Multiculturalism embraces diverse cultural backgrounds, fostering mutual respect and understanding within societies. It enhances social cohesion and promotes inclusive policies that celebrate differences while ensuring equal opportunities for all. Explore the rest of the article to discover how multiculturalism can enrich your community and personal experiences.
Table of Comparison
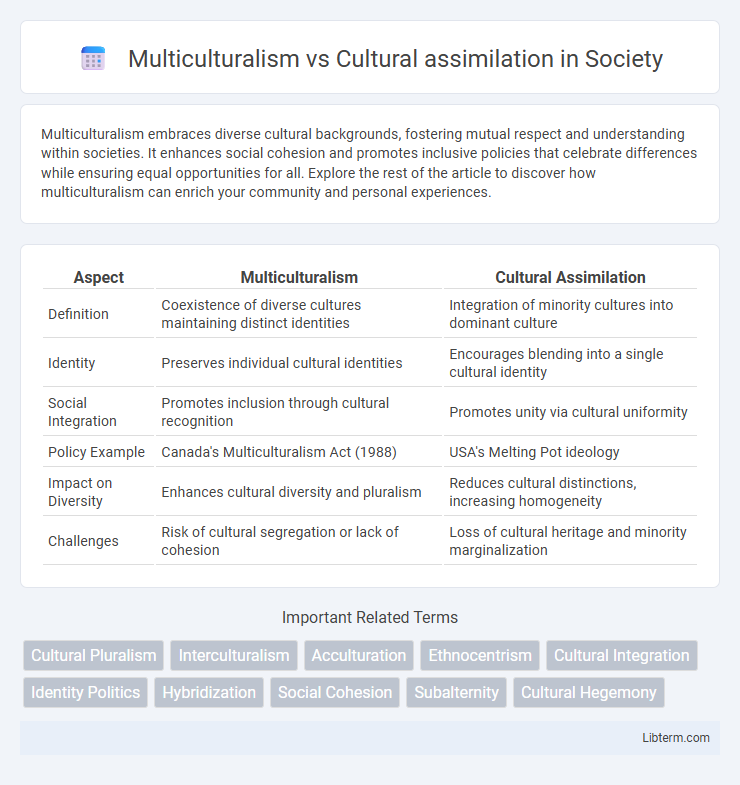
| Aspect | Multiculturalism | Cultural Assimilation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of diverse cultures maintaining distinct identities | Integration of minority cultures into dominant culture |
| Identity | Preserves individual cultural identities | Encourages blending into a single cultural identity |
| Social Integration | Promotes inclusion through cultural recognition | Promotes unity via cultural uniformity |
| Policy Example | Canada's Multiculturalism Act (1988) | USA's Melting Pot ideology |
| Impact on Diversity | Enhances cultural diversity and pluralism | Reduces cultural distinctions, increasing homogeneity |
| Challenges | Risk of cultural segregation or lack of cohesion | Loss of cultural heritage and minority marginalization |
Introduction to Multiculturalism and Cultural Assimilation
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a society, encouraging individuals to maintain their unique heritage while participating in the broader community. Cultural assimilation involves the process by which minority groups gradually adopt the dominant culture's norms, often leading to the diminishing of original cultural practices. These contrasting approaches shape social integration policies and influence the dynamics of cultural identity in multicultural nations.
Defining Multiculturalism: Core Concepts
Multiculturalism emphasizes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a society, promoting equal respect and inclusion of varied ethnic, linguistic, and religious groups. Core concepts include cultural pluralism, where multiple cultures maintain distinct traditions while participating equally in social, political, and economic life. This approach contrasts with cultural assimilation, which encourages minority groups to adopt the dominant culture, often at the expense of their original cultural identities.
Understanding Cultural Assimilation: Key Features
Cultural assimilation involves the process by which individuals or groups adopt the cultural traits of another, often dominant, society, leading to the reduction of cultural differences. Key features include language acquisition, adoption of social norms, and changes in identity that align with the host culture. This process contrasts with multiculturalism, which encourages the preservation of distinct cultural identities within a shared society.
Historical Contexts of Multiculturalism and Assimilation
Historical contexts of multiculturalism reveal a commitment to preserving diverse cultural identities within societies, particularly prominent in post-colonial and immigration-rich nations like Canada and Australia. Cultural assimilation, historically exemplified by U.S. Native American boarding schools and French colonial policies, aimed to integrate minority groups into dominant cultural norms, often eroding original identities. These contrasting approaches reflect differing national ideologies on social cohesion and identity in multicultural societies.
Social Integration: Blending vs. Preserving Cultures
Multiculturalism emphasizes preserving distinct cultural identities while promoting social integration through mutual respect and cultural exchange. Cultural assimilation encourages blending minority groups into the dominant culture, prioritizing uniformity over cultural diversity. Effective social integration balances maintaining unique cultural traditions with fostering shared community values.
Benefits of Multicultural Societies
Multicultural societies foster innovation and creativity by bringing together diverse perspectives and experiences, enhancing problem-solving and economic growth. Exposure to multiple cultures promotes social cohesion through increased empathy, tolerance, and cross-cultural communication skills. These societies also support the preservation of cultural heritage and individual identity, enriching the social fabric and promoting global understanding.
Challenges and Criticisms of Cultural Assimilation
Cultural assimilation faces significant challenges as it often leads to the erosion of minority cultural identities and traditions, sparking criticism for promoting conformity over diversity. Critics argue that assimilation policies can result in social exclusion, loss of language, and psychological stress among immigrant communities. The tension between preserving unique cultural heritage and achieving social cohesion highlights the limitations of cultural assimilation in multicultural societies.
Case Studies: Multiculturalism vs. Assimilation Around the World
Case studies such as Canada's multiculturalism policy emphasize preserving diverse cultural identities within a unified society, fostering inclusion and social cohesion. In contrast, France's approach of cultural assimilation promotes integration through a shared national identity, often requiring immigrants to adopt dominant cultural norms. Comparative analyses reveal that multiculturalism supports pluralism and individual rights, while assimilation prioritizes social conformity and national unity.
Impact on Identity and Social Cohesion
Multiculturalism promotes the preservation of diverse cultural identities, fostering mutual respect and a sense of belonging among different ethnic groups, which can enhance social cohesion by encouraging inclusivity. Cultural assimilation often leads to the blending or loss of distinct cultural traits, potentially weakening individual identity but aiming to create a unified societal identity that may reduce cultural conflicts. The balance between maintaining unique cultural identities and achieving social cohesion depends on societal values and policies that either support diversity or encourage conformity.
Future Perspectives: Balancing Multiculturalism and Assimilation
Future perspectives on multiculturalism and cultural assimilation emphasize creating inclusive societies that celebrate diversity while promoting social cohesion. Policies encouraging cultural exchange and mutual respect can foster integration without erasing individual cultural identities. Advances in education and technology play crucial roles in balancing cultural retention with the shared values necessary for societal harmony.
Multiculturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com