Theory provides a structured framework for understanding complex concepts and phenomena, offering insights that guide practical application and innovation. It helps you analyze patterns, predict outcomes, and develop new ideas by connecting abstract principles to real-world experiences. Explore the rest of the article to see how theory shapes advances across various fields and impacts your daily decisions.
Table of Comparison
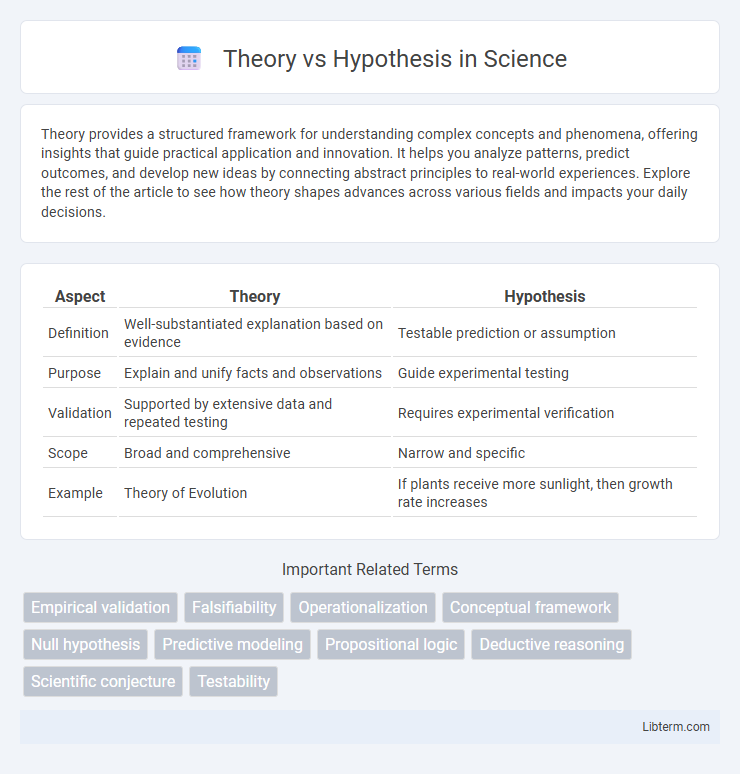
| Aspect | Theory | Hypothesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Well-substantiated explanation based on evidence | Testable prediction or assumption |
| Purpose | Explain and unify facts and observations | Guide experimental testing |
| Validation | Supported by extensive data and repeated testing | Requires experimental verification |
| Scope | Broad and comprehensive | Narrow and specific |
| Example | Theory of Evolution | If plants receive more sunlight, then growth rate increases |
Introduction to Theory and Hypothesis
A theory is a well-substantiated explanation of natural phenomena based on a body of evidence, providing a coherent framework for understanding observations. A hypothesis is a testable prediction or proposed explanation that can be empirically evaluated through experiments and data collection. The distinction lies in the scope and validation: theories integrate and explain multiple hypotheses and observations, while hypotheses serve as initial, specific claims subject to testing.
Defining a Theory
A theory is a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world, based on a body of evidence that has been repeatedly confirmed through observation and experimentation. Unlike a hypothesis, which is a tentative prediction or testable statement, a theory integrates and explains multiple hypotheses and empirical findings. Theories provide comprehensive frameworks that guide scientific inquiry and predict future phenomena.
Defining a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a precise, testable statement predicting the outcome of a specific experiment or observation, serving as the foundation for scientific investigation. It offers a provisional explanation based on limited evidence, guiding the collection and analysis of data. In contrast to theories, hypotheses are narrower in scope and require empirical testing to be either supported or refuted.
Key Differences Between Theory and Hypothesis
The key differences between theory and hypothesis lie in their scope and validation; a hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction about a phenomenon, while a theory is a well-substantiated explanation backed by extensive evidence and repeated testing. Hypotheses serve as the starting point for scientific investigation, guiding experiments and observations to either support or refute them. Theories synthesize and interpret broader sets of data, providing a comprehensive framework for understanding complex scientific principles.
The Role of Evidence in Theories and Hypotheses
Theories synthesize a broad range of evidence, providing comprehensive explanations supported by repeated testing and empirical validation. Hypotheses function as specific, testable predictions that require rigorous experimentation to gather evidence for confirmation or refutation. The role of evidence is crucial in transforming hypotheses into theories by systematically accumulating data that supports consistent, reliable conclusions across diverse observations.
Development Process: From Hypothesis to Theory
The development process from hypothesis to theory involves formulating a testable prediction based on observations and conducting rigorous experiments to validate or refute it. Repeated testing and accumulation of supporting evidence refine the hypothesis, often leading to its expansion or adjustment. Once a hypothesis consistently withstands scrutiny and integrates a wide range of phenomena, it evolves into a well-substantiated scientific theory.
Practical Examples of Theories and Hypotheses
A theory, such as the Theory of Evolution, explains broad patterns in biological diversity based on extensive evidence from multiple studies. A hypothesis, like predicting that a specific pesticide will reduce insect populations in a garden, offers a testable statement that can be confirmed or refuted through experimentation. Practical examples show theories provide comprehensive frameworks, while hypotheses guide targeted investigations within those frameworks.
Importance in Scientific Research
A theory provides a well-substantiated explanation of natural phenomena based on extensive evidence, guiding scientific understanding and prediction. A hypothesis serves as a testable, provisional statement that can be empirically investigated to support or refute a theory. Both are crucial in scientific research: theories offer comprehensive frameworks while hypotheses drive experimentation and data collection to advance knowledge.
Common Misunderstandings
A common misunderstanding is that theories and hypotheses are interchangeable, but a theory is a well-substantiated explanation backed by extensive evidence, while a hypothesis is a testable prediction or proposed explanation for a specific phenomenon. Many mistakenly believe a hypothesis becomes a theory after proving correct, yet theories arise from repeated testing and validation of multiple hypotheses. Confusing these terms can undermine the scientific process and the weight of empirical evidence supporting established scientific knowledge.
Conclusion and Summary
A hypothesis is a testable prediction derived from observations, serving as the starting point for scientific investigation, whereas a theory is a comprehensive explanation supported by extensive evidence and experimentation. Conclusions drawn from hypotheses guide further testing and refinement, while theories represent well-substantiated frameworks that summarize and interpret a wide range of data. Summarizing scientific knowledge, theories provide robust explanations, whereas hypotheses remain provisional and subject to validation.
Theory Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com