Experience vivid imagery and detailed portrayals that bring every scene to life, enhancing your understanding and connection to the subject. Descriptive writing paints a mental picture through sensory details, making information more engaging and memorable. Dive into the rest of the article to discover how powerful descriptive techniques can transform your communication.
Table of Comparison
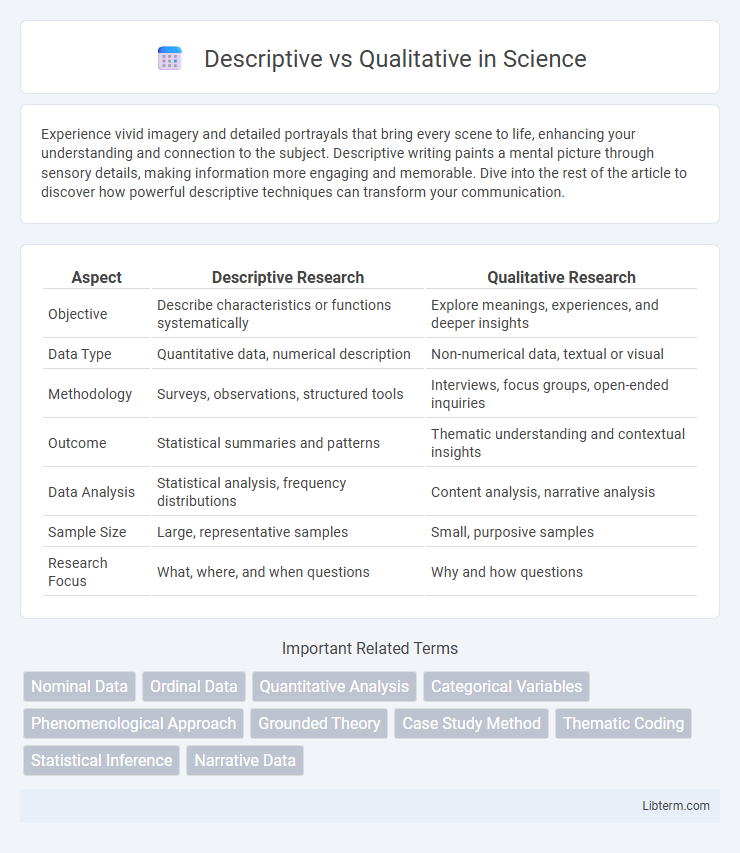
| Aspect | Descriptive Research | Qualitative Research |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Describe characteristics or functions systematically | Explore meanings, experiences, and deeper insights |
| Data Type | Quantitative data, numerical description | Non-numerical data, textual or visual |
| Methodology | Surveys, observations, structured tools | Interviews, focus groups, open-ended inquiries |
| Outcome | Statistical summaries and patterns | Thematic understanding and contextual insights |
| Data Analysis | Statistical analysis, frequency distributions | Content analysis, narrative analysis |
| Sample Size | Large, representative samples | Small, purposive samples |
| Research Focus | What, where, and when questions | Why and how questions |
Introduction to Descriptive and Qualitative Approaches
Descriptive approaches in research focus on accurately portraying characteristics, behaviors, or functions of a specific population or phenomenon using structured methods such as surveys and observational tools. Qualitative approaches emphasize understanding the deeper meanings, experiences, and social contexts through methods like interviews, focus groups, and thematic analysis. Both approaches serve distinct purposes: descriptive methods quantify and summarize data, while qualitative methods explore underlying motivations and perceptions.
Key Definitions: Descriptive vs Qualitative Research
Descriptive research involves systematically describing characteristics or functions of a specific population or phenomenon, focusing on quantifiable data and statistical analysis to provide an accurate snapshot. Qualitative research explores underlying reasons, meanings, and motivations through non-numerical data such as interviews, observations, and text analysis, emphasizing depth and context. While descriptive research answers "what" questions with structured data, qualitative research addresses "why" and "how" through interpretive methods.
Purpose and Scope of Descriptive Research
Descriptive research aims to systematically describe characteristics or functions of a specific population or phenomenon, focusing on "what" rather than "why." Its purpose is to provide an accurate portrayal of variables, events, or conditions within a defined scope, often using quantitative data for measurement and analysis. The scope of descriptive research includes surveys, observational methods, and case studies that generate statistical summaries to inform hypotheses or further qualitative exploration.
Purpose and Scope of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research aims to explore complex phenomena by understanding participants' perspectives, behaviors, and social contexts, providing rich, detailed insights that descriptive research cannot capture. Its purpose is to uncover underlying meanings, patterns, and motivations through open-ended data collection methods such as interviews, focus groups, and observations. Unlike descriptive research that quantifies and summarizes data with statistical methods, qualitative research offers depth and context, making it essential for theory development and exploring new or ambiguous topics.
Data Collection Methods: Descriptive vs Qualitative
Descriptive data collection methods primarily involve structured techniques such as surveys, questionnaires, and observational checklists to quantify variables and capture measurable information. Qualitative data collection emphasizes unstructured or semi-structured approaches like interviews, focus groups, and ethnographic observations to explore participants' experiences and underlying meanings. Both methods are essential for research, with descriptive methods providing statistical clarity and qualitative methods offering deep contextual insights.
Data Analysis Techniques: Comparing Approaches
Descriptive data analysis techniques primarily involve summarizing and quantifying data using statistical measures such as mean, median, mode, and frequency distribution to provide a clear overview of data patterns. Qualitative data analysis employs thematic coding, content analysis, and narrative examination to interpret subjective information and uncover underlying meanings and patterns. Comparing these approaches highlights that descriptive analysis focuses on numerical data representation, while qualitative analysis explores deeper contextual insights and experiences.
Strengths of Descriptive Research
Descriptive research excels in providing a detailed and systematic account of characteristics, behaviors, and phenomena, making it ideal for establishing clear patterns and trends within a population. Its strength lies in quantifying variables and enabling statistical analysis, which supports generalizability and objective conclusions. This research type effectively captures large sample sizes, enhancing reliability and providing a strong foundation for further hypothesis-driven studies.
Strengths of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research excels in exploring complex phenomena through in-depth understanding of participants' experiences, emotions, and social contexts, which is less accessible through descriptive methods. It provides rich, detailed data that captures the nuances and meanings behind behaviors, attitudes, and interactions. This approach is particularly valuable for generating theories, identifying patterns, and gaining insights where quantitative measures fall short.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Method
Descriptive research faces limitations such as inability to establish causality and potential bias from self-reported data, restricting its use in explaining relationships between variables. Qualitative research challenges include subjectivity in data interpretation and difficulties in generalizing findings due to small, non-random samples. Both methods require careful consideration of context and researcher influence to mitigate validity and reliability concerns.
Choosing Between Descriptive and Qualitative Research
Choosing between descriptive and qualitative research depends on the study's goals and data needs. Descriptive research quantifies characteristics or phenomena, providing statistical analysis of variables such as frequency, averages, or percentages. Qualitative research explores underlying meanings, experiences, and patterns through methods like interviews or observations, ideal for in-depth insights when numerical data cannot capture complexity.
Descriptive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com