Relocation involves moving your home or business to a new location, requiring careful planning and organization to ensure a smooth transition. Efficient relocation services can minimize stress and downtime, helping you settle quickly into your new environment. Discover essential tips and strategies to make your relocation experience seamless by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
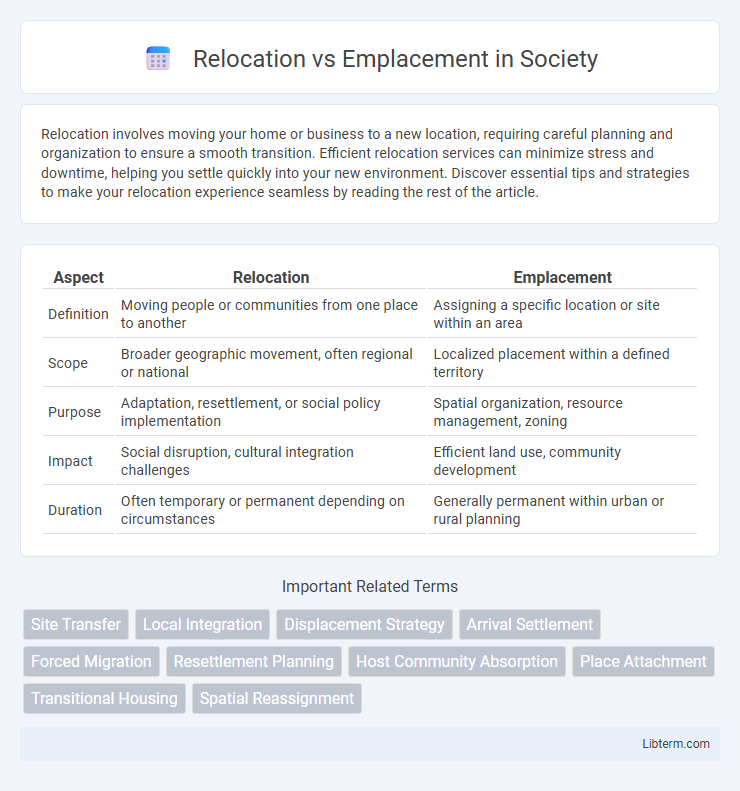
| Aspect | Relocation | Emplacement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Moving people or communities from one place to another | Assigning a specific location or site within an area |
| Scope | Broader geographic movement, often regional or national | Localized placement within a defined territory |
| Purpose | Adaptation, resettlement, or social policy implementation | Spatial organization, resource management, zoning |
| Impact | Social disruption, cultural integration challenges | Efficient land use, community development |
| Duration | Often temporary or permanent depending on circumstances | Generally permanent within urban or rural planning |
Understanding Relocation and Emplacement
Relocation involves moving a person or object from one place to another, emphasizing the physical transfer and adjustment to a new environment. Emplacement refers to the precise positioning or installation of an object within a specific location, often for functional or strategic purposes. Understanding the distinction clarifies how relocation addresses broader movement, while emplacement focuses on exact placement within a given context.
Key Differences Between Relocation and Emplacement
Relocation involves physically moving an object or entity from one place to another, whereas emplacement refers to placing or installing something in a specific location with precision. Relocation emphasizes the act of transportation and changing location, while emplacement focuses on positioning and securing the object for operational use. Key differences include the purpose--relocation is about movement, and emplacement is about strategic placement and readiness.
Factors Influencing the Choice: Relocation vs Emplacement
Factors influencing the choice between relocation and emplacement primarily include cost, environmental impact, and logistical feasibility. Relocation often demands higher financial resources and complex planning due to transportation and reestablishment challenges, whereas emplacement focuses on optimizing existing site conditions to minimize disruption. Regulatory compliance, community acceptance, and long-term strategic goals also play critical roles in determining the most suitable approach.
Cost Analysis: Relocation vs Emplacement
Cost analysis of relocation versus emplacement highlights distinct financial impacts; relocation often incurs high expenses including transportation, temporary housing, and operational downtime, while emplacement typically demands significant initial investment in infrastructure and setup but offers long-term savings through stability. Detailed examination reveals relocation's variable costs fluctuate based on distance and complexity, whereas emplacement's fixed costs provide predictable budgeting advantages. Strategic decision-making depends on weighing immediate relocation expenses against the sustained cost efficiency of emplacement infrastructure.
Impact on Workforce and Productivity
Relocation often leads to temporary declines in workforce productivity due to disruptions in employee routines, increased stress, and adjustment periods. Emplacement involves integrating new processes or systems within the existing location, minimizing downtime and maintaining workforce stability. Effective management of emplacement strategies enhances productivity by leveraging familiar environments, while poorly handled relocation can result in talent attrition and prolonged operational inefficiencies.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Relocation involves moving individuals or businesses to a new location, often triggering compliance with varying local zoning laws, environmental regulations, and labor policies. Emplacement typically refers to the proper installation or setup at a fixed site, requiring adherence to building codes, safety standards, and permits specific to the site's jurisdiction. Navigating the legal and regulatory frameworks for both processes demands thorough due diligence to avoid penalties and ensure smooth operational transitions.
Environmental Implications
Relocation often involves significant environmental disruption due to land clearance, habitat loss, and increased carbon emissions from transportation activities. Emplacement minimizes these impacts by optimizing the use of existing infrastructure and reducing the need for extensive construction or alteration of natural landscapes. Choosing emplacement supports sustainable development goals by preserving ecosystems and lowering overall ecological footprints.
Technological Requirements and Challenges
Relocation demands extensive technological infrastructure including advanced transportation systems, real-time tracking, and robust cybersecurity measures to ensure data integrity during transit. Emplacement involves precise technological requirements such as site-specific installation tools, environmental controls, and integration with existing systems to guarantee operational efficiency. Both processes face significant challenges including compatibility issues, resource allocation, and minimizing downtime to maintain business continuity.
Case Studies: Successful Relocation and Emplacement Strategies
Case studies reveal that successful relocation strategies often involve comprehensive planning, stakeholder engagement, and logistical coordination to minimize disruption and ensure smooth transitions. Emplacement strategies highlight the importance of site-specific adaptation, cultural integration, and infrastructure readiness to optimize long-term operational effectiveness. Comparative analyses demonstrate that combining relocation with strategic emplacement considerations enhances sustainability and scalability in diverse industries.
Making the Right Decision for Your Organization
Choosing between relocation and emplacement involves evaluating factors such as cost, employee impact, and business continuity to align with your organization's strategic goals. Relocation offers opportunities for market expansion and operational efficiency, while emplacement emphasizes stability and local expertise retention. Analyzing these elements through a thorough cost-benefit analysis ensures an informed decision that supports long-term organizational growth and employee satisfaction.
Relocation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com