The biosphere encompasses all living organisms and their interactions within Earth's atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere. Understanding the delicate balance of ecosystems and the impact of human activities on this global life-support system is crucial for environmental sustainability. Explore the rest of the article to learn how your actions influence the biosphere and what steps you can take to protect it.
Table of Comparison
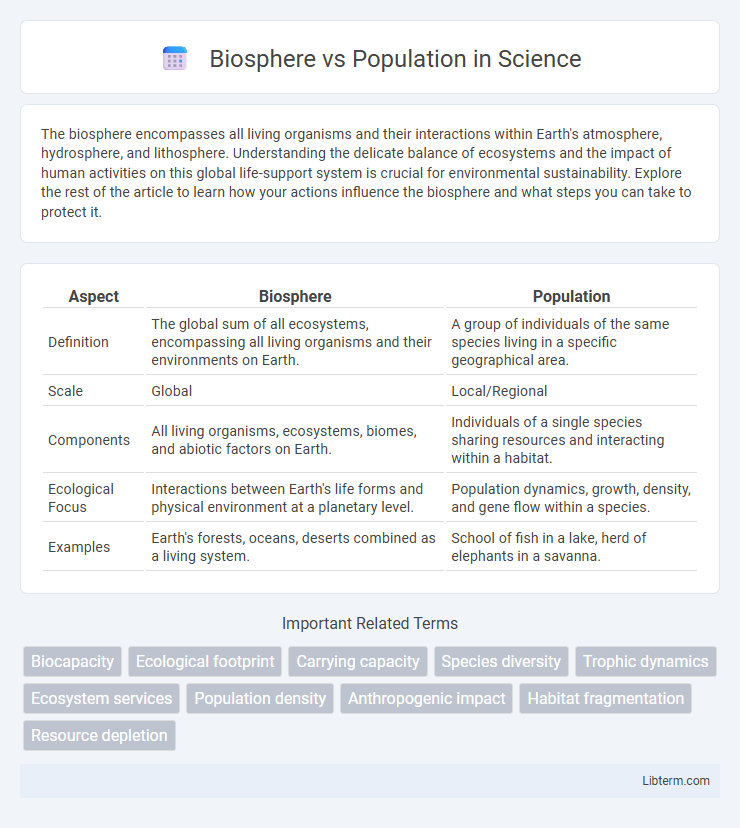
| Aspect | Biosphere | Population |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The global sum of all ecosystems, encompassing all living organisms and their environments on Earth. | A group of individuals of the same species living in a specific geographical area. |
| Scale | Global | Local/Regional |
| Components | All living organisms, ecosystems, biomes, and abiotic factors on Earth. | Individuals of a single species sharing resources and interacting within a habitat. |
| Ecological Focus | Interactions between Earth's life forms and physical environment at a planetary level. | Population dynamics, growth, density, and gene flow within a species. |
| Examples | Earth's forests, oceans, deserts combined as a living system. | School of fish in a lake, herd of elephants in a savanna. |
Introduction to the Biosphere and Population
The biosphere encompasses all ecosystems on Earth, including land, water, and atmosphere, where living organisms interact with their physical environment. Population refers to a group of individuals of the same species living in a specific area, whose dynamics influence ecological balance. Understanding the biosphere and population interactions is crucial for studying biodiversity, resource management, and environmental sustainability.
Defining the Biosphere: Structure and Function
The biosphere encompasses all ecosystems on Earth, integrating the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere to support diverse life forms and their interactions. It functions as a global ecological system where energy flows and biogeochemical cycles sustain organism populations and communities. Understanding the biosphere's structure involves examining its layered complexity and dynamic processes that regulate environmental stability and biodiversity.
Population Dynamics: Growth, Density, and Distribution
Population dynamics involve the study of how populations grow, change in density, and distribute across ecosystems within the biosphere. Growth rates depend on birth, death, immigration, and emigration patterns, influencing population size over time. Density and distribution are affected by resource availability, habitat conditions, and interspecies interactions, shaping the spatial arrangement of populations in different biosphere regions.
Human Impact on the Biosphere
Human activity significantly alters the biosphere by reducing biodiversity through habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. Population growth intensifies resource consumption and waste production, exacerbating environmental degradation and straining ecosystems. Sustainable development and conservation efforts are critical to mitigating the adverse effects of human impact on the global biosphere.
Population Growth and Resource Consumption
Population growth directly impacts resource consumption within the biosphere, increasing demand for food, water, and energy. Rapidly expanding populations accelerate habitat loss, depletion of renewable resources, and environmental degradation. Sustainable management of resources is critical to balance population pressures and preserve biosphere integrity.
Urbanization and Biodiversity Loss
Urbanization drives significant biodiversity loss by transforming natural habitats within the biosphere into urban areas, disrupting ecosystems and diminishing species diversity. The expansion of human populations in cities increases resource consumption and pollution, exacerbating habitat fragmentation and threatening flora and fauna. Protecting biodiversity requires sustainable urban planning and preserving green spaces to maintain ecological balance amidst growing urban populations.
Carrying Capacity of the Biosphere
The carrying capacity of the biosphere represents the maximum population size of a species that the Earth's ecosystems can sustainably support, given the availability of resources such as food, water, and habitat. When a population exceeds this capacity, resource depletion, habitat degradation, and increased competition lead to environmental stress and potential population decline. Understanding the biosphere's carrying capacity is crucial for managing population growth and maintaining ecological balance.
Sustainable Population Management
Sustainable population management balances the human population size with the biosphere's carrying capacity, ensuring resource availability and ecosystem health are maintained. Overpopulation strains natural systems, leading to biodiversity loss, habitat degradation, and increased carbon emissions. Strategies such as family planning, education, and resource-efficient technologies promote long-term equilibrium between population growth and environmental sustainability.
Strategies for Balancing Population and Ecosystem Health
Sustainable land use planning and conservation policies are essential strategies for balancing biosphere health and population growth. Integrating ecosystem services valuation into development decisions helps maintain biodiversity while supporting human needs. Promoting education on resource efficiency and family planning reduces environmental stress and fosters long-term ecological resilience.
Future Challenges and Solutions for Biosphere-Population Balance
Future challenges for maintaining a biosphere-population balance include resource depletion, habitat loss, and climate change impacts exacerbated by increasing human populations. Solutions involve implementing sustainable development practices, advancing renewable energy adoption, and promoting conservation efforts to preserve biodiversity. Integrating population control measures with environmental policies can help ensure ecosystem resilience and long-term planetary health.
Biosphere Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com