Stereotype threat occurs when individuals fear confirming negative stereotypes about their social group, which can impair performance and increase stress. Understanding how this psychological phenomenon affects your behavior is crucial for creating supportive environments that foster success. Explore the rest of this article to learn effective strategies for overcoming stereotype threat.
Table of Comparison
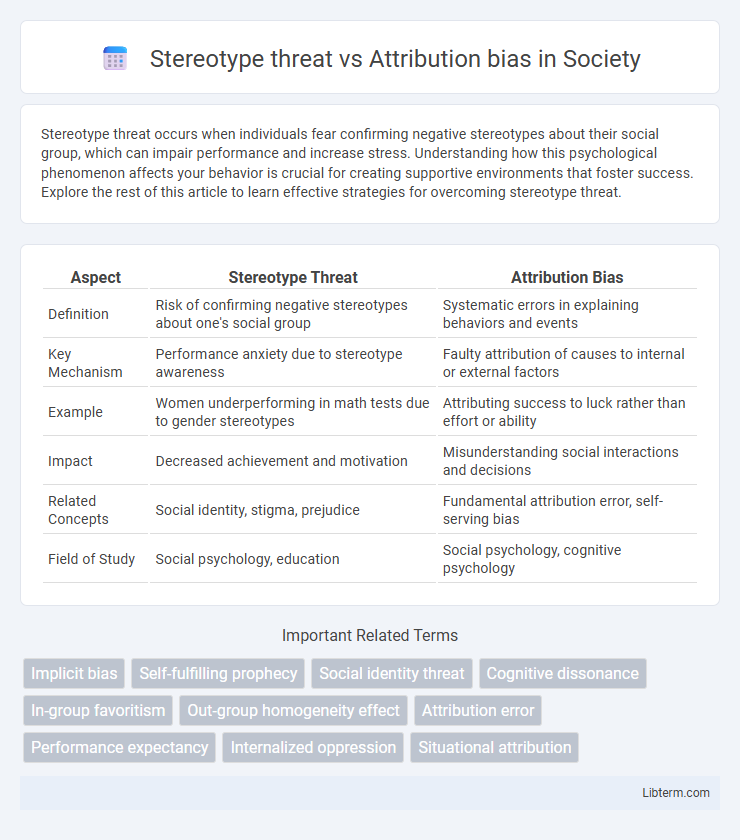
| Aspect | Stereotype Threat | Attribution Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Risk of confirming negative stereotypes about one's social group | Systematic errors in explaining behaviors and events |
| Key Mechanism | Performance anxiety due to stereotype awareness | Faulty attribution of causes to internal or external factors |
| Example | Women underperforming in math tests due to gender stereotypes | Attributing success to luck rather than effort or ability |
| Impact | Decreased achievement and motivation | Misunderstanding social interactions and decisions |
| Related Concepts | Social identity, stigma, prejudice | Fundamental attribution error, self-serving bias |
| Field of Study | Social psychology, education | Social psychology, cognitive psychology |
Understanding Stereotype Threat
Stereotype threat occurs when individuals fear confirming negative stereotypes about their social group, which can impair performance and increase anxiety during tasks. This psychological phenomenon impacts areas such as academic testing and workplace evaluations by inducing stress that undermines confidence and cognitive capacity. Understanding stereotype threat involves recognizing how social identity and situational cues trigger self-doubt, leading to decreased motivation and poorer outcomes.
Defining Attribution Bias
Attribution bias refers to the systematic errors individuals make when interpreting the causes of behavior, often attributing others' actions to internal traits while overlooking situational factors. This cognitive distortion influences judgment and decision-making, leading to inaccurate perceptions of motives and responsibility. In contrast, stereotype threat involves anxiety about confirming negative group stereotypes, impacting performance and behavior.
Key Differences Between Stereotype Threat and Attribution Bias
Stereotype threat occurs when individuals fear confirming negative stereotypes about their social group, leading to increased anxiety and reduced performance, while attribution bias involves misinterpreting others' behaviors based on flawed assumptions, such as attributing success to external factors or failure to internal traits. The key difference lies in stereotype threat being a situational pressure affecting performance directly, whereas attribution bias affects social perception and judgment of causes behind actions. Understanding these mechanisms is essential in addressing disparities in educational and workplace settings.
Psychological Mechanisms Involved
Stereotype threat operates through heightened anxiety and reduced working memory capacity when individuals fear confirming negative stereotypes about their group, impairing performance. Attribution bias involves distorted cognitive processing where individuals attribute successes or failures to internal or external causes based on preexisting beliefs, affecting self-perception and motivation. Both mechanisms engage distinct psychological processes: stereotype threat triggers stress responses and self-monitoring, while attribution bias influences causal reasoning and judgment accuracy.
Impact on Academic and Workplace Performance
Stereotype threat causes individuals to underperform in academic and workplace settings by increasing anxiety and reducing working memory capacity when they fear confirming negative stereotypes about their group. Attribution bias affects performance evaluation by leading supervisors or peers to misinterpret behaviors, often attributing failures to personal traits rather than external factors, which can hinder fair assessments and limit growth opportunities. Both cognitive biases undermine confidence and motivation, ultimately impairing productivity and the potential for success in education and professional environments.
Stereotype Threat in Social Contexts
Stereotype threat in social contexts occurs when individuals fear confirming negative stereotypes about their social group, leading to decreased performance and increased anxiety in situations such as academic testing or workplace evaluations. This psychological phenomenon significantly impacts marginalized groups, as the pressure to disprove stereotypes can undermine confidence and cognitive functioning. Unlike attribution bias, which involves misinterpreting the causes of behavior, stereotype threat directly impairs performance through heightened stress linked to social identity.
Attribution Bias and Decision-Making
Attribution bias significantly influences decision-making by altering how individuals interpret causes of behavior, often leading to distorted judgments that affect outcomes in organizational and social contexts. This bias causes decision-makers to overly attribute success or failure to internal traits rather than external circumstances, which can perpetuate misunderstandings and reduce objectivity. Understanding attribution bias helps improve decision-making accuracy, fostering fairer assessments and mitigating the impact of stereotypes on evaluations and performance appraisals.
Strategies to Mitigate Stereotype Threat
Strategies to mitigate stereotype threat include creating an inclusive environment that emphasizes individual abilities over group stereotypes, providing role models from diverse backgrounds to inspire confidence, and encouraging a growth mindset that frames intelligence and skills as developable traits. Techniques such as self-affirmation exercises and reframing challenging tasks as opportunities for learning rather than tests of fixed ability help reduce anxiety linked to stereotype threat. These approaches contrast with addressing attribution bias, which focuses on how people explain others' behavior rather than the impact of societal stereotypes on performance.
Reducing Attribution Bias in Everyday Life
Reducing attribution bias in everyday life involves consciously acknowledging the complexity of others' behavior rather than simplifying it to personality traits. Practicing empathy and considering situational factors helps minimize errors such as the fundamental attribution error. Encouraging open communication and perspective-taking supports more accurate social judgments and fosters healthier relationships.
The Interplay Between Stereotype Threat and Attribution Bias
Stereotype threat and attribution bias interact to influence individuals' cognitive performance and self-perception, where stereotype threat activates anxiety about confirming negative stereotypes, leading to diminished outcomes. Attribution bias affects how people interpret these performance results, often attributing failure to inherent ability rather than external factors, reinforcing stereotype threat's impact. This interplay creates a feedback loop, intensifying stress and reducing motivation in stigmatized groups, thereby perpetuating social inequalities in educational and professional settings.
Stereotype threat Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com