An allele is one of the different forms of a gene found at the same place on a chromosome, influencing specific traits in an organism. These genetic variations contribute to the diversity of traits such as eye color, blood type, and susceptibility to certain diseases. Explore the rest of the article to understand how alleles impact your genetic makeup and inheritance.
Table of Comparison
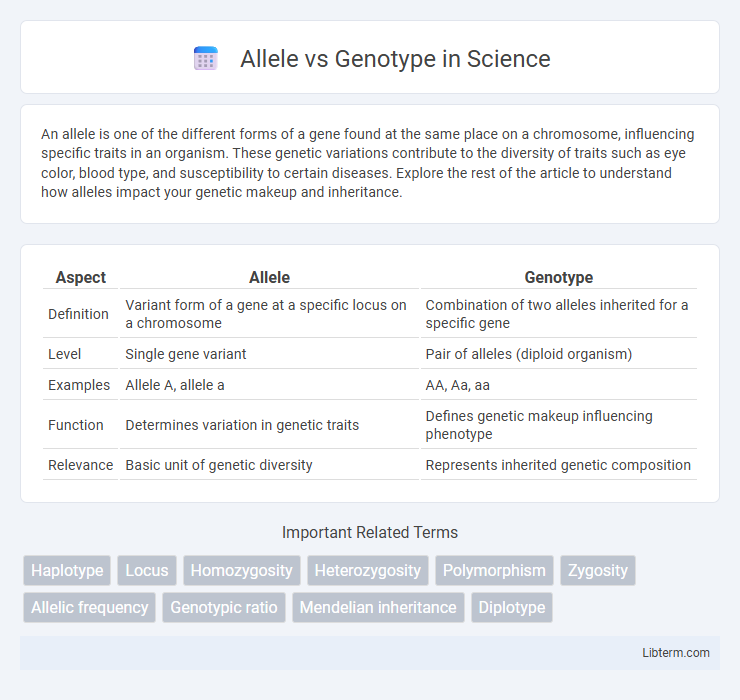
| Aspect | Allele | Genotype |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Variant form of a gene at a specific locus on a chromosome | Combination of two alleles inherited for a specific gene |
| Level | Single gene variant | Pair of alleles (diploid organism) |
| Examples | Allele A, allele a | AA, Aa, aa |
| Function | Determines variation in genetic traits | Defines genetic makeup influencing phenotype |
| Relevance | Basic unit of genetic diversity | Represents inherited genetic composition |
Understanding Alleles: Basic Definitions
Alleles are different forms of a gene found at the same locus on a chromosome, determining specific traits in an organism. A genotype refers to the combination of alleles inherited from both parents, representing the genetic makeup for a particular trait. Understanding alleles provides insight into how variations in gene sequences contribute to phenotypic diversity and hereditary patterns.
What is a Genotype?
A genotype refers to the specific combination of alleles inherited from both parents that determines an organism's genetic makeup for a particular trait. It represents the pair of alleles at a given gene locus, such as AA, Aa, or aa, influencing the organism's phenotype. Understanding genotypes is essential in genetics for predicting trait inheritance, studying genetic variation, and conducting molecular biology research.
Key Differences Between Allele and Genotype
An allele is a specific variant of a gene located at a particular position on a chromosome, representing different forms that a gene can take. A genotype refers to the complete set of alleles an organism possesses for one or multiple genes, determining its genetic makeup and inherited traits. While alleles are individual gene variants, genotypes encompass the combination of alleles that influence phenotypic expression and hereditary characteristics.
The Role of Alleles in Genetic Variation
Alleles are different forms of a gene that contribute to genetic variation by providing diverse traits within a population. Each genotype is composed of two alleles, inherited from each parent, that determine specific phenotypic expressions. The combination and interaction of alleles lead to unique genetic profiles, driving evolution and adaptation through natural selection.
How Genotypes Shape Organisms
Genotypes, composed of specific combinations of alleles inherited from both parents, directly influence the physical and biochemical traits of organisms by dictating protein synthesis and cellular functions. The interaction between dominant and recessive alleles within the genotype determines observable characteristics, from eye color to susceptibility to genetic disorders. Complex traits often result from polygenic inheritance, where multiple gene loci contribute additive or epistatic effects shaping an organism's phenotype.
Homozygous vs Heterozygous Alleles
A homozygous genotype consists of two identical alleles for a specific gene, either both dominant or both recessive, while a heterozygous genotype contains two different alleles, one dominant and one recessive. The expression of traits depends on whether the alleles are homozygous or heterozygous, affecting phenotypic variation within populations. Understanding homozygous versus heterozygous alleles is crucial for predicting inheritance patterns and genetic diversity.
Alleles in Mendelian Genetics
Alleles are different versions of a gene located at the same position (locus) on homologous chromosomes, responsible for variations in inherited traits. In Mendelian genetics, dominant and recessive alleles determine phenotype expression, where dominant alleles mask the effect of recessive ones in heterozygotes. Understanding allele interactions and segregation patterns is crucial for predicting genotypic and phenotypic ratios in offspring according to Mendel's laws.
Genotype-Phenotype Relationships
Genotype-phenotype relationships are determined by the specific alleles an organism inherits and how these alleles interact to produce observable traits. The genotype consists of the full set of alleles at particular gene loci, while the phenotype is the expressed physical or biochemical characteristic influenced by these alleles and environmental factors. Understanding the interaction between dominant, recessive, and co-dominant alleles within the genotype is crucial for predicting phenotypic outcomes and inheritance patterns.
Real-World Examples: Allele and Genotype Explained
An allele represents one of the variant forms of a gene found at a specific locus on a chromosome, while a genotype refers to the complete set of alleles an organism carries for a particular gene. For example, in Mendelian genetics, the eye color gene may have alleles for blue or brown eyes, with a genotype such as Bb indicating heterozygosity. Real-world applications include genetic testing for diseases like cystic fibrosis, where identifying specific alleles within a genotype helps predict disease risk and guide personalized treatment.
Importance of Allele and Genotype in Genetic Studies
Alleles represent different versions of a gene that contribute to genetic diversity and influence phenotypic traits. Understanding the genotype, which is the combination of alleles an organism possesses, allows researchers to predict inheritance patterns and identify genetic disorders. Both alleles and genotypes are crucial in mapping gene functions, studying population genetics, and advancing personalized medicine.
Allele Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com