Voluntary organizations play a crucial role in addressing social issues by mobilizing community members to contribute time and resources toward common goals. These groups foster a sense of belonging and empowerment, enabling individuals to make a meaningful impact beyond monetary support. Discover how your involvement with voluntary organizations can transform communities and enrich your personal growth in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
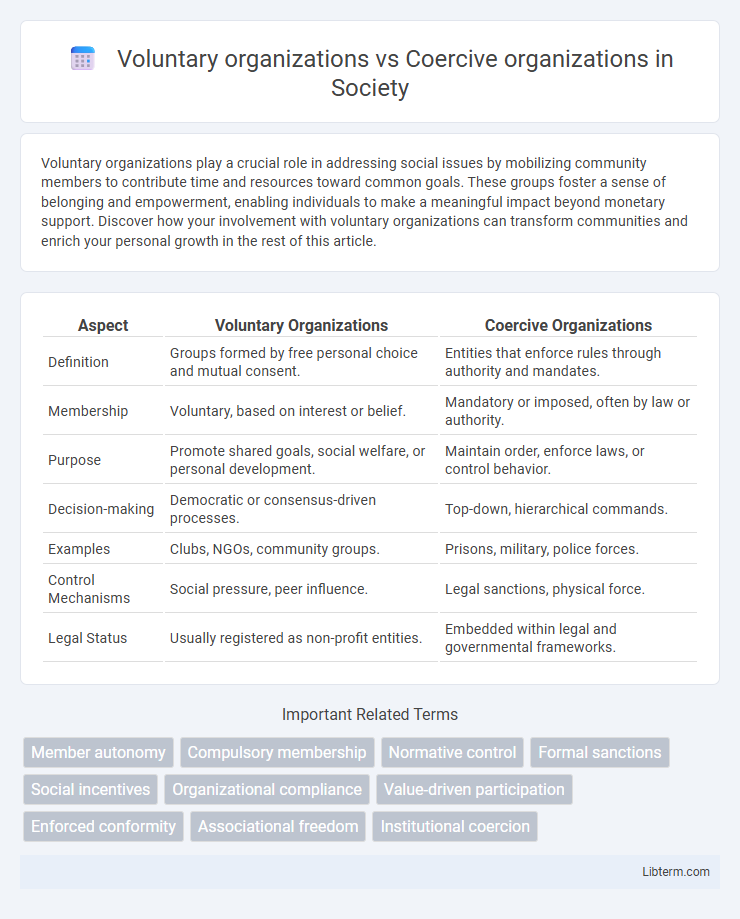
| Aspect | Voluntary Organizations | Coercive Organizations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Groups formed by free personal choice and mutual consent. | Entities that enforce rules through authority and mandates. |
| Membership | Voluntary, based on interest or belief. | Mandatory or imposed, often by law or authority. |
| Purpose | Promote shared goals, social welfare, or personal development. | Maintain order, enforce laws, or control behavior. |
| Decision-making | Democratic or consensus-driven processes. | Top-down, hierarchical commands. |
| Examples | Clubs, NGOs, community groups. | Prisons, military, police forces. |
| Control Mechanisms | Social pressure, peer influence. | Legal sanctions, physical force. |
| Legal Status | Usually registered as non-profit entities. | Embedded within legal and governmental frameworks. |
Defining Voluntary Organizations
Voluntary organizations are entities composed of individuals who join freely based on shared interests, values, or goals without external pressure or enforcement. These organizations rely on mutual consent and active participation, fostering collaboration and community engagement. Membership is typically characterized by personal commitment rather than obligation, distinguishing voluntary groups from coercive organizations that enforce compliance through authority or force.
Understanding Coercive Organizations
Coercive organizations impose strict compliance through formal rules, regulations, and often enforce authority using penalties or sanctions, distinguishing them from voluntary organizations where participation is freely chosen. Examples include prisons, military units, and total institutions, characterized by limited individual autonomy and controlled environments designed to regulate behavior. Understanding coercive organizations requires analyzing their structural mechanisms that prioritize order and conformity over voluntary cooperation.
Key Characteristics of Voluntary Organizations
Voluntary organizations are primarily characterized by the free and conscious participation of members who share common interests or goals, without external pressure or mandatory involvement. These organizations emphasize democratic decision-making, collective action, and the promotion of social, cultural, or charitable objectives through voluntary commitment. Unlike coercive organizations, which rely on hierarchical control and enforcement, voluntary organizations foster collaboration and intrinsic motivation among their members.
Key Features of Coercive Organizations
Coercive organizations are characterized by compulsory membership and strict control through force or authoritative measures, often seen in prisons and military institutions. These organizations rely on confinement, surveillance, and punishment to enforce compliance and maintain order among members. Unlike voluntary organizations, coercive entities restrict individual autonomy and prioritize obedience to hierarchical rules and regulations.
Membership and Participation Differences
Voluntary organizations rely on members who willingly join based on shared interests or goals, promoting active and enthusiastic participation. Coercive organizations enforce membership through external pressures or legal mandates, often resulting in passive or compulsory involvement. The key difference lies in the motivation driving membership: voluntary organizations foster commitment through choice, while coercive organizations depend on obligation or authority.
Governance and Decision-Making Structures
Voluntary organizations rely on participatory governance, with decisions often made through consensus or democratic voting among members, reflecting shared values and collective interests. Coercive organizations maintain hierarchical governance, where decision-making is centralized, and authority flows top-down to enforce compliance and control. These structural differences influence accountability, transparency, and the mechanisms through which power is exercised within each organization type.
Methods of Social Control and Discipline
Voluntary organizations rely on informal methods of social control and discipline, emphasizing shared values, peer influence, and mutual consent to maintain order and cooperation among members. Coercive organizations use formal mechanisms such as rules, regulations, surveillance, and the threat or application of penalties to enforce compliance and discipline. The distinction lies in the voluntary adherence to norms in voluntary organizations versus the imposed obedience and control in coercive organizations.
Impacts on Individual Freedom and Autonomy
Voluntary organizations enhance individual freedom and autonomy by allowing members to participate based on personal choice, fostering a sense of agency and self-determination. Coercive organizations restrict freedom through mandatory compliance and control, often limiting personal autonomy to enforce uniformity and order. The contrasting nature of these organizations significantly shapes individuals' capacity to express themselves and make independent decisions.
Social Functions and Community Roles
Voluntary organizations foster social cohesion by encouraging individual participation in shared goals and providing a platform for community engagement, thereby enhancing social capital and collective identity. Coercive organizations, often structured around authority and control, primarily enforce societal norms and regulations to maintain order and compliance within communities. Both types of organizations play distinct but complementary roles in social functions: voluntary groups promote empowerment and social support, while coercive entities ensure stability and rule enforcement.
Challenges and Controversies in Both Organization Types
Voluntary organizations often face challenges related to funding instability and volunteer retention, which can hinder long-term project sustainability and impact effectiveness. Coercive organizations encounter controversies stemming from ethical concerns about authority and control, including potential human rights violations and resistance from those subject to their power. Both organization types struggle with issues of accountability and transparency, affecting public trust and legitimacy in their operations.
Voluntary organizations Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com