Market dynamics constantly evolve, influenced by consumer behavior, economic trends, and technological advancements. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Explore the full article to gain deeper insights into market strategies and growth potential.
Table of Comparison
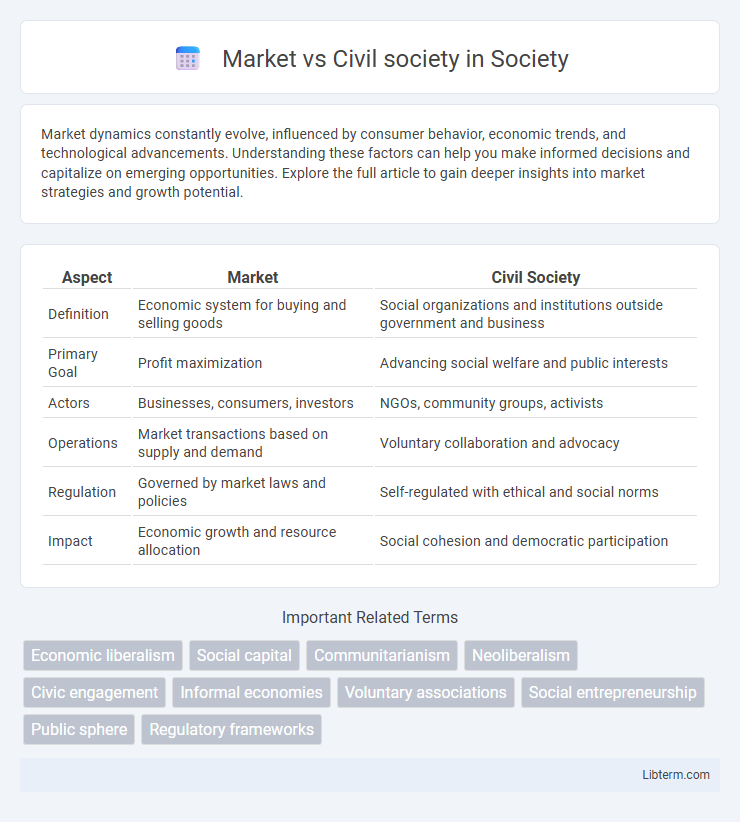
| Aspect | Market | Civil Society |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic system for buying and selling goods | Social organizations and institutions outside government and business |
| Primary Goal | Profit maximization | Advancing social welfare and public interests |
| Actors | Businesses, consumers, investors | NGOs, community groups, activists |
| Operations | Market transactions based on supply and demand | Voluntary collaboration and advocacy |
| Regulation | Governed by market laws and policies | Self-regulated with ethical and social norms |
| Impact | Economic growth and resource allocation | Social cohesion and democratic participation |
Understanding the Concepts: Market and Civil Society
The market is an economic system where goods and services are exchanged based on supply and demand, driven by profit and competition. Civil society encompasses the network of voluntary associations, non-governmental organizations, and social movements that operate independently from the state and market to promote social values and collective interests. Understanding the concepts highlights the market's role in economic transactions versus civil society's function in fostering community engagement and social accountability.
Historical Evolution of Markets and Civil Society
Markets originated as early exchange systems in ancient civilizations where goods and services were bartered or traded using primitive forms of currency, evolving significantly during the Industrial Revolution with the rise of capitalism and global trade networks. Civil society developed parallelly through the formation of social institutions, voluntary associations, and organized communities that advocated for collective interests, social justice, and governance beyond state control. The historical evolution of both markets and civil society reflects a complex interplay where economic activities shaped social structures, while civic organizations influenced regulatory frameworks and ethical norms within capitalist economies.
Key Differences Between Market and Civil Society
Markets operate on the principles of supply, demand, and profit maximization, facilitating transactions for goods and services within competitive environments. Civil society consists of organizations and institutions independent of the government and market influences, promoting social values, public welfare, and collective interests. Key differences include the market's focus on economic efficiency and individual gain, whereas civil society emphasizes community well-being, voluntary participation, and social accountability.
Roles and Functions in Modern Societies
Markets drive economic activities by facilitating the exchange of goods, services, and capital, ensuring resource allocation through supply and demand mechanisms. Civil society encompasses non-governmental organizations, community groups, and social movements that advocate for social justice, public interests, and collective well-being outside of market or state control. Together, markets promote efficiency and innovation, while civil society fosters social cohesion, accountability, and the protection of rights in modern societies.
Economic Objectives vs Social Goals
Market systems prioritize economic objectives such as profit maximization, resource allocation efficiency, and innovation-driven growth, emphasizing monetary incentives and competitive exchange. Civil society focuses on social goals including equity, community welfare, and collective empowerment, aiming to address social inequalities and promote civic participation. Balancing these dimensions requires integrating market efficiency with social accountability to achieve sustainable development outcomes.
Interaction and Interdependence
Market and civil society exhibit significant interaction and interdependence, as markets rely on civil society for norms, trust, and social capital that facilitate economic transactions. Civil society organizations influence market regulations, promote ethical business practices, and address social inequalities that markets alone may overlook. This dynamic interplay sustains economic efficiency and social cohesion, highlighting the necessity for balanced collaboration between market mechanisms and civil societal values.
Conflicts and Synergies
Market dynamics often create conflicts with civil society by prioritizing profit maximization over social welfare, leading to issues like inequality and environmental degradation. However, synergies arise when businesses adopt corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives, aligning market goals with civil society values such as sustainability and community development. Collaborative frameworks, including public-private partnerships and social enterprises, demonstrate how market efficiency can coexist with civil society's emphasis on social justice and collective well-being.
Influence on Governance and Policy
Market forces shape governance and policy primarily through economic power, lobbying efforts, and influence on regulatory frameworks, which often prioritize business interests and efficiency. Civil society drives governance and policy by advocating for public accountability, social justice, and inclusive participation, ensuring diverse community voices impact decision-making. The dynamic tension between market-driven agendas and civil society activism critically shapes democratic governance and policy outcomes.
Impact on Social Justice and Equality
Markets prioritize efficiency and wealth generation but often produce unequal access to resources, disproportionately benefiting those with capital and perpetuating social stratification. Civil society organizations actively promote social justice by advocating for marginalized groups, influencing policy changes, and fostering inclusive practices that address systemic inequalities. The interplay between market forces and civil society efforts shapes the landscape of social equality, with civil society acting as a critical counterbalance to market-driven disparities.
Future Prospects: Collaboration and Challenges
Market and civil society will increasingly intersect through innovative partnerships that leverage corporate resources and community-driven initiatives to address social and environmental challenges. Emerging technologies and digital platforms facilitate transparency and stakeholder engagement, enhancing collaborative potential while raising concerns about data privacy and equity. Balancing profit motives with social responsibility remains a critical challenge requiring adaptive governance models and multi-sector dialogue to ensure sustainable and inclusive development.
Market Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com