Taxonomy is the scientific practice of classifying organisms into hierarchical groups based on shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships. This system provides a structured framework that helps scientists organize biological diversity and understand the connections between different species. Discover more about how taxonomy shapes our understanding of the natural world in the following article.
Table of Comparison
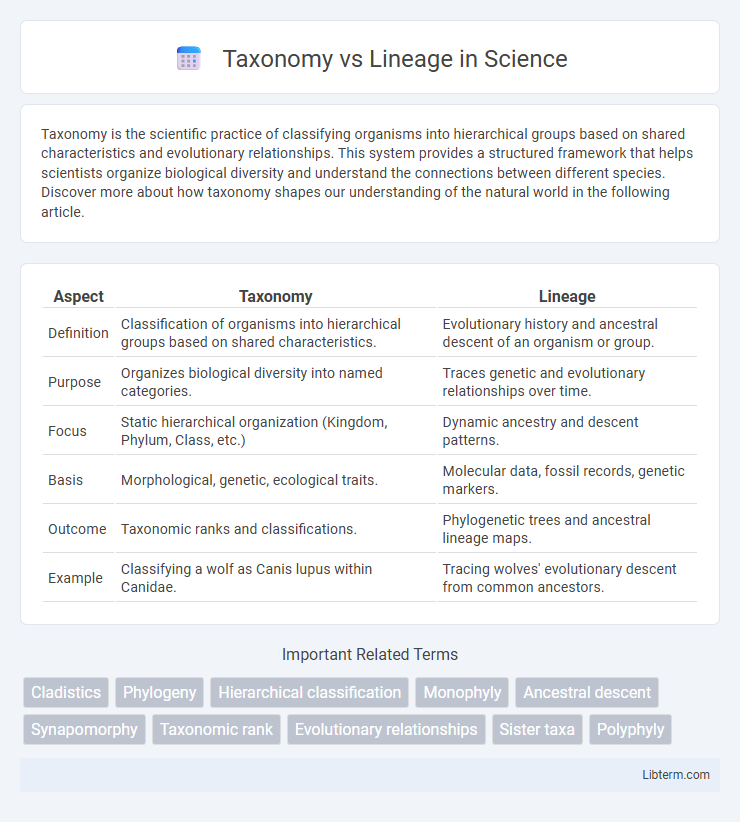
| Aspect | Taxonomy | Lineage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Classification of organisms into hierarchical groups based on shared characteristics. | Evolutionary history and ancestral descent of an organism or group. |
| Purpose | Organizes biological diversity into named categories. | Traces genetic and evolutionary relationships over time. |
| Focus | Static hierarchical organization (Kingdom, Phylum, Class, etc.) | Dynamic ancestry and descent patterns. |
| Basis | Morphological, genetic, ecological traits. | Molecular data, fossil records, genetic markers. |
| Outcome | Taxonomic ranks and classifications. | Phylogenetic trees and ancestral lineage maps. |
| Example | Classifying a wolf as Canis lupus within Canidae. | Tracing wolves' evolutionary descent from common ancestors. |
Understanding Taxonomy: Definition and Purpose
Taxonomy organizes data by categorizing entities into a hierarchical structure based on their characteristics, enabling easier classification and retrieval. It serves the primary purpose of creating a systematic framework that simplifies data management and enhances searchability. Understanding taxonomy is essential for effective data organization, as it ensures consistent labeling and grouping within complex datasets.
What is Lineage in Biological Classification?
Lineage in biological classification refers to the direct descent or evolutionary line connecting ancestors and descendants within a group of organisms. It traces the genetic heritage and evolutionary history, illustrating how species or taxa evolve over time from common ancestors. This concept is crucial for understanding phylogenetic relationships, distinguishing it from taxonomy, which focuses more broadly on the classification and naming of organisms.
Key Differences Between Taxonomy and Lineage
Taxonomy organizes data into hierarchical classifications based on shared characteristics, enabling structured categorization and easy retrieval. Lineage traces the data's origin and transformation history, providing a detailed record of its journey through systems and processes. The key difference lies in taxonomy's focus on categorization and lineage's emphasis on data provenance and lifecycle tracking.
Historical Evolution of Taxonomy and Lineage Concepts
Taxonomy, rooted in the work of Carl Linnaeus in the 18th century, originally focused on hierarchical classification based on observable traits, establishing a structured system for naming and categorizing organisms. Lineage concepts evolved with advancements in evolutionary biology and molecular genetics, emphasizing ancestral relationships and genetic descent to trace the phylogenetic history of species. The historical evolution from classical taxonomy to lineage-based approaches reflects a shift from static classification to dynamic evolutionary perspectives in biological sciences.
The Role of Taxonomy in Modern Science
Taxonomy plays a crucial role in modern science by providing a structured classification system that organizes and categorizes living organisms based on shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships. This hierarchical framework enables precise communication, data analysis, and biodiversity conservation by facilitating the identification and comparison of species. Unlike lineage, which traces the direct ancestry and genetic descent of organisms, taxonomy emphasizes grouping organisms to reflect overall similarities and natural relationships within the tree of life.
How Lineage Traces Evolutionary Relationships
Lineage traces evolutionary relationships by mapping the direct descent of species through ancestral connections, revealing how traits and genetic material are inherited over generations. Unlike taxonomy, which classifies organisms based on shared characteristics into hierarchical groups, lineage emphasizes the chronological sequence of descent and evolutionary divergence. This approach allows scientists to reconstruct phylogenetic trees that illustrate the pathways of evolution and speciation events.
Practical Applications: Taxonomy vs Lineage
Taxonomy organizes data by categorizing entities into hierarchical groups based on shared characteristics, enabling efficient information retrieval and structured data management in practical applications like content management and e-commerce. Lineage tracks the origin and movement of data through its lifecycle, crucial for data governance, compliance, and impact analysis in industries such as finance and healthcare. Combining taxonomy and lineage enhances data quality and decision-making by providing both structured classification and transparent data provenance.
Challenges in Defining Taxonomy and Lineage
Defining taxonomy poses challenges due to the dynamic nature of classification criteria, where evolving data and perspectives complicate the establishment of fixed hierarchies. Lineage tracking faces difficulties related to incomplete or inconsistent historical records, making it hard to accurately trace origins and relationships over time. Both taxonomy and lineage require continuous validation and updates to maintain relevance amid expanding datasets and shifting scientific understanding.
Future Trends in Biological Classification Systems
Future trends in biological classification systems emphasize integrating taxonomy with genetic lineage data to enhance species identification accuracy and evolutionary understanding. Advances in genomics and bioinformatics enable dynamic, data-driven taxonomies that reflect real-time phylogenetic relationships and organismal diversity. Machine learning algorithms and large-scale DNA sequencing projects are transforming traditional hierarchical classifications into more nuanced, lineage-based models for precise biological categorization.
Choosing Between Taxonomy and Lineage Approaches
Choosing between taxonomy and lineage approaches depends on the specific data management goals and use cases. Taxonomy provides a hierarchical classification system ideal for organizing data into well-defined categories, improving searchability and data governance. Lineage focuses on tracking the data's origin, transformations, and movement across systems, which is crucial for ensuring data quality, compliance, and impact analysis.
Taxonomy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com