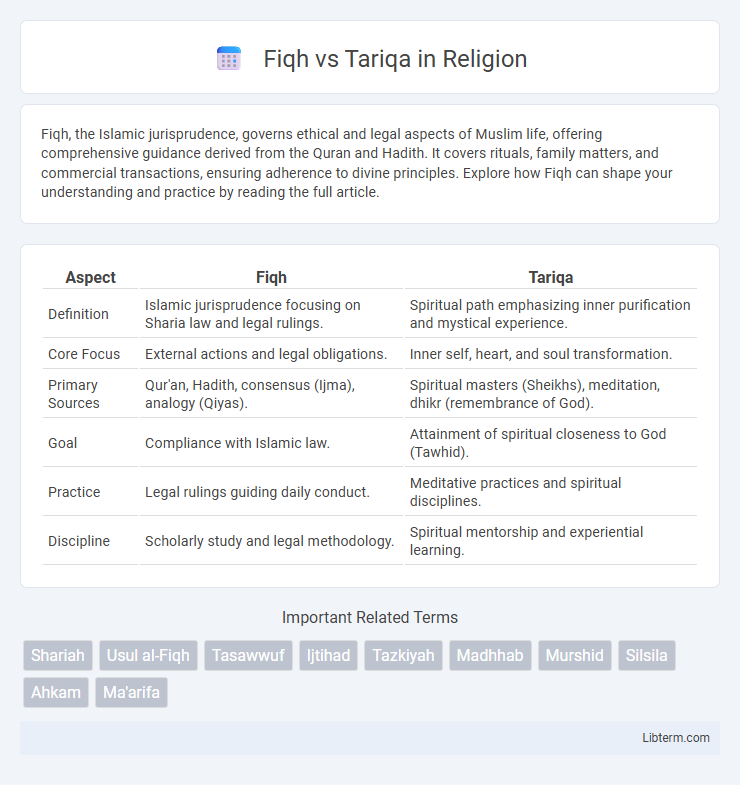
| Aspect | Fiqh | Tariqa |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Islamic jurisprudence focusing on Sharia law and legal rulings. | Spiritual path emphasizing inner purification and mystical experience. |
| Core Focus | External actions and legal obligations. | Inner self, heart, and soul transformation. |
| Primary Sources | Qur'an, Hadith, consensus (Ijma), analogy (Qiyas). | Spiritual masters (Sheikhs), meditation, dhikr (remembrance of God). |
| Goal | Compliance with Islamic law. | Attainment of spiritual closeness to God (Tawhid). |
| Practice | Legal rulings guiding daily conduct. | Meditative practices and spiritual disciplines. |
| Discipline | Scholarly study and legal methodology. | Spiritual mentorship and experiential learning. |
Introduction to Fiqh and Tariqa
Fiqh represents the Islamic jurisprudence focusing on the codified laws derived from the Quran, Hadith, Ijma, and Qiyas, guiding Muslims on legal and ethical conduct. Tariqa refers to the spiritual path in Sufism aimed at purifying the soul and achieving closeness to Allah through practices like dhikr, meditation, and guidance from a spiritual master. While Fiqh governs external religious obligations and social interactions, Tariqa emphasizes inner transformation and mystical experience in Islamic spirituality.
Defining Fiqh: Islamic Jurisprudence
Fiqh, Islamic jurisprudence, encompasses the comprehensive understanding and application of Sharia law through detailed rules and regulations derived from the Quran, Hadith, consensus (Ijma), and analogical reasoning (Qiyas). It defines Muslims' practical obligations in worship, transactions, and ethics, ensuring adherence to divine commandments. Unlike Tariqa, which focuses on spiritual purification and mystical practices, Fiqh provides a structured legal framework guiding daily life.
Understanding Tariqa: The Sufi Spiritual Path
Tariqa represents the inner, spiritual path of Sufism, emphasizing personal transformation and direct experience of the Divine beyond the formal Islamic law outlined in Fiqh. Rooted in mystical practices, Tariqas guide adherents through meditation, dhikr (remembrance), and spiritual mentorship to achieve closer union with God. While Fiqh governs external behaviors and religious obligations, Tariqa focuses on cultivating the heart's purity and divine love through esoteric knowledge and spiritual discipline.
Core Objectives: Law versus Spirituality
Fiqh centers on Islamic jurisprudence, providing a legal framework that governs rituals, social transactions, and ethical conduct based on the Quran and Hadith. Tariqa represents the spiritual path within Sufism, focusing on inner purification, mystical experience, and direct connection with the Divine through practices like dhikr and meditation. Both serve distinct core objectives: Fiqh establishes external law and order, while Tariqa emphasizes the cultivation of the soul and spiritual enlightenment.
Sources and Methodologies
Fiqh derives its principles primarily from the Quran, Hadith, Ijma (consensus), and Qiyas (analogical reasoning), employing a systematic jurisprudential methodology to interpret Islamic law. Tariqa emphasizes spiritual methods rooted in the teachings and practices of Sufi masters, relying heavily on direct experiential knowledge, spiritual exercises, and transmission (silsila) from a recognized spiritual lineage. While Fiqh focuses on external legal obligations through textual analysis, Tariqa centers on inner purification and mystical union using practices like dhikr and meditation.
Key Differences Between Fiqh and Tariqa
Fiqh centers on Islamic jurisprudence, detailing the legal rulings, rituals, and daily practices derived from the Quran and Hadith to govern a Muslim's outward conduct. Tariqa, in contrast, emphasizes the spiritual path within Sufism, focusing on inner purification, mystical experience, and closer union with God through esoteric practices and guidance from a Sufi master. While Fiqh addresses the external framework of Islamic law, Tariqa nurtures the inner spiritual journey, blending legal observance with deeper devotional insight.
Interrelationship and Harmony
Fiqh, the Islamic jurisprudence governing legal rulings, and Tariqa, the spiritual path focused on inner purification, complement each other in shaping a Muslim's holistic practice. Fiqh provides the external framework of rituals and obligations, while Tariqa cultivates the internal state of sincerity and divine love, ensuring that legal compliance is imbued with spiritual depth. The interrelationship between Fiqh and Tariqa fosters harmony by balancing adherence to Shariah with the transformative experience of spiritual awakening.
Misconceptions and Conflicts
Fiqh, the Islamic jurisprudence, governs practical religious obligations, while Tariqa represents the spiritual path towards inner purification and closeness to God. Misconceptions arise when Tariqa practices are mistakenly viewed as deviations from the Shariah, causing conflicts between legal scholars and Sufi practitioners. Clarifying that Fiqh provides the external framework and Tariqa nurtures the internal spiritual experience helps resolve tensions and highlights their complementary roles in Islamic tradition.
Contemporary Relevance
Fiqh, the Islamic jurisprudence guiding daily rituals and legal matters, remains essential for contemporary Muslims seeking structured religious practice. Tariqa, representing the spiritual path and mystical experience within Sufism, addresses modern spiritual needs by fostering inner purification and direct divine connection. Both frameworks offer complementary approaches, with Fiqh ensuring communal order and Tariqa enhancing personal spiritual fulfillment in today's complex world.
Conclusion: Integrating Fiqh and Tariqa
Integrating Fiqh and Tariqa creates a balanced approach to Islamic practice by combining legal rigor with spiritual depth. Fiqh provides the necessary framework of Shariah law, while Tariqa fosters inner transformation and closeness to Allah through mystical disciplines. Together, they empower believers to fulfill religious obligations while cultivating a sincere, experiential connection to faith.
Fiqh Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com