Authenticity fosters trust and genuine connections in both personal and professional relationships, enhancing your credibility and self-confidence. Embracing your true self encourages deeper interactions and promotes mental well-being through honest expression. Discover how authenticity can transform your life by reading the rest of the article.
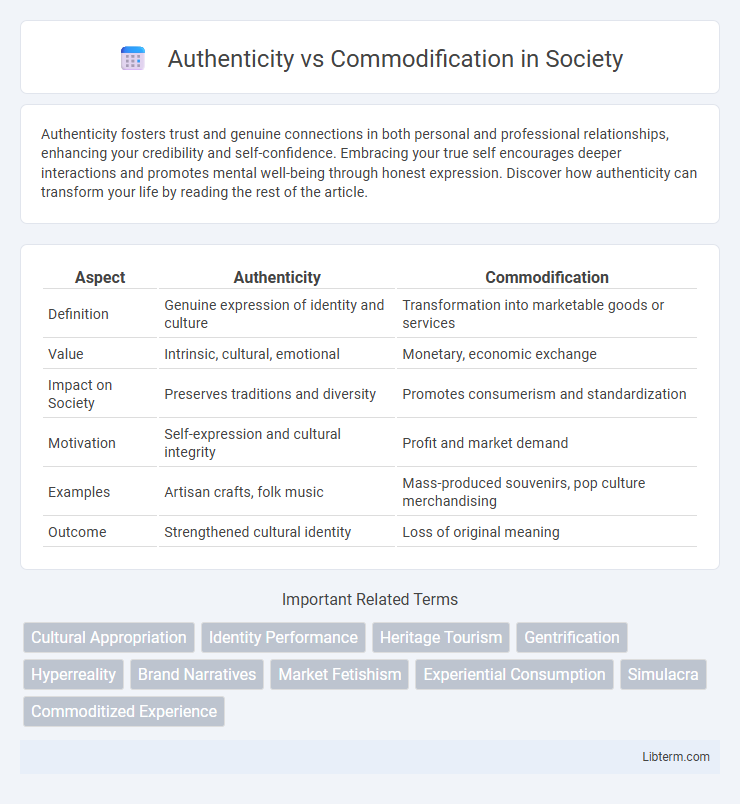
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Authenticity | Commodification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Genuine expression of identity and culture | Transformation into marketable goods or services |
| Value | Intrinsic, cultural, emotional | Monetary, economic exchange |
| Impact on Society | Preserves traditions and diversity | Promotes consumerism and standardization |
| Motivation | Self-expression and cultural integrity | Profit and market demand |
| Examples | Artisan crafts, folk music | Mass-produced souvenirs, pop culture merchandising |
| Outcome | Strengthened cultural identity | Loss of original meaning |
Understanding Authenticity in Modern Culture
Authenticity in modern culture revolves around genuine self-expression, rooted in personal values, traditions, and unique experiences rather than mass-produced or commercialized identities. It resists commodification by emphasizing originality, emotional sincerity, and cultural integrity over market-driven replication. Contemporary society increasingly values authenticity as a counterpoint to pervasive consumerism, seeking meaningful connections and trust in both personal interactions and cultural products.
The Rise of Commodification: Definition and Drivers
The rise of commodification refers to the process where cultural goods, traditions, or experiences are transformed into marketable products driven by consumer demand, commercialization, and globalization. Key drivers include technological advancements enhancing mass production and distribution, as well as economic incentives that prioritize profit over cultural significance. This shift often results in the dilution of authenticity, as unique cultural elements are standardized and marketed to appeal to a broad audience.
Historical Perspectives on Authenticity
Historical perspectives on authenticity emphasize the evolving concept of genuine cultural expressions as societies shift from traditional to modern contexts. Early anthropologists highlighted authenticity as rooted in unaltered cultural practices and artifacts, contrasting with commodification where cultural elements become marketable goods detached from original meanings. This tension illustrates how globalization and tourism have transformed authenticity from an inherent value to a negotiable attribute shaped by consumer demand and economic interests.
How Commodification Shapes Identity
Commodification transforms cultural symbols and personal expressions into marketable products, often simplifying complex identities into easily digestible forms. This process can dilute authentic experiences as individuals and communities alter behaviors to meet consumer expectations, prioritizing profitability over genuine self-representation. As a result, identity becomes a fluid construct shaped by commercial interests rather than intrinsic cultural or personal values.
The Impact of Commercialization on Art and Creativity
Commercialization often shifts artistic focus from genuine expression to market demands, compromising authenticity and originality in creative works. The pressure to produce commercially viable art can lead to formulaic content, diminishing artistic risk-taking and innovation. This commodification of art prioritizes profit over cultural value, altering the intrinsic meaning and impact of artistic expression.
Authenticity vs Commodification in Social Media
Authenticity in social media fosters genuine connections by showcasing unfiltered personal experiences and sincere engagement, which builds trust and loyalty among followers. Commodification, conversely, transforms authentic content into marketable assets, often prioritizing monetization over truth, leading to curated personas that may distort reality. The tension between these forces challenges content creators to maintain credibility while navigating commercial pressures and algorithm-driven visibility.
Consumer Demand: The Paradox of Realness and Marketability
Consumer demand for authenticity often conflicts with the commodification of experiences and products, creating a paradox where genuine appeal is packaged and sold for mass consumption. Brands capitalize on realness by marketing the illusion of uniqueness, which can dilute the original cultural or emotional value sought by consumers. This tension challenges businesses to balance marketability with maintaining the integrity and trust that define authentic engagement.
Authentic Brands: Marketing or Genuine Connection?
Authentic brands cultivate genuine connections by emphasizing transparency, storytelling, and customer engagement rather than solely relying on marketing tactics. Their value lies in aligning core values with audience expectations, fostering trust and long-term loyalty. Authenticity drives brand differentiation in a saturated market, resisting commodification that reduces brands to mere products.
Preserving Authenticity Amidst Globalization
Preserving authenticity amidst globalization requires safeguarding cultural heritage and traditional practices from being diluted or commercialized for mass consumption. Authentic cultural expressions maintain their unique identity through community involvement and respectful representation, resisting the pressures of commodification. Effective preservation strategies involve legal protections, education, and sustainable tourism that prioritize genuine experiences over profit-driven replication.
Navigating the Future: Balancing Authenticity and Commodification
Navigating the future requires striking a delicate balance between preserving cultural authenticity and the pressures of commodification in global markets. Businesses and creators must prioritize genuine storytelling and community engagement to maintain the integrity of cultural expressions while exploring sustainable economic opportunities. Emphasizing transparency and ethical practices fosters trust, ensuring authenticity thrives alongside commercialization in evolving industries.
Authenticity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com