Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms, which results in distinct physical and chemical properties. Understanding isomers is crucial for fields such as chemistry and pharmaceuticals since their unique structures influence how substances behave and interact. Explore the rest of the article to discover the various types of isomers and their significant roles.
Table of Comparison
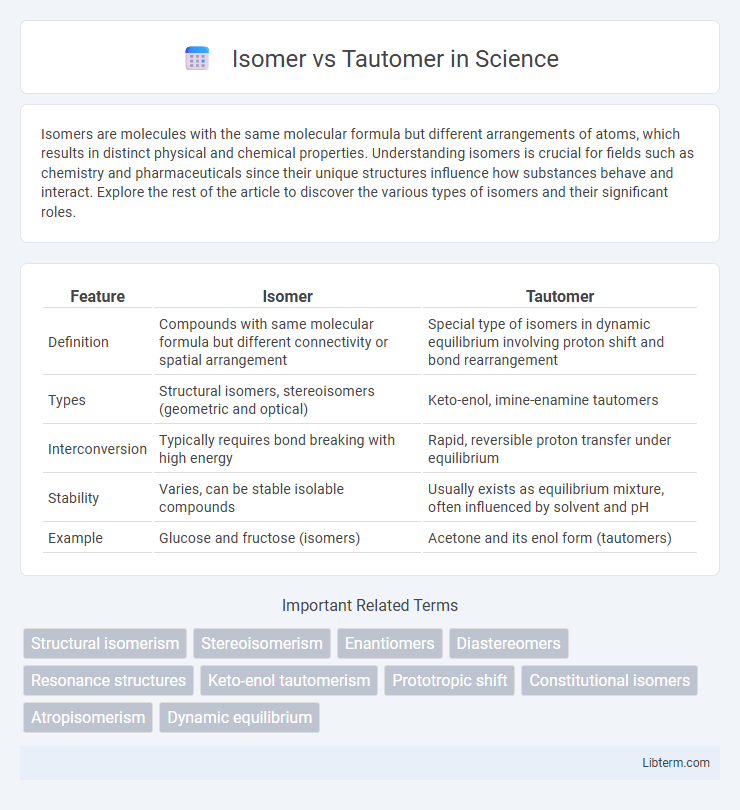
| Feature | Isomer | Tautomer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Compounds with same molecular formula but different connectivity or spatial arrangement | Special type of isomers in dynamic equilibrium involving proton shift and bond rearrangement |
| Types | Structural isomers, stereoisomers (geometric and optical) | Keto-enol, imine-enamine tautomers |
| Interconversion | Typically requires bond breaking with high energy | Rapid, reversible proton transfer under equilibrium |
| Stability | Varies, can be stable isolable compounds | Usually exists as equilibrium mixture, often influenced by solvent and pH |
| Example | Glucose and fructose (isomers) | Acetone and its enol form (tautomers) |
Introduction to Isomers and Tautomers
Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements, leading to distinct physical and chemical properties. Tautomers are a specific subset of isomers that rapidly interconvert through chemical reactions, usually involving the relocation of a proton and a shift in bonding electrons, such as keto-enol tautomerism. Understanding the differences between isomers and tautomers is crucial for interpreting molecular behavior and reactivity in organic chemistry.
Definition of Isomers
Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements or spatial orientations of atoms, resulting in distinct chemical properties. This broad category includes structural isomers, which differ in connectivity, and stereoisomers, which differ in spatial configuration. Tautomers are a specific subset of isomers that readily interconvert through the relocation of a proton and a double bond, highlighting dynamic equilibrium between two forms.
Definition of Tautomers
Tautomers are specific types of isomers that differ by the position of a proton and the double bond within a molecule, typically existing in dynamic equilibrium. Unlike general isomers, tautomers rapidly interconvert, resulting in unique chemical properties and biological activities. Understanding tautomerism is crucial in fields such as drug design and organic synthesis due to its impact on molecular stability and reactivity.
Key Differences Between Isomers and Tautomers
Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural or spatial arrangements, classified into structural isomers and stereoisomers. Tautomers are a specific type of isomer that exist in dynamic equilibrium, differing primarily by the relocation of a proton and a double bond, as seen in keto-enol tautomerism. The key difference lies in tautomers interconverting rapidly under certain conditions, whereas isomers typically represent distinct, stable forms without such equilibrium.
Types of Isomerism
Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements, categorized primarily into structural (or constitutional) isomers and stereoisomers. Structural isomers differ in the connectivity of atoms, including chain isomerism, position isomerism, and functional group isomerism, while stereoisomers have the same connectivity but differ in spatial orientation, such as enantiomers and diastereomers. Tautomers, a special type of isomer, exist in equilibrium and involve the relocation of a proton and a shift of double bonds, exemplified by keto-enol tautomerism, which is critical in biochemical processes.
Types of Tautomerism
Tautomerism involves the rapid interconversion between two structural isomers, typically differing by the placement of a proton and a double bond, with keto-enol and lactam-lactim being common types. Isomers refer broadly to compounds sharing the same molecular formula but differing in connectivity or spatial arrangement, encompassing structural, geometric, and stereoisomers beyond tautomeric forms. Understanding keto-enol tautomerism is critical in organic chemistry, as it influences compound stability, reactivity, and biological activity, distinguishing it from static isomerism where no dynamic equilibrium exists.
Structural Features of Isomers vs Tautomers
Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements, including positional, geometric, and stereoisomers, characterized by stable and distinct connectivity of atoms. Tautomers are a specific type of isomer that exist in dynamic equilibrium, differing mainly by the position of a proton and a double bond, commonly seen in keto-enol tautomerism. The key structural feature of tautomers is their ability to rapidly interconvert, making their structures less stable and more flexible compared to the fixed, discrete structures of conventional isomers.
Mechanisms of Isomerization and Tautomerization
Isomerization involves the rearrangement of atoms within a molecule to form isomers with different connectivity or spatial orientation, commonly through bond rotations or shifts without breaking the molecular framework. Tautomerization specifically refers to a rapid, reversible chemical reaction where a proton relocates along with a change in the position of double bonds, typically between keto and enol forms, facilitated by acid or base catalysis. The mechanism of tautomerization requires proton transfer and electron delocalization, distinguishing it from general isomerization processes that may not involve proton shifts or equilibrium states.
Applications in Chemistry and Industry
Isomers and tautomers play crucial roles in chemistry and industry by influencing molecular behavior and reactivity. Isomers, with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements, are fundamental in pharmaceuticals for drug design and optimizing therapeutic effects. Tautomers, which rapidly interconvert through proton shifts, are essential in biochemical processes and are exploited in agrochemical development and material science for controlling stability and function.
Summary: Choosing Between Isomer and Tautomer Concepts
Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements, impacting physical and chemical properties, while tautomers are specific isomers that interconvert through proton shifts, usually involving keto-enol forms. Choosing between isomer and tautomer concepts depends on whether the focus is on static structural differences or dynamic equilibrium states in chemical behavior. Understanding this distinction aids in accurate interpretation of molecular behavior in fields like organic chemistry and pharmaceutical development.
Isomer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com